Difference between revisions of "Intussusception"
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
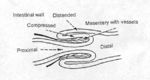
'''Intussusception''' is the invagination of one portion of the gastrointestinal tract into the lumen of the adjacent portion. The intussusceptum is the invaginated segment and the intussuscipien is the enveloping segment. | '''Intussusception''' is the invagination of one portion of the gastrointestinal tract into the lumen of the adjacent portion. The intussusceptum is the invaginated segment and the intussuscipien is the enveloping segment. | ||
| − | Intussusception results from abnormal peristalsis. Vigorous contractions force a segment of intestine to teloscope into the lumen of a more relaxed adjacent segment. | + | Intussusception results from abnormal peristalsis. Vigorous contractions force a segment of intestine to teloscope into the lumen of a more relaxed adjacent segment. A normograde intussusception is most common, but retrograde intussusception has also been reported. |
Intussusceptions can be classified according to their location in the gastrointestinal tract. They usually occur in regions where there is a significant change in lumen diameter, such as ileocolic and gastroesphageal junctions. Ileocolic intussusceptions are most common, they frequently protrude from the rectum and must be distinguished from a rectal prolapse. In the case of an intussusception, it is possible to pass a probe next to the anus, but not in [[Rectal Prolapse|rectal proplapse]]. | Intussusceptions can be classified according to their location in the gastrointestinal tract. They usually occur in regions where there is a significant change in lumen diameter, such as ileocolic and gastroesphageal junctions. Ileocolic intussusceptions are most common, they frequently protrude from the rectum and must be distinguished from a rectal prolapse. In the case of an intussusception, it is possible to pass a probe next to the anus, but not in [[Rectal Prolapse|rectal proplapse]]. | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
*Weight loss | *Weight loss | ||
| − | === | + | ===Radiography=== |
Plain abdominal radiographs do not always provide a definitive diagnosis. In cases of complete obstruction distented loops of intestine and a tubular soft tissue mass are usually obvious, but a partial obstruction will produce much more subtle signs which may be missed. | Plain abdominal radiographs do not always provide a definitive diagnosis. In cases of complete obstruction distented loops of intestine and a tubular soft tissue mass are usually obvious, but a partial obstruction will produce much more subtle signs which may be missed. | ||
A barium enema or upper gastrointestinal contrast study can be useful in identifying the site of obstruction but may result in delay of treatment and should be used with care as leakage of contrast into the abdominal cavity will result in peritonitis. | A barium enema or upper gastrointestinal contrast study can be useful in identifying the site of obstruction but may result in delay of treatment and should be used with care as leakage of contrast into the abdominal cavity will result in peritonitis. | ||
| + | ===Ultrasound=== | ||
Abdominal ultrasound will reveal a cylindrical mass with layering of the intestinal wall. On a transverse section, a hyperechoic target mass in the centre with multiple hyperechoic and hypoechoic concentric ring is seen. On a longitudinal section, multiple hyperechoic and hypoechoic lines are seen. The intestines may also be hypomotile and the intestine proximal to the obstruction may be distented with fluid. | Abdominal ultrasound will reveal a cylindrical mass with layering of the intestinal wall. On a transverse section, a hyperechoic target mass in the centre with multiple hyperechoic and hypoechoic concentric ring is seen. On a longitudinal section, multiple hyperechoic and hypoechoic lines are seen. The intestines may also be hypomotile and the intestine proximal to the obstruction may be distented with fluid. | ||
| + | ===Endoscopy=== | ||
Colonoscopy can identify ileocolic or caecocolic intussusception. Oesopgagoscopy can reveal a gastroesophageal intussusception, a soft tissue mass is visible in the lumen of the oesophagus. | Colonoscopy can identify ileocolic or caecocolic intussusception. Oesopgagoscopy can reveal a gastroesophageal intussusception, a soft tissue mass is visible in the lumen of the oesophagus. | ||
Revision as of 19:44, 6 July 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
Description
Intussusception is the invagination of one portion of the gastrointestinal tract into the lumen of the adjacent portion. The intussusceptum is the invaginated segment and the intussuscipien is the enveloping segment.
Intussusception results from abnormal peristalsis. Vigorous contractions force a segment of intestine to teloscope into the lumen of a more relaxed adjacent segment. A normograde intussusception is most common, but retrograde intussusception has also been reported.
Intussusceptions can be classified according to their location in the gastrointestinal tract. They usually occur in regions where there is a significant change in lumen diameter, such as ileocolic and gastroesphageal junctions. Ileocolic intussusceptions are most common, they frequently protrude from the rectum and must be distinguished from a rectal prolapse. In the case of an intussusception, it is possible to pass a probe next to the anus, but not in rectal proplapse.
Pathogenesis
The proximal intestine invaginates into the adjacent distal portion, taking its mesenteric attachment with it. Compression of the mesenteric vessels obstructs venous drainage of the gut, resulting in venous congestion, leading to swelling and oedema. An inflammatory exudate is released from the serosal surface, fibrinous adhesions may form between surfaces making the structure irreducible this may progress to necrosis of the tissue. There is functional obstruction to bowel. May rupture, leading to peritonitis and death. Intussusception normally occurs due to gastrointestinal disease, although it is often hard to identify the cause. Parasites, infectious enteritis, metabolic disorders, foreign bodies, history of recent intestinal surgery, intestinal masses have all been known to associate with intussusception. Chronic intussusception can occur with little haemodynamic changes.
- Associated with any condition that increases peristalsis
- Enteritis
- Foreign body
- Heavy parasitism
- Previous intestinal surgery
- Intramural abscess/tumour
- Motility disorders.
- Change in diet
- Bacterial infection
Signalment
Species
Intussusception occurs in dogs and cats, but gastroesophageal intussusception has only been reported in dogs.
Breed
German shepherd dogs and Siamese cats are over represented. German Shepherd dogs are particularly predisposed to gastroesophageal intussusception.
Age
Young animals are most commonly affected, 80% of cases are less than a year old.
Diagnosis
Clinical Signs
Clinical signs vary depending on location, duration and the degree of obstruction and vascular compromise.
Acute Intussusception
- Vomiting
- Regurgitation
- Haematemesis
- Abdominal discomfort
- collapse
- Palpable sausage-shaped mass in the abdomen
- Diarrhoea; bloody and mucoid
- Tenesmus and Haematochezia; in cases of ileocaecocolic intussusception
Chronic Intussusception
- Intermittent diarrhoea, which may be bloody and mucoid
- Tenesmus
- Depression
- Anorexia
- Weight loss
Radiography
Plain abdominal radiographs do not always provide a definitive diagnosis. In cases of complete obstruction distented loops of intestine and a tubular soft tissue mass are usually obvious, but a partial obstruction will produce much more subtle signs which may be missed. A barium enema or upper gastrointestinal contrast study can be useful in identifying the site of obstruction but may result in delay of treatment and should be used with care as leakage of contrast into the abdominal cavity will result in peritonitis.
Ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound will reveal a cylindrical mass with layering of the intestinal wall. On a transverse section, a hyperechoic target mass in the centre with multiple hyperechoic and hypoechoic concentric ring is seen. On a longitudinal section, multiple hyperechoic and hypoechoic lines are seen. The intestines may also be hypomotile and the intestine proximal to the obstruction may be distented with fluid.
Endoscopy
Colonoscopy can identify ileocolic or caecocolic intussusception. Oesopgagoscopy can reveal a gastroesophageal intussusception, a soft tissue mass is visible in the lumen of the oesophagus.
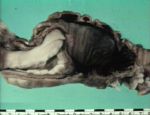
Pathology
The degree of damage to the intestine depends on the severity of the intussusception. In severe or chronic cases fibrinous adhesions form between surfaces making the structure irreducible. Necrosis of the tissue usually follows.
Intussusception may occur due to post mortem change, in this case there are no other associated changes and the invaginated intestine is easily reducible.
Treatment
Medical
Fluid therapy and correction of electrolyte and acid-base abnormalities should be carried out prior to surgical correction.
Surgery
Surgery is required to manually reduce the intussusception, it may be necessary to resect and anastomose the intestine in cases where the adhesions have formed. This decision depends on the viability of the intestines, as determined by the colour, vascular supply and presence or absence of peristalsis. Complications include dehiscence at the site of anastomosis, peritonitis, recurrence (11-20%, most common within 1-5 days post surgery), ileus, intestinal obstruction and short bowel syndrome. Recurrence can be treated with motility altering drugs or intestinal pexy or plication. It is important to preserve as much of the intestine as possible to avoid short bowel syndrome.
Prognosis
This depends on the location, completeness and duration of the intusussception. The prognosis is good in animals treated with early surgical intervention and aggressive supportive care. The prognosis is poor for animals with perforated intestine and peritonitis.
References
- Barreau, P. (2008) Intussusception: Diagnosis and Treatment 33rd WSAVA Congress
- Ettinger, S.J. and Feldman, E. C. (2000) Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine Diseases of the Dog and Cat Volume 2 (Fifth Edition) W.B. Saunders Company.
- Fossum, T. W. et. al. (2007) Small Animal Surgery (Third Edition) Mosby Elsevier
- Hall, E.J, Simpson, J.W. and Williams, D.A. (2005) BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Gastroenterology (2nd Edition) BSAVA
- Nelson, R.W. and Couto, C.G. (2009) Small Animal Internal Medicine (Fourth Edition) Mosby Elsevier.