Difference between revisions of "Otodectes cynotis"
(Created page with '*Causes otodectic skin infestation *Commonest mange of dogs and cats in the world *Inhabits the inner ear *Also found…') |
|||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} | |
| + | {{Taxobox | ||
| + | |name =''Otodectes cynotis'' | ||
| + | |phylum =Arthropoda | ||
| + | |class =[[:Category:Arachnida|Arachnida]] | ||
| + | |order =Astigmata | ||
| + | |family =Psoroptidia | ||
| + | |genus =Otodectes | ||
| + | |species =''O.cynotis'' | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | Also known as: '''''Ear mite''' | ||
| + | [[File:Otodectes cynotis.jpg|thumb|200px|right|''Otodectes cynotis'' C. Antonczyk 2008]] | ||
| + | [[File:Otodectes.jpg|thumb|200px|right|''Otodectes cynotis'' Caroldermoid 2006, wikimedia commons]] | ||
| − | + | ==Introduction== | |
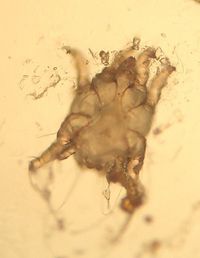
| + | ''Otodectes cynotis'' mites are [[Non-Burrowing Mites|surface mites]]. They are the cause of [[Otitis Externa - Cat and Dog|otodectic otitis]], the most common mange of dogs and cats in the world. They are also found in the fox and the ferret. The mites inhabit the inner ear and feed on ear debris, they appear white in colour. | ||
| − | + | Pruritus is caused by irritation and the saliva of the mites, which is immunogenic. '''Secondary bacterial infection''' is common, resulting in purulent otitis externa which will require more treatment. | |
| − | + | In cats, another presentation can be seen, which is that of an ectopic infection where signs are seen on other body parts such as the tail. This is due to contact e.g. cats sleeping in a curled position would allow mites to infest that area. Transmission of the mites can occur to kittens whilst they are suckling. | |
| − | + | ==Identification== | |
| + | The mites have closed keratinous bars, '''apodemes''' on their ventral surface. They are smaller in size than [[psoroptes cuniculi]] and have short pedicles on their first and second pairs of legs. | ||
| − | + | ==Lifecycle== | |
| + | The Life cycle of an ''Otodectes'' mite takes '''3 weeks'''. The females lay around five eggs a day on the surface of the ear canal. Four days later, larvae hatch and become nymphs. There are two nymphal stages before an adult mite is formed. | ||
| − | + | ==Clinical Signs== | |
| + | Clinical signs include '''head shaking, scratching of the ear''' and even the development of an '''aural haematoma''' because of the two above signs. The animal may often resent this area being touched. | ||
| + | A '''brown waxy exudate''' is produced and this later becomes crusty. If secondary bacterial infection has occurred then pus will also be seen in the ear canal. | ||
| − | + | ==Diagnosis== | |
| − | + | Clinical signs and history are indicative of the disease. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Visualisation''' of the mites via an auroscope will provide definitive diagnosis. | |
| − | + | == Treatment == | |
| + | Topical ear drops usually contain '''acaricide, fungicide, antibiotics and steroids'''. These should be dropped into the ear and the base of the ear then massaged to help the drops disperse. In cases of severe wax build up, ceruminolytics may be useful. | ||
| − | + | '''Selamectin''' as a spot on also acts to prevent ''Otodectes''. | |
| − | + | '''All in contact animals should be treated''' in the household as these may be asymptomatic carriers. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | Blood, D.C. and Studdert, V. P. (1999) '''Saunders Comprehensive Veterinary Dictionary''' (2nd Edition),'' Elsevier Science''. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Bond, R. (2008) '''Dermatology Study Guide,''''' Royal Veterinary College.'' | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Foster, A, and Foll, C. (2003) '''BSAVA small animal dermatology''' (second edition), ''British Small Animal Veterinary Association '' | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Fox, M and Jacobs, D. (2007) '''Parasitology Study Guide Part 1: Ectoparasites, '''''Royal Veterinary College '' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <big><b>Also see: | |
| + | :[[Otitis Externa - Cat and Dog|Ear Mites in Cats and Dogs]] | ||
| + | :[[Mites - Ferrets#Ear Mites|Ear Mites in Ferrets]] | ||
| + | </b></big> | ||
| − | + | {{Learning | |
| − | + | |flashcards = [[Mites_Flashcards|Mites Flashcards]] | |
| + | |literature search = [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?rowId=1&options1=AND&q1=%22Otodectes+cynotis%22&occuring1=title&rowId=2&options2=AND&q2=&occuring2=freetext&rowId=3&options3=AND&q3=&occuring3=freetext&x=67&y=17&publishedstart=yyyy&publishedend=yyyy&calendarInput=yyyy-mm-dd&la=any&it=any&show=all ''Otodectes cynotis'' publications] | ||
| + | |Vetstream = [https://www.vetstream.com/canis/search?s=mite Mites] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [[Category:Non-Burrowing_Mites]][[Category: | + | |
| + | {{review}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Non-Burrowing_Mites]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Expert_Review]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:17, 4 June 2016
| Otodectes cynotis | |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Arthropoda |
| Class | Arachnida |
| Order | Astigmata |
| Family | Psoroptidia |
| Genus | Otodectes |
| Species | O.cynotis |
Also known as: Ear mite
Introduction
Otodectes cynotis mites are surface mites. They are the cause of otodectic otitis, the most common mange of dogs and cats in the world. They are also found in the fox and the ferret. The mites inhabit the inner ear and feed on ear debris, they appear white in colour.
Pruritus is caused by irritation and the saliva of the mites, which is immunogenic. Secondary bacterial infection is common, resulting in purulent otitis externa which will require more treatment.
In cats, another presentation can be seen, which is that of an ectopic infection where signs are seen on other body parts such as the tail. This is due to contact e.g. cats sleeping in a curled position would allow mites to infest that area. Transmission of the mites can occur to kittens whilst they are suckling.
Identification
The mites have closed keratinous bars, apodemes on their ventral surface. They are smaller in size than psoroptes cuniculi and have short pedicles on their first and second pairs of legs.
Lifecycle
The Life cycle of an Otodectes mite takes 3 weeks. The females lay around five eggs a day on the surface of the ear canal. Four days later, larvae hatch and become nymphs. There are two nymphal stages before an adult mite is formed.
Clinical Signs
Clinical signs include head shaking, scratching of the ear and even the development of an aural haematoma because of the two above signs. The animal may often resent this area being touched.
A brown waxy exudate is produced and this later becomes crusty. If secondary bacterial infection has occurred then pus will also be seen in the ear canal.
Diagnosis
Clinical signs and history are indicative of the disease.
Visualisation of the mites via an auroscope will provide definitive diagnosis.
Treatment
Topical ear drops usually contain acaricide, fungicide, antibiotics and steroids. These should be dropped into the ear and the base of the ear then massaged to help the drops disperse. In cases of severe wax build up, ceruminolytics may be useful.
Selamectin as a spot on also acts to prevent Otodectes.
All in contact animals should be treated in the household as these may be asymptomatic carriers.
References
Blood, D.C. and Studdert, V. P. (1999) Saunders Comprehensive Veterinary Dictionary (2nd Edition), Elsevier Science.
Bond, R. (2008) Dermatology Study Guide, Royal Veterinary College.
Foster, A, and Foll, C. (2003) BSAVA small animal dermatology (second edition), British Small Animal Veterinary Association
Fox, M and Jacobs, D. (2007) Parasitology Study Guide Part 1: Ectoparasites, Royal Veterinary College
Also see:
| Otodectes cynotis Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Mites Flashcards |
 Search for recent publications via CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Otodectes cynotis publications |
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69565365ce9699_71523762 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69565365e0ce98_18019394 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69565365f418f4_01076627
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |