Difference between revisions of "Feline Leukaemia Virus"
(Created page with "Feline Leukemia Virus is commonly abbreviated to FeLV ====Antigenicity==== *Main envelope protein: gp70 *3 antigenic subgroups: *Group A **is transmitted between cats **is mono...") |
|||
| (40 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | Also known as '''''FeLV | |
| + | [[Image:FeLV Electron Micrograph.jpg|thumb|right|175px|FeLV Electron Micrograph [http://phil.cdc.gov/phil/home.asp Public Health Image Library] Image #5610]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Introduction== |
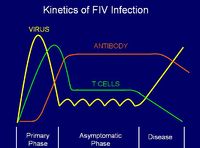
| − | + | [[Image:Kinetics of FeLV 2.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Kinetics of FeLV - Copyright Dr Brian Catchpole BVetMed PhD MRCVS]] | |
| − | + | FeLV is an oncogenic mammalian type C retrovirus which causes neoplasia ([[Lymphoma|lymphoma]]), myelosuppression ([[Regenerative and Non-Regenerative Anaemias|anaemia]]) and immunosuppression (of [[Lymphocytes#T cells|T cells]]). Three different strains are currently recognised: | |
| − | * | + | *FeLV-A -natural strain |
| − | * | + | *FeLV-B which formed through FeLV-A recombining with endogenous retroviral sequences in the feline genome. |
| − | + | *FeLV-C which formed from the spontaneous mutation of FeLV-A | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The virus replicates in the oropharyngeal lymphoid tissue causing a viraemia (the virus circulates in the bloodstream) which then spreads to the systemic lymphoid tissue. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Clinical Signs | + | ==Pathogenesis== |
| − | *'''Leukemia''' | + | FeLV is the "disease of friends": transmission usually occurs through mutual grooming. From the oropharynx, the virus spreads to most tissues in the body to replicate, notably: |
| + | *Bone marrow | ||
| + | *Thymus | ||
| + | *Salivary glands | ||
| + | *Reproductive tract | ||
| + | Most kittens but only 30% of adults become '''viraemic''' for life without producing antibody. The condition progresses in various forms: | ||
| + | *20% of viraemic cats die of tumors | ||
| + | *30% of viraemic cats die of FeLV-associated disease | ||
| + | *80% die within three years of exposure | ||
| + | 30% of adults exposed become '''latently infected''' and can become viraemic when immunosuppressed. | ||
| + | 40% of exposed adults remain healthy and develop Ab and CD8+ T cells after clearing the virus, without becoming reinfected or silent carriers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Clinical Signs== | ||
| + | *'''Leukemia''' - a neoplastic increase in blood cell numbers - usually white blood cells | ||
*'''Multicentric lymphosarcoma''': B or T cell tumors, which may be palpable as enlarged lymph nodes (particularly mesenteric) | *'''Multicentric lymphosarcoma''': B or T cell tumors, which may be palpable as enlarged lymph nodes (particularly mesenteric) | ||
| − | *'''Thymic lymphosarcoma''': T cell tumors, with only the thymus enlarged | + | *'''Thymic lymphosarcoma''': T cell tumors, with only the thymus enlarged -this may result in dyspnoea and can be confirmed by radiography |
| − | |||
| − | |||
*'''Alimentary lymphosarcoma''': B cell tumors of the Peyer's patches | *'''Alimentary lymphosarcoma''': B cell tumors of the Peyer's patches | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *Cutaneous horns on foot pads | ||
| + | *Epidermal and follicular epithelial hyperplasia, epidermal giant cells, dyskeratosis, necrosis, ulceration | ||
FeLV-associated disease: | FeLV-associated disease: | ||
*'''Immunodepression''' causing secondary disease | *'''Immunodepression''' causing secondary disease | ||
| − | *'''Reproductive failure''': FeLV crosses the placenta, causing fetal resorption or | + | *'''Reproductive failure''': FeLV crosses the placenta, causing fetal resorption or viraemic kittens with thymic aplasia |
| + | |||
| + | ==Epidemiology== | ||
| + | Vertical transmission of FeLV-A occurs from mother to kittens either via placenta, grooming, or milk. Horizontal transmission occurs via saliva during mutual grooming. FeLV is of particular concern for intensively bred cats because of close living conditions shared with other cats. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Recovery is linked to age and the presence of maternal antibody | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Antigenicity== | ||
| + | Viral subgroups have been categorised based on the different abnormalities detected in the host cellular envelope protein gp70. This protein interacts with a cellular receptor, and can prevent already infected cells from being targeted by further viral organisms. | ||
| − | + | There are 3 antigenic subgroups which are defined by the gp70 regulated viral response: | |
| − | * | + | *Group A is transmitted between cats and is monotypic: one vaccine covers all isolates. Infection with this viral subgroup leads to '''[[Lymphoma|lymphosarcoma]]'''. |
| − | * | + | *Group B is recombinant with transmissible FeLV-A; infection with viruses of this subgroup increases the chance of developing '''[[Thymus Neoplasia|thymic tumours]]'''. |
| − | + | *Group C is a mutant of subgroup A. Isolates are rare, and occur as A+C mixes, leading to an increased chance of developing '''[[Regenerative and Non-Regenerative Anaemias|anaemia]]'''. | |
| − | * | ||
| − | + | ==Diagnosis== | |
| − | *FeLV should be suspect in any cat with '''recurrent bacterial infections''', '''anemia''' or '''weight loss''' | + | *FeLV should be suspect in any cat with '''recurrent bacterial infections''', '''anemia''' or '''weight loss'''. Diagnostic tests available for confirmation of disease status include: |
| − | *'''ELISA''' for | + | *'''[[ELISA testing|ELISA]]''' for FeLV antigens (capsid protein p27 or envelope protein gp70) |
| − | *'''Immunochromatography''' is now | + | *'''Immunochromatography''' is now preferred as ELISA testing can give false positives |
| − | *'''Virus isolation''' from heparinised blood can | + | *'''Virus isolation''' from heparinised blood can be performed to confirm a positive diagnosis |
| + | *[[Immunofluorescence]] | ||
| + | *PCR | ||
| + | *Rapid-Immuno-Migration | ||
| + | *[[Western blot|Western Blot]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Infection Control== |
| − | + | Antigen positive cats with significant symptoms require euthanasia. Healthy positive cats should have the diagnosis confirmed by a second alternate testing method. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Vaccination=== | |
| − | + | Ideally, this should take place once antigen-negative status has been determined by laboratory testing. 'Leukogen' is a subunit vaccine (using envelope protein gp70) produced in ''E. coli'' mixed with Quill-A and alhydrogel. Others include inactivated virus and canarypox recombinants, but all MUST include FeLV-A. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==Treatment== | ||
| + | Where treatment is undertaken, anti-retroviral therapy is indicated with antibiotics to control secondary infections. Prevention is a key element in the control and treatment of FeLV overall. | ||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |Vetstream = [https://www.vetstream.com/felis/Content/Disease/dis60141 Feline leukemia virus disease] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | [[Category:Mammalian Type C retrovirus ]][[Category:Cat]][[Category: | + | [[Category:Mammalian Type C retrovirus ]][[Category:Cat Viruses]][[Category:Lymphoreticular and Haematopoietic Diseases - Cat]][[Category:Alimentary Diseases - Cat]][[Category:Secondary Immunodeficiency]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Lymphoreticular and Haemopoietic Diseases]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Anaemia|6]] |
| + | [[Category:Integumentary System - Viral Infections]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:16, 8 March 2022
Also known as FeLV
Introduction
FeLV is an oncogenic mammalian type C retrovirus which causes neoplasia (lymphoma), myelosuppression (anaemia) and immunosuppression (of T cells). Three different strains are currently recognised:
- FeLV-A -natural strain
- FeLV-B which formed through FeLV-A recombining with endogenous retroviral sequences in the feline genome.
- FeLV-C which formed from the spontaneous mutation of FeLV-A
The virus replicates in the oropharyngeal lymphoid tissue causing a viraemia (the virus circulates in the bloodstream) which then spreads to the systemic lymphoid tissue.
Pathogenesis
FeLV is the "disease of friends": transmission usually occurs through mutual grooming. From the oropharynx, the virus spreads to most tissues in the body to replicate, notably:
- Bone marrow
- Thymus
- Salivary glands
- Reproductive tract
Most kittens but only 30% of adults become viraemic for life without producing antibody. The condition progresses in various forms:
- 20% of viraemic cats die of tumors
- 30% of viraemic cats die of FeLV-associated disease
- 80% die within three years of exposure
30% of adults exposed become latently infected and can become viraemic when immunosuppressed. 40% of exposed adults remain healthy and develop Ab and CD8+ T cells after clearing the virus, without becoming reinfected or silent carriers.
Clinical Signs
- Leukemia - a neoplastic increase in blood cell numbers - usually white blood cells
- Multicentric lymphosarcoma: B or T cell tumors, which may be palpable as enlarged lymph nodes (particularly mesenteric)
- Thymic lymphosarcoma: T cell tumors, with only the thymus enlarged -this may result in dyspnoea and can be confirmed by radiography
- Alimentary lymphosarcoma: B cell tumors of the Peyer's patches
- Cutaneous horns on foot pads
- Epidermal and follicular epithelial hyperplasia, epidermal giant cells, dyskeratosis, necrosis, ulceration
FeLV-associated disease:
- Immunodepression causing secondary disease
- Reproductive failure: FeLV crosses the placenta, causing fetal resorption or viraemic kittens with thymic aplasia
Epidemiology
Vertical transmission of FeLV-A occurs from mother to kittens either via placenta, grooming, or milk. Horizontal transmission occurs via saliva during mutual grooming. FeLV is of particular concern for intensively bred cats because of close living conditions shared with other cats.
Recovery is linked to age and the presence of maternal antibody
Antigenicity
Viral subgroups have been categorised based on the different abnormalities detected in the host cellular envelope protein gp70. This protein interacts with a cellular receptor, and can prevent already infected cells from being targeted by further viral organisms.
There are 3 antigenic subgroups which are defined by the gp70 regulated viral response:
- Group A is transmitted between cats and is monotypic: one vaccine covers all isolates. Infection with this viral subgroup leads to lymphosarcoma.
- Group B is recombinant with transmissible FeLV-A; infection with viruses of this subgroup increases the chance of developing thymic tumours.
- Group C is a mutant of subgroup A. Isolates are rare, and occur as A+C mixes, leading to an increased chance of developing anaemia.
Diagnosis
- FeLV should be suspect in any cat with recurrent bacterial infections, anemia or weight loss. Diagnostic tests available for confirmation of disease status include:
- ELISA for FeLV antigens (capsid protein p27 or envelope protein gp70)
- Immunochromatography is now preferred as ELISA testing can give false positives
- Virus isolation from heparinised blood can be performed to confirm a positive diagnosis
- Immunofluorescence
- PCR
- Rapid-Immuno-Migration
- Western Blot
Infection Control
Antigen positive cats with significant symptoms require euthanasia. Healthy positive cats should have the diagnosis confirmed by a second alternate testing method.
Vaccination
Ideally, this should take place once antigen-negative status has been determined by laboratory testing. 'Leukogen' is a subunit vaccine (using envelope protein gp70) produced in E. coli mixed with Quill-A and alhydrogel. Others include inactivated virus and canarypox recombinants, but all MUST include FeLV-A.
Treatment
Where treatment is undertaken, anti-retroviral therapy is indicated with antibiotics to control secondary infections. Prevention is a key element in the control and treatment of FeLV overall.
| Feline Leukaemia Virus Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |