Difference between revisions of "Abomasum - Anatomy & Physiology"
m (Text replace - "[[Forestomach - Anatomy & Physiology|" to "[[Monogastric Stomach - Anatomy & Physiology|") |
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| − | + | ==Overview== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | The abomasum is the fourth chamber in the ruminant. It functions | + | The '''abomasum''' is the fourth chamber in the ruminant. It functions similarly to the [[Monogastric Stomach - Anatomy & Physiology|carnivore stomach]] as it is glandular and digests food chemically, rather than mechanically or by fermentation like the other 3 chambers of the ruminant stomach. |
| − | The abomasum differs in its position within the abdomen, depending on fullness of the other chambers of the stomach, intrinsic abomasonal activity, contractions of the [[ | + | The '''abomasum''' differs in its position within the abdomen, depending on fullness of the other chambers of the stomach, intrinsic abomasonal activity, contractions of the '''[[Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology|rumen]]''' and '''[[Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|reticulum]]''' (to which it is attached) and by age and pregnancy status. |
[[Displaced Abomasum|Displacement of the abomasum]] to the left or to the right is a common disorder affecting dairy cows due to high concentrate feed. | [[Displaced Abomasum|Displacement of the abomasum]] to the left or to the right is a common disorder affecting dairy cows due to high concentrate feed. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 11: | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| − | [[Image:Abomasum Anatomy Sheep.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:Abomasum Anatomy Sheep.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Abomasum Anatomy (Sheep) - Copyright RVC 2008]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | The '''abomasum''' lies upon the abdominal floor. The cranial part is split into the '''pylorus''' and '''body'''. There is also a caudal part. It is covered by the '''lesser omentum'''. It has 15-20 folds inside. The '''torus''' is at the pyloric exit. The outflow is fairly constant. There is motility at the '''pylorus''' (peristalsis) and some control at the '''pyloric sphincter'''. The abomasum is large in newborn animals. The proximal ends of the abomasal folds form a plug preventing reflux into the '''[[Omasum - Anatomy & Physiology|omasum]]'''. It has thin walls and a serosa covering. | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
| − | + | The function of the abomasum is the chemical breakdown of food. It secretes '''hydrochloric acid''' and '''pepsinogen'''. It has some intrinsic motility. Impaired motility can cause distension. The movements are slow, contractions occur first in the proximal part and are more forceful at the pyloric part. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Vasculature== | ==Vasculature== | ||
| − | + | The vasculature of the abomasum includes the '''cranial mesenteric artery''', the '''celiac artery''' and the '''left gastric''' and '''left gastroepiploic''' arteries. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Innervation== | ==Innervation== | ||
| − | + | The innervation of the abomasum includes the '''dorsal vagus nerve''' ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN X]]) and the '''ventral vagus nerve''' ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN X]]) (most important). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Lymphatics== | ==Lymphatics== | ||
| − | + | Single lymph nodules are present at the junction between the epithelium and the lamina propria. Numerous small lymph nodes are scattered in the abomasal curvatures. The lymph drains to larger atrial nodes between the '''cardia''' and '''[[Omasum - Anatomy & Physiology|omasum]]''', then to the hepatic lymph nodes. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Histology== | ==Histology== | ||
[[Image:Abomasum Histology Sheep.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Abomasum Histology (Sheep) - Copyright RVC 2008]] | [[Image:Abomasum Histology Sheep.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Abomasum Histology (Sheep) - Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
| − | + | The abomasum has a simple columnar epithelium. There are 3 layers of '''''tunica muscularis''''' - inner oblique, middle circular and outer longitudinal. The '''''lamina muscularis''''' is thicker and has 3 separate layers. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Gastric glands are present in the '''''lamina propria''''' of the mucosal layer in the pyloric region (lighter part). The abomasum is heavily coated by mucous for protection. The submucosa contains loose connective tissue, many blood vessels and unilocular adipocytes. The coiled glands in the ''lamina propria'' open into deep gastric pits. The inner mucosa is pink. '''Rugae''' are present in the pyloric region and a '''torus''' (large swelling) is present at the pyloric passage to narrow the lumen. The dark mucosa of the fundus and body contains peptic glands. | ||
==Species Differences== | ==Species Differences== | ||
===Small Ruminants=== | ===Small Ruminants=== | ||
| − | + | The abomasum can contact the [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|liver]]. The abomasum is proportionately larger than in cattle. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
| − | [[ | + | '''Click here for [[Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology|Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology]]''' |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | '''Click here for [[Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology]]''' | ||
| + | '''Click here for [[Omasum - Anatomy & Physiology|Omasum - Anatomy & Physiology]]''' | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |flashcards = [[Abomasum Flashcards]] | ||
| + | <!-----|videos = [http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Anatomy/bovine/Pot0052.mp4 Lateral view of the Abdomen of a young Ruminant]<br>[http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Anatomy/bovine/pot0175.mp4 Sections of the Ruminant Stomach]<br>[http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Anatomy/ovine/Pot0047.mp4 Ovine Omasum and Abomasum]<br>[http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Frean/sheep/LeftSideTopography.mp4 Left sided topography of the Ovine Abdomen and Thorax]<br>[http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Frean/sheep/RightSideTopography.mp4 Right sided topography of the Ovine Abdomen]<br>[http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Frean/sheep/RuminantStomachStructure.mp4 Structure of the ruminant forestomachs]----> | ||
| + | |powerpoints = [[Ruminant Gastrointestinal Tract Histology resource|Histology of the ruminant gastrointestinal tract]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | ==Webinars== |
| + | <rss max="10" highlight="none">https://www.thewebinarvet.com/gastroenterology-and-nutrition/webinars/feed</rss> | ||
| + | [[Category:Stomach - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| + | [[Category:A&P Done]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Alimentary Anatomy - Cattle]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:04, 2 November 2022
Overview
The abomasum is the fourth chamber in the ruminant. It functions similarly to the carnivore stomach as it is glandular and digests food chemically, rather than mechanically or by fermentation like the other 3 chambers of the ruminant stomach.
The abomasum differs in its position within the abdomen, depending on fullness of the other chambers of the stomach, intrinsic abomasonal activity, contractions of the rumen and reticulum (to which it is attached) and by age and pregnancy status.
Displacement of the abomasum to the left or to the right is a common disorder affecting dairy cows due to high concentrate feed.
Structure
The abomasum lies upon the abdominal floor. The cranial part is split into the pylorus and body. There is also a caudal part. It is covered by the lesser omentum. It has 15-20 folds inside. The torus is at the pyloric exit. The outflow is fairly constant. There is motility at the pylorus (peristalsis) and some control at the pyloric sphincter. The abomasum is large in newborn animals. The proximal ends of the abomasal folds form a plug preventing reflux into the omasum. It has thin walls and a serosa covering.
Function
The function of the abomasum is the chemical breakdown of food. It secretes hydrochloric acid and pepsinogen. It has some intrinsic motility. Impaired motility can cause distension. The movements are slow, contractions occur first in the proximal part and are more forceful at the pyloric part.
Vasculature
The vasculature of the abomasum includes the cranial mesenteric artery, the celiac artery and the left gastric and left gastroepiploic arteries.
Innervation
The innervation of the abomasum includes the dorsal vagus nerve (CN X) and the ventral vagus nerve (CN X) (most important).
Lymphatics
Single lymph nodules are present at the junction between the epithelium and the lamina propria. Numerous small lymph nodes are scattered in the abomasal curvatures. The lymph drains to larger atrial nodes between the cardia and omasum, then to the hepatic lymph nodes.
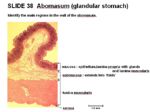
Histology
The abomasum has a simple columnar epithelium. There are 3 layers of tunica muscularis - inner oblique, middle circular and outer longitudinal. The lamina muscularis is thicker and has 3 separate layers.
Gastric glands are present in the lamina propria of the mucosal layer in the pyloric region (lighter part). The abomasum is heavily coated by mucous for protection. The submucosa contains loose connective tissue, many blood vessels and unilocular adipocytes. The coiled glands in the lamina propria open into deep gastric pits. The inner mucosa is pink. Rugae are present in the pyloric region and a torus (large swelling) is present at the pyloric passage to narrow the lumen. The dark mucosa of the fundus and body contains peptic glands.
Species Differences
Small Ruminants
The abomasum can contact the liver. The abomasum is proportionately larger than in cattle.
Links
Click here for Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology
Click here for Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology
Click here for Omasum - Anatomy & Physiology
| Abomasum - Anatomy & Physiology Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Abomasum Flashcards |
 Selection of relevant PowerPoint tutorials |
Histology of the ruminant gastrointestinal tract |
Webinars
Failed to load RSS feed from https://www.thewebinarvet.com/gastroenterology-and-nutrition/webinars/feed: Error parsing XML for RSS