Difference between revisions of "Nephron Microscopic Anatomy"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(New page: {{toplink |backcolour = C1F0F6 |linkpage =The Nephron - Anatomy & Physiology |linktext =THE NEPHRON |maplink = Urinary System (Content Map) - Anatomy & Physiology |pagetype =Anatomy }} <br...) |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
}} | }} | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | |||
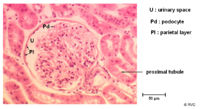
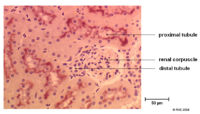
| + | ==Glomerulus== | ||
| + | [[Image:normcorpusclekidapx.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<small><center>Histology section of a normal renal corpuscle (© RVC 2008)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | [[Image:normcorpusclekidap2.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<small><center>Histology section of a normal renal corpuscle (© RVC 2008)</center></small>]] | ||
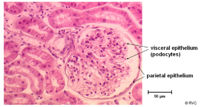
| + | [[Image:normcorpusclebowmankidap.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<small><center>Histology section of a normal renal corpuscle showing the layers of the bowmans capsule (© RVC 2008)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | * Made up of many parallel capillaries | ||
| + | * These capillaries do not connect to venules as with other capillaries | ||
| + | * Blood flows into these capillaries through a wide afferent arteriole and leaves through a narrower efferent arteriole | ||
| + | * The flow from the efferant arteriole enters the [[Peritubular Capillaries - Anatomy & Physiology|peritubular capillaries]] surrounding the [[Proximal Tubule - Anatomy & Physiology| Proximal Tubule]] | ||
| + | * This change in diameter maintains a high filtration pressure which is essential for filtration | ||
| + | * Also the blood entering the afferent arteriole is at very high pressure already as it from the renal artery | ||
| + | * The pressure actually forces molecules through the '''glomerular filtration barrier''' which is responsible for selectively filtering the blood forming the glomerular filtrate. | ||
| + | * As well as the the cells in the blood vessels the other component of the glomerulus are the mesangial cells: | ||
| + | ** These give support to the glomerulus | ||
| + | ** Maintain glomerular basal lamina | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Bowmans Capsule== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Surrounds the capillaries of the glomerulus | ||
| + | * Has two layers | ||
| + | ** Inner visceral layer - Podocytes | ||
| + | ** Outer parietal layer | ||
| + | * It is here where the filtrate is collected before entering the proximal tubule | ||
Revision as of 13:08, 3 September 2008
|
|
Glomerulus
- Made up of many parallel capillaries
- These capillaries do not connect to venules as with other capillaries
- Blood flows into these capillaries through a wide afferent arteriole and leaves through a narrower efferent arteriole
- The flow from the efferant arteriole enters the peritubular capillaries surrounding the Proximal Tubule
- This change in diameter maintains a high filtration pressure which is essential for filtration
- Also the blood entering the afferent arteriole is at very high pressure already as it from the renal artery
- The pressure actually forces molecules through the glomerular filtration barrier which is responsible for selectively filtering the blood forming the glomerular filtrate.
- As well as the the cells in the blood vessels the other component of the glomerulus are the mesangial cells:
- These give support to the glomerulus
- Maintain glomerular basal lamina
Bowmans Capsule
- Surrounds the capillaries of the glomerulus
- Has two layers
- Inner visceral layer - Podocytes
- Outer parietal layer
- It is here where the filtrate is collected before entering the proximal tubule