Difference between revisions of "Listeria monocytogenes"
m (→Introduction) |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{Taxobox | |
| − | + | |name =''Listeria monocytogenes'' | |
| − | + | |phylum =Firmicutes | |
| − | + | |class =Bacilli | |
| − | + | |order =Bacillales | |
| − | + | |family =Listeriaceae | |
| − | + | |genus =[[:Category:Listeria species|Listeria]] | |
| − | + | |species =''L.monocytogenes'' | |
| − | + | }} | |
| − | + | ==Introduction== | |
| − | + | [[File:listeria 2.jpg|right|thumb|250px|<small><center>''Listeria monocytogenes'' (MarcoTolo 2006, Wikimedia commons)</center></small>]] | |
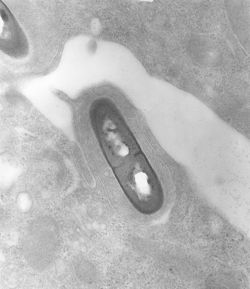
| − | + | ''Listeria monocytogenes'' is one of the six species belonging to the genus [[Listeria species - Overview|''Listeria'']]. It is gram positive bacteria. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | Outbreaks of [[Listeriosis|listeriosis]] in the human population are caused by ''L. monocytogenes''. The outbreaks are seasonal and linked to silage feeding. In most cases, the symptoms are those of a mild gastroenteritis or gripe. However, people who belong to the high - risk groups (elderly, infants, pregnant women or people with immunosuppression) might develop more serious symptoms (invasive disease) caused by meningoencephalitis, septicemia, miscarriage and mortality rate of approximately 30%. |
| − | [[Category: | + | |
| + | ''Listeria monocytogenes'' replicates in poor quality silage, where the pH exceeds 5.5. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Animals are highly susceptible during pregnancy due to lowered cell-mediated immunity. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |literature search = [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title%3A%28%22Listeria+monocytogenes%22%29+AND+od%3A%28cattle%29 ''Listeria monocytogenes'' cattle publications] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title%3A%28%22Listeria+monocytogenes%22%29+AND+od%3A%28sheep%29 ''Listeria monocytogenes'' in sheep publications] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title%3A%28%22Listeria+monocytogenes%22%29+AND+od%3A%28goats%29 ''Listeria monocytogenes'' in goats publications] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title%3A%28%22Listeria+monocytogenes%22%29+AND+od%3A%28dogs%29 ''Listeria monocytogenes'' in dogs publications] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title%3A%28%22Listeria+monocytogenes%22%29+AND+od%3A%28cats%29 ''Listeria monocytogenes'' in cats publications] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title%3A%28%22Listeria+monocytogenes%22%29+AND+od%3A%28horses%29 ''Listeria monocytogenes'' in horses publications] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Listeria species]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:07, 21 February 2021
| Listeria monocytogenes | |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Firmicutes |
| Class | Bacilli |
| Order | Bacillales |
| Family | Listeriaceae |
| Genus | Listeria |
| Species | L.monocytogenes |
Introduction
Listeria monocytogenes is one of the six species belonging to the genus Listeria. It is gram positive bacteria.
Outbreaks of listeriosis in the human population are caused by L. monocytogenes. The outbreaks are seasonal and linked to silage feeding. In most cases, the symptoms are those of a mild gastroenteritis or gripe. However, people who belong to the high - risk groups (elderly, infants, pregnant women or people with immunosuppression) might develop more serious symptoms (invasive disease) caused by meningoencephalitis, septicemia, miscarriage and mortality rate of approximately 30%.
Listeria monocytogenes replicates in poor quality silage, where the pH exceeds 5.5.
Animals are highly susceptible during pregnancy due to lowered cell-mediated immunity.
| Listeria monocytogenes Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Search for recent publications via CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Listeria monocytogenes cattle publications
Listeria monocytogenes in sheep publications Listeria monocytogenes in goats publications Listeria monocytogenes in dogs publications |