Difference between revisions of "Tooth Developmental Problems"
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{OpenPagesTop}} | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Problems with [[Tooth Development|normal tooth development]] fall into three main categories: | Problems with [[Tooth Development|normal tooth development]] fall into three main categories: | ||
| Line 7: | Line 8: | ||
==Abnormalities of the Crown== | ==Abnormalities of the Crown== | ||
| − | + | Abnormalities of the [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Crown|crown]] may occur during development resulting in '''microdontia''' (smaller crown), '''macrodontia''' (larger crown), '''peg teeth (conically shaped teeth) as well as '''geminated crowns''' (double crown) or '''fused teeth''' (two separate tooth buds fused at the crown by [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Enamel|enamel]] and sometimes [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Dentin|dentine]]).<br> | |
| − | + | This is clinically important from a periodontal health aspect to avoid plaque stagnation areas between overcrowded teeth. It is also important when planning extraction of an abnormal tooth to take [[Intra-Oral Radiography - Small Animal|radiographs]] as abnormal [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Root|root]] formation is not uncommon with these teeth. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Abnormalities of the [[ | ||
| − | This is clinically important from a periodontal health aspect to avoid plaque stagnation areas between overcrowded teeth. It is also important when planning extraction of an abnormal tooth to take [[Intra-Oral Radiography - Small Animal|radiographs]] as abnormal [[ | ||
===Enamel Dysplasia=== | ===Enamel Dysplasia=== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 24: | ||
Local factors causing enamel dysplasia mostly involve trauma. A blow to the face, a jaw fracture, a fractured deciduous tooth with pulp necrosis or a localised infection may all affect the developing permanent crown. Systemic factors usually result in many teeth being affected. | Local factors causing enamel dysplasia mostly involve trauma. A blow to the face, a jaw fracture, a fractured deciduous tooth with pulp necrosis or a localised infection may all affect the developing permanent crown. Systemic factors usually result in many teeth being affected. | ||
| − | '''Hypoplasia''' vs '''hypocalcification''' - During enamel formation, [[ | + | '''Hypoplasia''' vs '''hypocalcification''' - During enamel formation, [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Ameloblasts|ameloblasts]] are susceptible to various external factors that may damage or cause malfunction of the cells. <br> |
Defective enamel, which is when there is not enough of it but what there is, is of normal hardness, is known as enamel hypoplasia. Damage to the actual ameloblasts has occurred resulting in areas where there is no enamel formation. Defective enamel, in which normal amounts of enamel are produced but the enamel is hypomineralised is known as enamel hypocalcification. In this defect, the enamel is softer than normal. It is often not possible to distinguish the two types on clinical appearance alone. | Defective enamel, which is when there is not enough of it but what there is, is of normal hardness, is known as enamel hypoplasia. Damage to the actual ameloblasts has occurred resulting in areas where there is no enamel formation. Defective enamel, in which normal amounts of enamel are produced but the enamel is hypomineralised is known as enamel hypocalcification. In this defect, the enamel is softer than normal. It is often not possible to distinguish the two types on clinical appearance alone. | ||
'''Generalised enamel dysplasia''' - Historically, the most common cause of enamel dysplasia was [[Distemper|distemper virus]] - the virus caused a febrile reaction which affected the developing tooth, but it is also an epitheliotropic virus, affecting developing epithelium, from which ameloblasts originate. Virus particles have been demonstrated in the actual ameloblasts. Other causes of generalised enamel dysplasia usually result from a febrile reaction, and, in rare cases [[Hypocalcaemia|hypocalcaemia]], excessive fluoride ingestion and nutritional deficiencies. There have been case reports of dysplasia associated with [[:Category: Kidney - Developmental Pathology|congenital renal disease]]. | '''Generalised enamel dysplasia''' - Historically, the most common cause of enamel dysplasia was [[Distemper|distemper virus]] - the virus caused a febrile reaction which affected the developing tooth, but it is also an epitheliotropic virus, affecting developing epithelium, from which ameloblasts originate. Virus particles have been demonstrated in the actual ameloblasts. Other causes of generalised enamel dysplasia usually result from a febrile reaction, and, in rare cases [[Hypocalcaemia|hypocalcaemia]], excessive fluoride ingestion and nutritional deficiencies. There have been case reports of dysplasia associated with [[:Category: Kidney - Developmental Pathology|congenital renal disease]]. | ||
| − | '''''Amelogenesis imperfecta''''' - A term often incorrectly used in veterinary dentistry to mean any condition resulting in enamel dysplasia. ''Amelogenesis imperfecta'' is a hereditary condition of humans in which the genes that encode for enamel proteins (amelogenin, enamelin and others) are mutated. Most cases are inherited as an autosomal-dominant trait. The condition affects both the primary and secondary dentition. One study of enamel defects in standard poodles in Sweden confirmed histologically that ''Amelogenesis imperfecta'' is a common cause of discoloured teeth in standard poodles < | + | '''''Amelogenesis imperfecta''''' - A term often incorrectly used in veterinary dentistry to mean any condition resulting in enamel dysplasia. ''Amelogenesis imperfecta'' is a hereditary condition of humans in which the genes that encode for enamel proteins (amelogenin, enamelin and others) are mutated. Most cases are inherited as an autosomal-dominant trait. The condition affects both the primary and secondary dentition. One study of enamel defects in standard poodles in Sweden confirmed histologically that ''Amelogenesis imperfecta'' is a common cause of discoloured teeth in standard poodles <ref>Mannerfelt, T. (2009) '''Enamel defects in standard poodle dogs in Sweden. '''''Journal of Veterinary Dentistry ''26(4).</ref>. This report is the first report to describe the condition in dogs. |
====Clinical Significance==== | ====Clinical Significance==== | ||
| − | Enamel forms the outer covering of the tooth and forms an impermeable barrier protecting the underlying tooth components. If enamel is poorly formed or missing completely the underlying dentine is exposed, resulting in sensitivity and severe pain in some cases. The sensitivity is caused by changes in the hydrostatic pressure in the dentinal tubules which contain odontoblast processes which trigger a pain pathway. In mild cases, the pulp will often respond to the stimulation by laying down more dentine, reparative (tertiary) dentine, which obliterates the dentinal tubule space. In severe cases of dysplasia, the pulp can become chronically inflamed and undergo irreversible pulpitis as a result of bacterial ingression through the exposed dentinal tubules; periapical disease then develops. < | + | Enamel forms the outer covering of the tooth and forms an impermeable barrier protecting the underlying tooth components. If enamel is poorly formed or missing completely the underlying dentine is exposed, resulting in sensitivity and severe pain in some cases. The sensitivity is caused by changes in the hydrostatic pressure in the dentinal tubules which contain odontoblast processes which trigger a pain pathway. In mild cases, the pulp will often respond to the stimulation by laying down more dentine, reparative (tertiary) dentine, which obliterates the dentinal tubule space. In severe cases of dysplasia, the pulp can become chronically inflamed and undergo irreversible pulpitis as a result of bacterial ingression through the exposed dentinal tubules; periapical disease then develops. |
| + | |||
| + | <center><gallery widths=250px heights=180px mode="traditional"> | ||
| + | File:Enamel dysplasia.jpg|Enamel dysplasia | ||
| + | File:Generalised enamel dysplasia.jpg|Generalised enamel dysplasia | ||
| + | File:Localised enamel dysplasia.jpg|Localised enamel dysplasia | ||
| + | File:Enamel dysplasia radiograph.jpg|Radiograph showing enamel dysplasia | ||
| + | </gallery></center> | ||
===Dens in Dente === | ===Dens in Dente === | ||
| Line 41: | Line 45: | ||
Dens in dente - tooth within a tooth | Dens in dente - tooth within a tooth | ||
| − | This occurs when the tooth bud folds in on itself resulting in [[ | + | This occurs when the tooth bud folds in on itself resulting in [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Enamel|enamel]], [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Dentin|dentine]] and pulp being produced with the tooth itself. Usually the invagination results in pulp exposure, and ultimately pulp necrosis. Often the crown has an abnormal shape but the diagnosis is made radiographically. |
| + | |||
| + | <center><gallery widths=250px heights=180px mode="traditional"> | ||
| + | File:Dens in dente.jpg|Dens in dente | ||
| + | </gallery></center> | ||
==Root Abnormalities == | ==Root Abnormalities == | ||
* Extra roots | * Extra roots | ||
* Dilacerated roots (misshapen roots) | * Dilacerated roots (misshapen roots) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><gallery widths=250px heights=180px mode="traditional"> | ||
| + | File:Extra tooth root 1.jpg|Extra root | ||
| + | File:Extra tooth root 2.jpg|Extra root | ||
| + | </gallery></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dubielzig, R. et al., (1986) '''Dental dysplasia in two young uremic dogs. '''''Veterinary Pathology ''23:333-5. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gorrel, C. (2008) '''Small Animal Dentistry.''''' Saunders Elsevier.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Regezi, J. A. et al., (2008) '''Oral Pathology – Clinical Pathologic Correlations, '''5th edn. ''Saunders Elsevier,''Missouri. | ||
{{Learning | {{Learning | ||
|flashcards = [[Veterinary Dentistry Q&A 13]] | |flashcards = [[Veterinary Dentistry Q&A 13]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Lisa Milella written | ||
| + | |date = 1 October 2014}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Waltham}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
[[Category:Developmental Dental Conditions]] | [[Category:Developmental Dental Conditions]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Waltham reviewed]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 14:19, 2 November 2014
Introduction
Problems with normal tooth development fall into three main categories:
- Abnormal crown formation
- Abnormal root formation
- Other
Abnormalities of the Crown
Abnormalities of the crown may occur during development resulting in microdontia (smaller crown), macrodontia (larger crown), peg teeth (conically shaped teeth) as well as geminated crowns (double crown) or fused teeth (two separate tooth buds fused at the crown by enamel and sometimes dentine).
This is clinically important from a periodontal health aspect to avoid plaque stagnation areas between overcrowded teeth. It is also important when planning extraction of an abnormal tooth to take radiographs as abnormal root formation is not uncommon with these teeth.
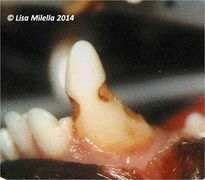
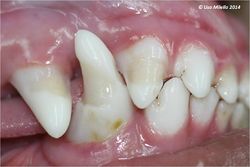
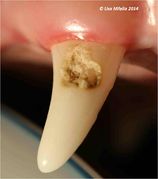
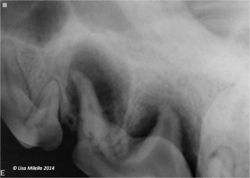
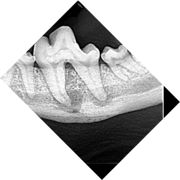
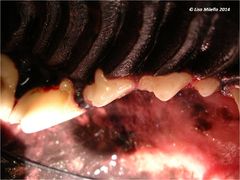
Enamel Dysplasia
Enamel dysplasia results from abnormal enamel formation on the crown of the tooth. This occurs when an injury or other disruption occurs during the formation of enamel. All enamel formation occurs prior to eruption of the tooth. The crown formation of the permanent/secondary teeth occurs from the second week postpartum to the age of three months. The crown of the first permanent mandibular molar, however, begins to undergo development and mineralisation prior to birth. Only those areas of the crown undergoing active formation at the time of the injury will be affected, giving the banded appearance sometimes seen.
If only a small area of dysplasia is seen this is usually asscociated with localized trauma to the developing crown. Teeth with enamel dysplasia may appear completely normal at the time of eruption but, as soon as the animal begins to use the teeth, defective enamel flakes off and the remaining porous defective enamel and exposed dentine begins to discolour. It is important to remember that the insult to the developing tooth happened months before and not after full eruption.
The extent of the enamel defect is dependent on:
- the intensity of the aetiological factor
- the duration of the factor’s presence
- the stage at which the factor occurs during crown development.
Local factors causing enamel dysplasia mostly involve trauma. A blow to the face, a jaw fracture, a fractured deciduous tooth with pulp necrosis or a localised infection may all affect the developing permanent crown. Systemic factors usually result in many teeth being affected.
Hypoplasia vs hypocalcification - During enamel formation, ameloblasts are susceptible to various external factors that may damage or cause malfunction of the cells.
Defective enamel, which is when there is not enough of it but what there is, is of normal hardness, is known as enamel hypoplasia. Damage to the actual ameloblasts has occurred resulting in areas where there is no enamel formation. Defective enamel, in which normal amounts of enamel are produced but the enamel is hypomineralised is known as enamel hypocalcification. In this defect, the enamel is softer than normal. It is often not possible to distinguish the two types on clinical appearance alone.
Generalised enamel dysplasia - Historically, the most common cause of enamel dysplasia was distemper virus - the virus caused a febrile reaction which affected the developing tooth, but it is also an epitheliotropic virus, affecting developing epithelium, from which ameloblasts originate. Virus particles have been demonstrated in the actual ameloblasts. Other causes of generalised enamel dysplasia usually result from a febrile reaction, and, in rare cases hypocalcaemia, excessive fluoride ingestion and nutritional deficiencies. There have been case reports of dysplasia associated with congenital renal disease.
Amelogenesis imperfecta - A term often incorrectly used in veterinary dentistry to mean any condition resulting in enamel dysplasia. Amelogenesis imperfecta is a hereditary condition of humans in which the genes that encode for enamel proteins (amelogenin, enamelin and others) are mutated. Most cases are inherited as an autosomal-dominant trait. The condition affects both the primary and secondary dentition. One study of enamel defects in standard poodles in Sweden confirmed histologically that Amelogenesis imperfecta is a common cause of discoloured teeth in standard poodles [1]. This report is the first report to describe the condition in dogs.
Clinical Significance
Enamel forms the outer covering of the tooth and forms an impermeable barrier protecting the underlying tooth components. If enamel is poorly formed or missing completely the underlying dentine is exposed, resulting in sensitivity and severe pain in some cases. The sensitivity is caused by changes in the hydrostatic pressure in the dentinal tubules which contain odontoblast processes which trigger a pain pathway. In mild cases, the pulp will often respond to the stimulation by laying down more dentine, reparative (tertiary) dentine, which obliterates the dentinal tubule space. In severe cases of dysplasia, the pulp can become chronically inflamed and undergo irreversible pulpitis as a result of bacterial ingression through the exposed dentinal tubules; periapical disease then develops.
Dens in Dente
Dens in dente - tooth within a tooth
This occurs when the tooth bud folds in on itself resulting in enamel, dentine and pulp being produced with the tooth itself. Usually the invagination results in pulp exposure, and ultimately pulp necrosis. Often the crown has an abnormal shape but the diagnosis is made radiographically.
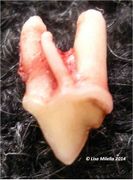
Root Abnormalities
- Extra roots
- Dilacerated roots (misshapen roots)
References
- ↑ Mannerfelt, T. (2009) Enamel defects in standard poodle dogs in Sweden. Journal of Veterinary Dentistry 26(4).
Dubielzig, R. et al., (1986) Dental dysplasia in two young uremic dogs. Veterinary Pathology 23:333-5.
Gorrel, C. (2008) Small Animal Dentistry. Saunders Elsevier.
Regezi, J. A. et al., (2008) Oral Pathology – Clinical Pathologic Correlations, 5th edn. Saunders Elsevier,Missouri.
| Tooth Developmental Problems Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Veterinary Dentistry Q&A 13 |
| This article was written by Lisa Milella BVSc DipEVDC MRCVS. Date reviewed: 1 October 2014 |
| Endorsed by WALTHAM®, a leading authority in companion animal nutrition and wellbeing for over 50 years and the science institute for Mars Petcare. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt6984a7877424e3_42846967 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt6984a78778c9b4_03629621 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt6984a7877ec619_13025093
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |