Difference between revisions of "Gastric Ulceration - Horse"
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
*'''Gastrodudodenal motility''': critically ill neonatal foals can have a substantially different pH profile compared to clinically normal foals, possibly due to changes in gastric motility and acid secretion.(45 in Sanhcez) | *'''Gastrodudodenal motility''': critically ill neonatal foals can have a substantially different pH profile compared to clinically normal foals, possibly due to changes in gastric motility and acid secretion.(45 in Sanhcez) | ||
| − | ====Intrinsic | + | ====Intrinsic ulcerogenic factors==== |
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and a sustained gastric pH<4.0 are the most significant factors in gastric ulceration. Volatile fatty acids (VFAs), lactic acid and bile acids act synergistically with HCl to cause changes in squamous mucosal bioelectric properties (the first sign of acidic damage). VFAs and lactic acid are by-products of bacterial fermentation of sugars in concentrate diets. | Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and a sustained gastric pH<4.0 are the most significant factors in gastric ulceration. Volatile fatty acids (VFAs), lactic acid and bile acids act synergistically with HCl to cause changes in squamous mucosal bioelectric properties (the first sign of acidic damage). VFAs and lactic acid are by-products of bacterial fermentation of sugars in concentrate diets. | ||
*'''Hydrochloric acid''' damages the squamous mucosa by compromising the outer cell barrier. It then diffuses into the squamous cells of the ''stratum spinosum'', inhibiting cellular sodium transport and causing cell swelling, necrosis and eventual ulceration. (Argenzio and Eismann 1987; Nadeau et al. 2003a,b) | *'''Hydrochloric acid''' damages the squamous mucosa by compromising the outer cell barrier. It then diffuses into the squamous cells of the ''stratum spinosum'', inhibiting cellular sodium transport and causing cell swelling, necrosis and eventual ulceration. (Argenzio and Eismann 1987; Nadeau et al. 2003a,b) | ||
| − | *'''Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs)''' (acetic, propionic, butyric and valeric acids) are lipid soluble. They readily diffuse into the squamous mucosal cells of the ''stratum spinosum'' | + | *'''Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs)''' (acetic, propionic, butyric and valeric acids) are lipid soluble. They readily diffuse into the squamous mucosal cells of the ''stratum spinosum'' causing similar damage to HCl. |
*'''Lactic acid''' may increase the permeability of the squamous mucosa in the presence of VFAs and/or HCl (Andrews et al. 2008). | *'''Lactic acid''' may increase the permeability of the squamous mucosa in the presence of VFAs and/or HCl (Andrews et al. 2008). | ||
Revision as of 21:19, 30 July 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
| Also known as: | Gastroduodenal ulceration Gastrointestinal ulceration |
| See also: | Gastric Ulceration - all species |
Description
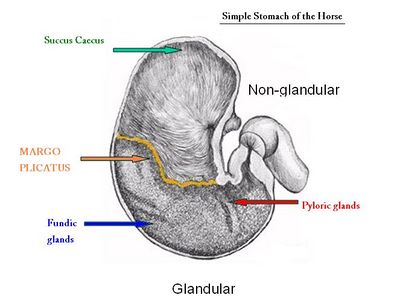
The term 'Equine gastric ulcer syndrome (EGUS)' encompasses a number of disease complexes[1] associated with ulceration of the oesophageal, gastric or duodenal mucosa[2] in horses. When such damage is caused by acidic gastric juice, the defect is described as a 'peptic ulcer'.[2] Ulceration of either or both[3] regions of the gastric mucosa is one of the most important problems of the equine stomach as it may limit performance[4] and compromise welfare.[5] The non-glandular (proximal or orad) region of the equine stomach is lined by stratified squamous mucosa and a glandular mucosa lines the distal (aborad) portion. The two regions meet abruptly at the margo plicatus[6], adjacent to where most ulcers occur.[2] Damage to these regions occurs via differing pathophysiological routes and varies in severity from inflammation, to cellular death and sloughing causing disruption of the superficial mucosa (erosion), penetration of the submucosa down to the level of the lamina propria[2](ulceration), full thickness ulceration (perforation)[6] and potentially duodenal stricture.[7] The occult nature of the disease typically precludes the observation of clinical signs until severe ulceration has developed.[2]
Prevalence
The prevalence of equine gastric ulceration has increased over the last century.[8] In a retrospective study of 3715 Swedish horses, ulcers were most often found in the squamous mucosa along the margo plicatus, then the glandular body, proximal squamous mucosa and antrum.[8] For the squamous region, reported prevalences are:
- Racehorses 66-93%[9][10][11]
- Racehorses in active race training 80-93% (incidence 100%)[12][13]
- Show horses 58%[14]
- Ponies 78%[15]
- Endurance horses 67%[16]
- Western performance horses 40%[17]
- Thoroughbred broodmares (67-77%)[18]
- Nonracing performance horses (17% pre-competition, 56% post-competition)[19]
- Pleasure horses in full work ~ 60%[4]
- Pleasure, riding lessons, showing 37%[20]
- Foals ~25-57%[21][22][23], the incidence increases dramatically in foals with clinical signs, especially gastrointestinal signs.[2]
The prevalence and severity of ulcers increases with work intensity[7] and duration[24][25], thus racehorses in active training are more often affected[9] and in half of these, the lesions are moderate to severe.[7] In one study, all horses developed gastric ulcers within 2 weeks of entering simulated race training.[12] Lesions are thought to be chronically progressive during race training, but to regress during retirement.[9] Horses with signs of gastrointestinal distress also demonstrate an increased frequency and severity of ulcerative lesions.[2]EGUS prevalence is high in horses with bowel, liver and oesophageal lesions.[8] Among show horses, 82% of those with signs of abdominal discomfort had gastric ulcers[26] Around 30% of adult horses and about 50% of foals have mild gastric erosions which heal without treatment or clinical signs.[7] In 201 clinically normal horses in Denmark, 53% had EGUS with severity score >2 and older horses were more likely to have lesions in both regions of the stomach[27]
Signalment
EGUS develops in horses of all ages[6] but is most common in young horses in training and foals. Gastric ulceration is considered to be rare in horses at pasture.[28]
Pathophysiology
Anatomy
In the horse, the squamous (non-glandular) mucosa covers the lining of the oesophagus and about one third of the gastric wall. It provides a protective barrier comprising a tightly bound superifcial layer of cornified cells.(EGUC) This squamous epithelium has no absorptive or secretory function. The glandular region of the stomach contains mucus-secreting cells and gastric glands. The margo plicatus is analagous to the gastro-oesophageal junction in man, however it lacks the lower oesophageal sphincter that helps to prevent acidic injury of the squamous mucosa(Sanchez). Equine gastric ulcers largely occur in the squamous region of the stomach. The predilection sites in various groups are:
- Neonatal foals: glandular mucosa
- Healthy suckling foals younger than 50 days: squamous mucosa adjacent to margo plicatus along the greater curvature, squamous epithelial desquamation
- Suckling foals with older than 50 days with clinical signs: squamous mucosa along lesser curvature, squamous mucosa of fundus and adjacent to margo plicatus.
- Sucklings and early weanlings: gastroduodenal ulcer disease (GDUD) – lesions in proximal duodenum, also severe lesions in squamous or glandular region
- Yearlings and adults: squamous epithelium, particularly adjacent to margo plicatus, glandular and antral involvement becoming more common (9, 23 in Sanchez), severe cases of ulceration can extend dorsally into squamous fundus (Sanchez)
Intrinsic protective factors
Glandular mucosal defence mechanisms
- Mucus: secreted by specialised mucous neck cells. A viscous, hydrophobic glycoproteinaceous gel that adheres to the mucosa and resists acid and pepsin contact. Also acts as a lubricant to minimise mechanical damage.(EGUC)
- Bicarbonate: secreted by gastric mucosal cells. Secretion triggered by luminal acid concentrations, mechanical irritation, and release of endogenous prostaglandins. Bicarbonate trapped in the mucous layer forms a pH gradient allowing a physiological pH at the mucosal surface and a gastric acid pH at the luminal surface.(EGUC)
- Epidermal growth factors: found in salivary gland secretions, promote DNA synthesis and proliferation of gastric mucosal cells. Also play a role in prostaglandin synthesis and inhibit HCl secretion by the parietal glands.(EGUC)
- Epithelial restitution mechanisms: important in the maintenance of gastric mucosal integrity (maintain tight junctions). Epithelial injury induces migration of adjacent cells to replace damaged cells within minutes without the need of new cell proliferation. Shear forces, induced by mixing of ingested material, are counteracted by epithlial restoration.(EGUC)
- Adequate mucosal blood supply: required to provide the mucosa with oxygen and nutrients to produce the mucus-bicarbonate layer and to support rapid turnover of epithelial cells. Also required to remove acid that has diffused through the mucous layer to the mucosa.(EGUC) Mucosal perfusion may be important in the stress-related ulceration of neonates(Sanchez)
- Prostaglandins: inhibit acid secretion, promote mucosal blood flow (through vasodilation), increase mucus and bicarbonate secretions and support mucosal cell repair. PGE2 is especially important in these functions.(EGUC)
Squamous mucosal defence mechanisms
The squamous mucosa has comparatively few defence mechansims:(EGUC)
- Intercellular tight junctions and intracellular buffering systems act as barriers
- Epidermal growth factor has also been found to contribute to the healthy maintenance and repair of gastric squamous epithelium (Jeffrey et al. 200 in(Martineau 2009)
- Leukotrienes provide mucosal protection
Other intrinsic defence mechanisms
- Gastrodudodenal motility: critically ill neonatal foals can have a substantially different pH profile compared to clinically normal foals, possibly due to changes in gastric motility and acid secretion.(45 in Sanhcez)
Intrinsic ulcerogenic factors
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and a sustained gastric pH<4.0 are the most significant factors in gastric ulceration. Volatile fatty acids (VFAs), lactic acid and bile acids act synergistically with HCl to cause changes in squamous mucosal bioelectric properties (the first sign of acidic damage). VFAs and lactic acid are by-products of bacterial fermentation of sugars in concentrate diets.
- Hydrochloric acid damages the squamous mucosa by compromising the outer cell barrier. It then diffuses into the squamous cells of the stratum spinosum, inhibiting cellular sodium transport and causing cell swelling, necrosis and eventual ulceration. (Argenzio and Eismann 1987; Nadeau et al. 2003a,b)
- Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) (acetic, propionic, butyric and valeric acids) are lipid soluble. They readily diffuse into the squamous mucosal cells of the stratum spinosum causing similar damage to HCl.
- Lactic acid may increase the permeability of the squamous mucosa in the presence of VFAs and/or HCl (Andrews et al. 2008).
Risk Factors
Exercise
There appears to be a high prevalence of gastric ulcers in horses performing in most disciplines including racing, endurance, show jumping, dressage and western performance.[29] Although this may be related to exercise, other confounding factors associated with these disciplines such as travel, diet, feeding regime, NSAIDs and stress may be significant. However, Vatistas and co-workers (1999) were able to induce and maintain EGUS in racehorses in fast work without the use of NSAIDs or fasting before exercise.[12] There is also evidence that training for just 8 days is suffcient to induce gastric ulcers.[30] Furthermore, the higher prevalence of gastric ulcers at post mortem in racehorses in training compared to those in retirement adds weight to the hypothesis that exercise is an important risk factor for EGUS.[9] Strenuous exercise is known to stimulate gastrin release which has effects on HCl secretion, gastric emptying and gastric blood flow. It is also thought that exposure of the squamous mucosa to acid is increased as the stomach is compressed by the abdominal viscera and diaphragm during excercise.[31]
Housing and Transport
Housing in stables has been proposed as a risk factor for gastric ulcers, with more lesions being found in confined horses compared to those out at grass.[32] However, when comparing solitary stable confinement with stabling next to a companion, and finally turn out in a paddock, Husted and colleagues (2008) found that the environmental situation had no effect on mucosal acid exposure in the equine stomach.[33] Transport has also been shown to induce squamous mucosal ulceration in horses.[34]
Diet
Feed deprivation encourages gastric ulceration in two ways: (1) it precludes the buffering capacity of protein leading to a reduced gastric pH[35] and (2) it empties the stomach and exposes the squamous mucosa to the more mobile gastric juice.[8] It is unsurprising, therefore, that an alternating feed-fast protocol would produce a consistent model of ulcer induction in the equine squamous mucosa.[36][37] Despite this, feed deprivation is not a prerequisite for gastric ulceration in the horse.[38] Diets that are plentiful in roughage prolong the mastication process and the production of salivary bicarbonate that protects the gastric mucosa. A diet of high grain and low roughage thus predisposes to EGUS.[39] This sort of diet is commonly fed to racehorses but dietary components have also been shown to influence EGUS risk in nonracehorses.[40] Ponies fed a concentrate diet had a greater prevalence of gastric ulcers than ponies fed hay alone.[12] and this may be because grain and pelleted feeds are asssociated with increased serum gastrin.[41] High starch meals are also a risk because they are fermented to volatile fatty acids (VFAs) and lactic acid and are emptied from the stomach relatively slowly.[42][43][44]
Other ailments
Conditions that produce abdominal pain and/or inappetance are likely to reduce food intake and predipose to gastric ulcers.[8] This may be the reason that colic and other gastrointestinal disorders have been associated with EGUS.[45] Alternatively, EGUS may be part of a more general gastrointestinal disease complex.[12] Stress induced by other clinical disorders has been reported to increase the prevalence of EGUS in neonatal foals[46] and a similar mechanism may exist for adult animals.[12]
NSAIDs
As in other species, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have been shown to cause gastric ulcers in horses. Typicaly this is associated with high doses or frequent administration of phenylbutazone or flunixin meglumine. However, although there is evidence to the contrary,[47]therapeutic doses of NSAIDs may be sufficient to induce EGUS. Other studies have suggested that suxibuzone causes significantly less ulcerogenic effects than phenylbutazone when administered orally[48]and that combination treatment with phenylbutazone and flunixin meglumine may be more risky than phenylbutazone alone.[49] The ulcers produced by NSAIDs are unusual in that they have a predilection for the glandular mucosa[50][51][52], they may look different endoscopically from ulcers that occur naturally,[53] and they appear to heal spontaneously.[54][55] Despite the well-established link bewteen NSAIDs and ulcers, NSAIDs are rarely responsible for the lesions in horses in race training.[56][57][38]
Temperament
A nervous disposition has been linked with gastric ulcers[58]but the same association was not seen in another study.[59] The physiological and psychological stresses of training, housing, boredom, travel, mixing, hospitalisation and entering new environments[12] may increase the risk of developing EGUS. In foals hypoxia may also be a risk factor.
Clinical syndrome
The clinical signs associated with gastric ulcers are often very non-sepcific, difficult to document and at times only subjective.[60] In addition, there appears to be a poor correlation between the severity of endoscopic lesions and the clinical presentation.[20] The significance of gastric ulceration in horses thus remains questionable. However, there have been instances where ulcer treatment has preceded an improvement in clinical status and/or racing perfomance, suggesting that in some horses, ulcers are a considerable burden.[60] Cases gastric ulceration are often asymptomatic, but signs that have been attributed to these lesions in mature horses include:
- Poor appetite (particularly decreased consumption of concentrates)[6]
- Poor condition
- Rough hair coat
- Weight loss
- Excessive recumbency[2]
- Mild to severe colic
- Changes in attitude (dullness or depression)[60]
- Poor racing performance and reluctance to train
Clinical signs in foals vary depending on age and severity:
- Neonatal foals: many ulcers are silent, some foals only exhibit signs when ulceration has become severe. Glandular ulcers are considered the most significant[6]
- Poor appetite
- Diarrhoea
- Intermittent colic
- Frequent dorsal recumbency
- Sucklings and weanlings:[6]
- Diarrhoea
- Poor appetite (off suck or partially off suck)
- Poor growth, failure to thrive
- Poor body condition
- Rough hair coat
- Potbelly appearance
- Bruxism (almost pathognomonic)
- Colic after feeding or tubing
- Chewing straw
- Dorsal recumbency
- Signs of gastroduodenal ulcer disease (GDUD):[6]
- Bruxism
- Colic
- Gastrooesophageal reflux after suckling
- Ptyalism (secondary to gastric outflow obstruction and gastroesophageal reflux)[7]
- Diarrhoea
In foals with outflow obstruction distal to the common bile duct, marked reflux may be seen even with limited nursing.[6] GDUD is the primary differential for ptyalism in foals, other possible diagnoses include oesophageal obstruction and Candida infection.[7]
Diagnosis
A presumptive diagnosis can be based on clinical signs and response to therapy,[6] however, a definitive diagnosis requires visualisation of the stomach. This can be achieved in the live horse using endsocopy or, alternatively, at post-mortem.[39]
EGUS was recently discussed at the 2010 Annual meeting between the Equine Insurers Forum (EIF) and the British Equine Veterinary Association (BEVA). The EIF maintained that in order to support claims for the long term costs associated with treatment of EGUS, there would be a requirement for veterinary surgeons to make a definitive diagnosis prior to prescribing omeprazole.
Endoscopy
Oesophagogastroscopy or duodenoscopy can be performed under mild sedation (e.g. 0.6-0.8mg/kg xylazine[60]) in the standing horse. Of these, duodenoscopy is the more specific but more technically demanding method.[6] Endoscopic examination requires preparatory starving of the patient for 6-8hours,[60] eliciting a certain degree of stress. As such, it is preferable not to carry out this technique in foals. In adult horses, a minimum endoscope length of two metres is essential to visualize the gastric body and fundus.[6] A 2.8-3.0 metre endoscope is needed to observe the gastric antrum, pylorus and proximal dudoenum.[6] In either case, fibreoptic or videoendoscopic equipment can be used.[2]
Based on a consensus, the Equine Gastric Ulcer Council (EGUC) published an EGUS Lesion Scoring System which they claimed to be simple and applicable to both regions of the equine gastric mucosa.[2] This last point has been debated, since most of the acquired data on gastric lesions refers only to the squamous mucosa.[1] At the time of writing however, the EGUC system appears to be the most well established and useful in practice:
| Lesion Grade | Description |
| Grade 0 | Intact epithelium with no appearance of hyperaemia (reddening) or hyperkeratosis (yellowing of the squamous mucosa) |
| Grade 1 | Intact mucosa with areas of reddening or hyperkeratosis (squamous) |
| Grade 2 | Small single of multifocal lesions |
| Grade 3 | Large single or multifocal lesions or extensive superficial lesions |
| Grade 4 | Extensive lesions with areas of deep ulceration |
Diffuse inflammation may be the only lesion observed in foals with early GDUD.[6] In contrast to other scoring systems,[65] the EGUC approach does not include bleeding when assigning lesion grades. The justification is that the 'snapshot' provided by endoscopy may by chance identify bleeding of superficial erosions whilst missing the intermittent haemorrhage of more severe lesions. [2] Endoscopy may assist in understanding the severity of the disease and assessing the therapeutic response, but it is not without disadvantages. Ulcer severity may be underestimated, particularly in the squamous region and glandular ulcers may be missed altogether.[66] Lesions that appear grossly similar may have different grades on histopathology.[39] This is important as varying lesions may have different causes, requiring a range of treatment approaches.
Radiography
In older foals with GDUD, detection of gastric outflow obstruction via abdominal radiography is essential to treatment and prognosis.[6] Liquid barium will demonstrate very delayed or no outflow depending on the degree of obstruction. Without contrast medium, a large, gas filled stomach will be obvious.[6]. The need to perform contrast radiography must be weighed against the stress it would place upon the foal.
Biopsy
A transendoscopic gastric biopsy technique was recently validated for obtaining samples from the gastric glandular mucosa in the live horse.[67]Unfortunately this technique failed to produce samples of squamous mucosa that would be suitable for histopathological analysis.
Laboratory tests
Currently, useful and reliable markers for EGUS are lacking.[2] The SUCCEED® Equine Fecal Blood Test™ uses specific equine monoclonal antibodies to albumin and haemoglobin to detect occult blood in faeces.[69][70]The test has a positive predictive value of 77% and a negative predictive value of 72% and thus cannot be relied upon alone to diagnose EGUS.[39] False positive results may arise from rectal trauma (e.g. recent biopsy or rectal examination) or protein losing enteropathy.[39] Other tests that require further analysis for sensitivity and specificity[6] include:
- Urine[71] and blood[72] sucrose absorption as an assay of gastric mucosal permeability
- Serum alpha1-antitrypsin may be released from damaged gastric tissue[39] and has been detected more frequently in foals with gastric ulceration[73]
Pathology
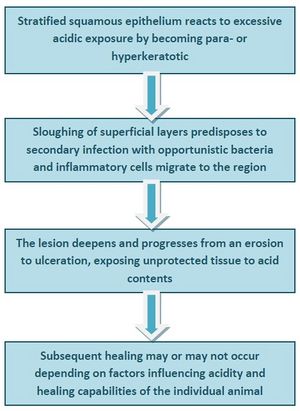
Martineau and co-workers (2009) demonstrated that in a mixed population of horses, a wide range of lesions associated with EGUS could be found at post-mortem.[5] These included hyperkeratosis, punctate scars, diffuse erosions or ulcerations and margo injuria in the squamous region and hyperaemia, focal erosions and ulcerations in the glandular region. A novel finding was glandular metaplasia which may be evidence of a protective mechanism developing in response to acid exposure.[5] The authors then devised a pathological scoring system - the Equine Gastritis Grading (EGG) system - which uses 5 samples of gastric mucosa taken from specific regions of the equine stomach. For each of these, the inflammatory infiltrate is graded by type, density and location, reactive changes are classified in both squamous and glandular samples and the presence or absence of infectious agents and lymphoid follicles is noted.[68] From their findings, a pathogenesis for the development of lesions in the squamous region was proposed:
Treatment
Histamine 2 receptor antagonists
Parietal cells secrete HCl upon stimulation of histamine, acetylcholine or gastrin receptors.[2] Competitive H2 receptor antagonists have successfully elevated gastric pH and treated gastric ulcers in mature horses and foals.(44,85,97 in Sachez) There appears to be a great variability among horses in their dose requirements for H2 antagonists which may be explained by individual bioavilability for these compounds.[2] Currently recommended doses proposed to be effective in the majority of horses[6] are:
- Cimetidine 20-30mg/kg PO every 8 hours or 6.6mg/kg IV every 6 hours
- Ranitidine 6.6mg/kg PO every 8 hours or 1.5-2mg/kg IV every 6 hours
- Famotidine 10-15mg/kg PO every 24 hours
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs)
PPIs irreversibly bind to the H+K+-ATPase proton pump of the parietal cell and block the secretion of hydrogen ions. These agents are more effective than H2 antagonsists as their action is receptor-independent,[2] blocking the final pathway of acid secretion and they have a prolonged effect allowing for once-daily dosing.((Brown and Rees 1994). Papich 1993, Sanchez) Omeprazole (Gastroguard™), a subsituted benzimidazole, is currently the only PPI licensed for use in horses. At a dose rate of 4mg/kg per day omeprazole has proven effective in reducing the severity of gastric ulcers in Thoroughbred horses in active race training[74] and no adverse effects have been observed. The paste formulation is easy to administer and generally well accepted by horses. Omeprazole has demonstrated efficacy in the resolution ofboth naturally-occurring and NSAID-induced gastric ulcers in horses.(103.104 in Sanchez) A single dose has also produced an increase in gastric pH in clinically ill neonatal foals[75] and has contributed to ulcer healing in neonates.[76] A potential concern is that altering gastric pH may encourage bacterial overgrowth. Thus further work is needed to evaluate the long-term safety of omeprazole in horses and particularly, foals.[74]
Antacids
The use of antacids to treat EGUS in the horse has not been critically evaluated[6] and some believe they are contraindicated due to potential rebound effects. Furthermore, the requirement for frequent dosing of large volumes of these products (owing to their poor efficacy) makes them an unattractive, stressful and impractical alternative to omeprazole.[60]
Mucosal protectants
Sucralfate is a complex salt of sucrose and aluminium hydroxide. It is thought to promote ulcer healing via several mechanisms: adherence to ulcerated mucosa, stimulation of mucus secretion, pepsin inibition, increasing prostgalandin E synthesis and enhancing the local production of epidermal growth factor.[6] It has been used effectively to treat and prevent stress-induced ulcers in man and has been recommended at 10-20mg/kg three times daily for the treatment of glandular ulcers in horses.[77] However, the effect of sucralfate on equine squamous gastric ulcers remains inconclusive[2] and the product may be ineffective in the alkaline conditions created by acid suppression agents.(123-125 in Sanchez)
Prostaglandin analogues
Synthetic prostaglandin E1 analogues are believed to inihibit gastric acid secretion and enhance mucosal cytoprotection.[78] Misoprostol has been an effective agent in the treatment of human gastric and duodenal ulcers and at 5µg/kg has been shown to increase gastric pH in horses.[79] Although contraindicated in pregnant mares, Misoprostol may be beneficial for mucosal recovery in the face of flunixin treatment.[80]
Gastric prokinetics
In cases of gastrooesophageal reflux, duodenal disease and delayed gastric emptying without a serious physical obstruction to gastric outflow, gastric prokinetics might be considered.[6] Such compounds include bethanechol, metaclopramide, erythromycin and cisapride which have been shown to hasten gastric empyting in adult horses.[2] To date only the parasympathomimetic agent bethanechol has been used as an adjunct for EGUS and cholinergic side effects are possible. Cisapride has been withdrawn from the US and UK markets over concern about its potential to cause adverse cardiac effects in man.[6]
Treatment problems
The prevalence of gastric ulcers in horses remains high regardless of the common use of antiulcer treatments. This has been attributed to the expense of recommended products encouraging subtherapeutic and curtailed dosing schedules(Orsini et al 2003 in Nadeau 2009). Omeprazole and ranitidine must be administered for at least 28 days for adequate ulcer healing.[39] In the USA, compounded omeprazole from bulk powders are used as a cheaper substitute for the FDA approved products. However, these formulations lack efficacy and are not regulated (Nieto et al. 2002; Merritt et al. 2003; Orsini et al. 2003).[39] A considerable challenge lies in the management of abdominal pain associated with EGUS, since the commonly used NSAIDs for pain control may worsen and even induce further ulcerative lesions.[81] Another challenge is the horse in which oral medication is prohibited. However, Andrews and colleagues (2006) have demonstrated the efficacy of an omeprazole powder, adminstered IV in sterile water, which signifcantly increases the pH of equine gastric contents and may be useful in problem horses.[82] An ongoing point of debate is the use of antiulcer medication in competition horses. In 2000, the Bureau of the The Fèdèration Equestre Internationale (FEI) permitted the use of cimetidine, ranitidine and omeprazole to prevent and treat gastric ulcers. This decision was based on evidence that the compounds were not performance enhancing and that EGUS was such a widespread concern. However, these drugs are still listed under prohibited substances in the 2009 Appendices of the American Endurance Ride Conference (AERC) Rules and Regulations. The argument is that a horse requiring such treatment is not suffciently well to compete and should be withdrawn form competition if it needs preventative medication. A related concern is that the AERC permits the use of hyperosmolar oral electrolyte pastes which may cause gastric ulcers.(Holbrook et al. 2005) Without the protection afforded by antiulcer agents, these horses may be at considerable risk for EGUS.[39]
Prognosis
Improvement in most clinical signs should be noted within 1-3 weeks of commencing treatment. Colic or diarrhoea should resolve within 48 hours.[6] Complications related to gastric ulcers are most frequent and severe in foals and include perforation, delayed gastric emptying, gastroesophageal reflux and oesophagitis, and megaoesophagus secondary to chronic gastroesophageal reflux. Sudden gastric perforation without prior signs occurs sporadically in foals.[7]Ulcers in the proximal duodenum or at the pylorus can cause fibrosis and stricture. The latter complication is seen in both foals and adult horses.[7] In mature animals, the most common complication is the recurrence of EGUS after treatment has ceased. This is typically because the inciting managemental causes have not been altered.
Potential complications of GDUD: delayed gastric emptying, gastrooesphageal reflux, gastric or duodenal rupture, pyloric or duodenal stricture, ascending cholangitis. Severe squamous and oesophageal ulceration and aspiration pnemonia can occur secondary to gastroesophageal reflux (24, 84-87 in Sanchez)
Prevention
Management
- Diet: ideally turnout to good quality grass.(Murray 1994) Stabled horses should have continuous access to hay and should be offered this before calorifc needs are met by concentrates.[60] Alfalfa, or another high calcium or high protein forage may be preventative by increasing gastric pH.(Nadeau et al. 2000; Lybbert et al. 2007; Ralston 2007) Concentrates should be fed at no more than 0.5kg per 100kg body weight and not more frequently than every 6 hours..[82] Horses prone to, or at risk of, EGUS should be fed the minimum amount of concentrates necessary.[39]
- Stress: minimise handling wherever possible, provide company and toys for stabled horses, encourage good feeding habits of foals.
Most of these suggestions would be difficult if not impossible to achieve for horses in race training, thus prophylactic medication should be considered.[60]
Prophylaxis
Omeprazole paste at a lower dose (1-2mg/kg) daily for 3-4 weeks.(100, 107-109 in Sanchez)
- Prevented ulcers in horses maintained under ulcerogenic conditions (White et al. 2003; McClure et al. 2005a,b,c;White et al. 2007).
- Treating ulcers in asymptomatic performance horses may lead to improved performance.[60]
- Prophylaxis in foals controversial as gastric acidity may be protective against bacterial translocation.[6]
- May benefit foals receiving substantial doses of NSAIDs for orthopaedic pain.[6]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Merritt, A M (2009) Appeal for proper usage of the term ʻEGUSʼ: Equine gastric ulcer syndrome. Equine Vet J, 41(7):616.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 The Equine Gastric Ulcer Council (1999) Tutorial Article: Recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of equine gastric ulcer syndrome (EGUS). Equine Vet Educ, 11(5):262-272.
- ↑ Andrews, F.M, Bernard, W.V, Byars, T.D et al. (1999) Recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of equine gastric ulcer syndrome (EGUS). Equine Vet Educ, 1:122-134. In: Sanchez, L.C (2010) 'Diseases Of The Stomach' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 15.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bell, R.J, Mogg, T, Kingston, J.K (2007) Equine gastric ulcer syndrome in adult horses: a review. N Z Vet J, 55(1):1-12).
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Martineau, H, Thompson, H, Taylor, D (2009) Pathology of gastritis and gastric ulceration in the horse. Part 1: Range of lesions present in 21 mature individuals. Equine Vet J, 41(7):638-644. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Martineau" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Martineau" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 6.00 6.01 6.02 6.03 6.04 6.05 6.06 6.07 6.08 6.09 6.10 6.11 6.12 6.13 6.14 6.15 6.16 6.17 6.18 6.19 6.20 6.21 6.22 6.23 Sanchez, L.C (2010) 'Diseases Of The Stomach' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 15.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 Merck & Co (2008) The Merck Veterinary Manual (Eighth Edition), Merial
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Sandin, A, Skidell, J, Haggstrom, J, Nilsson, G (2000) Postmortem findings of gastric ulcers in Swedish horses older than age one year: a retrospective study of 3715 horses (1924–1996). Equine Vet J, 32(1):36-42.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Hammond, C.J, Mason, D.K, Watkins, K.L (1986) Gastric ulceration in mature Thoroughbred horses. Equine Vet J, 18(4):284-287.
- ↑ Vatistas, N.J, Snyder, J.R, Carlson, G, et al (1994) Epidemiological study of gastric ulceration in the thoroughbred racehorse:202 horses 1992-1993. Proc Am Assoc Equine Pract, 40:125-126
- ↑ Murray, M.J, Schusser, G.F, Pipers, F.S, Gross, S.J (1996) Factors associated with gastric lesions in thoroughbred racehorses. Equine Vet J, 28:368-374.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 12.6 Vatistas, N.J, Sifferman, R.L, Holste, J, Cox, J.L, Pinalto, G, Schultz, K.T (1999) Induction and maintenance of gastric ulceration in horses in simulated race training. Equine Vet J Suppl, 29:40-44
- ↑ Vatistas, N.J, Snyder, J.R, Carlson, G, Johnson, B, Arthruy, R.M, Thurmond, M, Zhou, H, Lloyd, K.L.K (1999) Cross-sectional study of gastric ulcers of the squamous mucosa in Thoroughbred racehorses. Equine Vet J, Suppl 29:34-39.
- ↑ McClure, S.R, Glickman, L.T, Glickman, N.W (1999) Prevalence of gastric ulcers in show horses. J Am Vet Med Assoc, 215:1130-1133.
- ↑ MacAllister, C.G, Sangiah, S, Mauromoustakos, A (1992) Effect of a histamine H, type receptor antagonist (WY 45, 727) on the healing of gastric ulcers in ponies. J Vet Int Med, 6:271-275.
- ↑ Nieto, J.E, Snyder, J.R, Beldomenico, P et al. (2004) Prevalence of gastric ulcers in endurance horses: a preliminary report. Vet J, 167:33-37.
- ↑ Bertone, J (2000) Prevalence of gastric ulcers in elite, heavy use western performance horses. Proc Am Assoc Equine Pract, 46:256-259.
- ↑ LeJeune, S.S, Nieto, J.E, Dechant, J.E, Snyder, J.R (2009) Prevalence of gastric ulcers in Thoroughbred broodmares in pasture: a preliminary report. Vet J, 181(3):251-5.
- ↑ Hartmann, A.M, Frankeny, R.L (2003) A preliminary investigation into the association between competition and gastric ulcer formation in non-racing performance horses. J Equine Vet Sci, 23:560-561. In:Sanchez, L.C (2010) 'Diseases Of The Stomach' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 15.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Murray, M.J, Grodinsky, C, Anderson, C.W, Radue, P.F, Schmidt, G.R (1989) Gastric ulcers in horses: a comparison of endoscopic findings in horses with and without clinical signs. Equine Vet J Suppl, 7:68-72.
- ↑ Wilson, J.H (1986) Gastric and duodenal ulcers in foals: a retrospective study. Proc Equine Colic Res Symp 2nd:126-128.
- ↑ Murray, M.J, Grodinsky, C, Cowles, R.R, et al.(1990) Endoscopic evaluation of changes in gastric lesions of Thoroughbred foals. J Am Vet Med Assoc, 196:1623-1627.
- ↑ Murray, M.J (1989) Endoscopic appearance of gastric lesions in foals: 94 cases (1987-1988). J Am Vet Med Assoc, 195:1135-1141.
- ↑ Orsini, J.A, Pipers, F.S (1997) Endoscopic evaluation of the relationship between training, racing, and gastric ulcers. Vet Surg, 26:424. In: Orsini, J (2000) Tutorial Article Gastric ulceration in the mature horse: a review. Equine Vet Educ, 12(1):24-27.
- ↑ Murray, M.J (1994) Gastric ulcers in adult horses. Comp Cont Educ Pract Vet, 16:792-794. In:Orsini, J (2000) Tutorial Article Gastric ulceration in the mature horse: a review. Equine Vet Educ, 12(1):24-27.
- ↑ Murray, M. (1992) Gastric ulceration in horses: 91 cases (1987-1990). J Am Vet Med Assoc, 201:117-120. In: Martineau, H, Thompson, H, Taylor, D (2009) Pathology of gastritis and gastric ulceration in the horse. Part 1: Range of lesions present in 21 mature individuals. Equine Vet J, 41(7):638-644.
- ↑ Luthersson, N, Nielsen, K.H, Harris, P, Parkin, T.D (2009) The prevalence and anatomical distribution of equine gastric ulcer syndrome (EGUS) in 201 horses in Denmark. Equine Vet J, 41(7):619-24.
- ↑ Murray, M.J (1994) Characteristics of gastric ulcer pathophysiology. Proc Am Coll Vet Intern Med, 12:610-612. In: Sandin, A, Skidell, J, Haggstrom, J, Nilsson, G (2000) Postmortem findings of gastric ulcers in Swedish horses older than age one year: a retrospective study of 3715 horses (1924–1996). Equine Vet J, 32(1):36-42.
- ↑ Hartmann, A.M, Frankeny, R.L (2003) A preliminary investigation into the association between competition and gastric ulcer formation in non-racing performance horses. J Equine Vet Sci, 23:560-561. In: Nadeau, J.A, Andrews, F.M (2009) Science: Overviews Equine gastric ulcer syndrome: The continuing conundrum. Equine Vet J, 41(7):611-615.
- ↑ White, G, McClure, S.R, Siifferman, R, Holste, J.E, Fleishman, C, Murray, M.J, Cramer, L.G (2007) Effects of short-term light to heavy exercise on gastric ulcer development in horses and efficacy of omeprazole paste in preventing gastric ulceration. J Am Vet Med Assoc, 230(11):1680-2.
- ↑ Lorenzo-Figueras, M, Merritt, A.M (2002) Effects of exercise on gastric volume and pH in the proximal portion of the stomach of horses. Am J Vet Res, 63:1481-1487.
- ↑ Murray, M.J, Eichorn, E.S (1996) Effects of intermittent feed deprivation, intermittent feed deprivation with ranitidine administration, and stall confinement with ad libitum access to hay on gastric ulceration in horses. Am J Vet Res, 57:1599-1603.
- ↑ Husted, L, Sanchex, L.C, Olsen, S.N, Baptiste, K.E, Merritt, A.M (2008) Effect of paddock vs. stall housing on 24 hour gastric pH within the proximal and ventral equine stomach. Equine Vet J, 40(4):337-41.
- ↑ McClure, S.R, Carithers, D.S, Gross, S.J, Murray, M.J (2005) Gastric ulcer development in horses in a simulated show or training environment. J Am Vet Med Assoc, 227:775-777.
- ↑ Murray, M.J, Schusser, G.F (1993) Measurement of 24-h gastric pH using an indwelling pH electrode in horses unfed, fed and treated with ranitidine. Equine Vet J, 25:417-421. In: Sandin, A, Skidell, J, Haggstrom, J, Nilsson, G (2000) Postmortem findings of gastric ulcers in Swedish horses older than age one year: a retrospective study of 3715 horses (1924–1996). Equine Vet J, 32(1):36-42.
- ↑ Murray, M.J, Schusser, G.F (1993) Measurement of 24-h gastric pH using an indwelling pH electrode in horses unfed, fed and treated with ranitidine. Equine Vet J, 25:417-421. In: Sanchez, L.C (2010) 'Diseases Of The Stomach' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 15.
- ↑ Murray, M.J (1994) Equine model of inducing ulceration in alimentary squamous epithelial mucosa. Dig Dis Sci, 39:2530-2535. In: Sanchez, L.C (2010) 'Diseases Of The Stomach' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 15.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 Vatistas, N.J (1998) Gastric Ulceration in the Racing Thoroughbred. PhD Thesis. In: Vatistas, N.J, Sifferman, R.L, Holste, J, Cox, J.L, Pinalto, G, Schultz, K.T (1999) Induction and maintenance of gastric ulceration in horses in simulated race training. Equine Vet J Suppl, 29:40-44
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 39.2 39.3 39.4 39.5 39.6 39.7 39.8 39.9 In: Nadeau, J.A, Andrews, F.M (2009) Science: Overviews Equine gastric ulcer syndrome: The continuing conundrum. Equine Vet J, 41(7):611-615. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Nadeau" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Nadeau" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Nadeau" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Nadeau" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Nadeau" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Nadeau" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Nadeau" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Nadeau" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Nadeau" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Luthersson, N, Nielson, K.H, Harris, P, Parkin, T.D (2009) Risk factors associated with equine gastric ulceration syndrome (EGUS) in 201 horses in Denmark. Equine Vet J, 41(7):625-30.
- ↑ Smyth, G.B, Young, D.W, Hammond, L.S (1988) Effects of diet and feeding on post-prandial serum gastrin and insulin concentrations in adult horses. Equine Vet J Suppl 7:56-59.
- ↑ Mètayer, N, Lhôte, M, Bahr, A, Cohen, N.D, Kim, I, Rousell, A.J, Julliand, V (2004) Meal size and starch content affect gastric emptying in horses. Equine Vet J, 36:434-440. In: Nadeau, J.A, Andrews, F.M (2009) Science: Overviews Equine gastric ulcer syndrome: The continuing conundrum. Equine Vet J, 41(7):611-615.
- ↑ Taharaguchi, S, Okai, K, Orita, Y, Kuwano, M, Ueno, T, Taniyama, H (2004) Relation between amounts of concentrated feed given mares and gastric ulcers in foals. J Japan Vet Med Ass, 57:366-370. In: Nadeau, J.A, Andrews, F.M (2009) Science: Overviews Equine gastric ulcer syndrome: The continuing conundrum. Equine Vet J, 41(7):611-615.
- ↑ Boswinkel, A.M, Ellis, A.D, Sloet van Oldruitenborgh-Oosterbaan, M.M (2007) The influence of low versus high fibre haylage diets in combination with training or pasture rest on equine gastric ulceration syndrome (EGUS). Pferdeheilkunde, 23:123-130. In: Nadeau, J.A, Andrews, F.M (2009) Science: Overviews Equine gastric ulcer syndrome: The continuing conundrum. Equine Vet J, 41(7):611-615.
- ↑ Furr, M.O, Murray, M.J (1989) Treatment of gastric ulcers in horses with histamine type 2 receptor antagonists. Equine Vet J Suppl, 7:77-79.
- ↑ Furr, M.O, Murray, M.J, Ferguson, D.C (1992) The effects of stress on gastric ulceration, T3, T4, reverse T3 and cortisol in neonatal foals. Equine Vet J, 24:37-40.
- ↑ Andrews, F.M, Reinemeyer, C.R, Longhofer, S.L (2009) Effects of top-dress formulations of suxibuzone and phenylbutazone on development of gastric ulcers in horses. Vet Ther, 10(3):113-20.
- ↑ Monreal, L, Sabatè, D, Segura, D, Mayós, I, Homedes, J (2004) Lower gastric ulcerogenic effect of suxibuzone compared to phenylbutazone when administered orally to horses. Res Vet Sci, 76:145-149. In: Nadeau, J.A, Andrews, F.M (2009) Science: Overviews Equine gastric ulcer syndrome: The continuing conundrum. Equine Vet J, 41(7):611-615.
- ↑ Reed, S.K, Messer, N.T, Tessman, R.K, Keegan, K.G (2006) Effects of phenylbutazone alone or in combination with flunixin meglumine on blood protein concentrations in horses. Am J Vet Res, 67:398-402. In: Nadeau, J.A, Andrews, F.M (2009) Science: Overviews Equine gastric ulcer syndrome: The continuing conundrum. Equine Vet J, 41(7):611-615.
- ↑ MacAllister, C.G, Morgan, S.J, Borne, A.T, Pollet, R.A, (1993) Comparison of adverse effects of phenylbutazone, flunixin meglumine, and ketoprofen in horses. J Am Vet Med Ass, 202:71-77. In: Jonsson, H, Egenvall, A (2006) Prevalence of gastric ulceration in Swedish Standardbreds in race training. Equine Vet J, 38(3):209-213.
- ↑ Furr, M.O, Murray, M.J (1989) Treatment of gastric ulcers in horses with histamine type 2 receptor antagonists. Equine Vet J Suppl, 7:77-79. In: Vatistas, N.J, Sifferman, R.L, Holste, J, Cox, J.L, Pinalto, G, Schultz, K.T (1999) Induction and maintenance of gastric ulceration in horses in simulated race training. Equine Vet J Suppl, 29:40-44
- ↑ Kumaran, D, Bhuvanakumar, C.K (1994) Gastro duodenal ulceration in foals - a discussion. Cenfaur Mylapore, 10:83-86. In: Vatistas, N.J, Sifferman, R.L, Holste, J, Cox, J.L, Pinalto, G, Schultz, K.T (1999) Induction and maintenance of gastric ulceration in horses in simulated race training. Equine Vet J Suppl, 29:40-44
- ↑ Jonsson, H, Egenvall, A (2006) Prevalence of gastric ulceration in Swedish Standardbreds in race training. Equine Vet J, 38(3):209-213.
- ↑ Jones, W.E (1983) Gastrointestinal ulcers [foal]. Equine Vet Data, 4:305-308. In: Vatistas, N.J, Sifferman, R.L, Holste, J, Cox, J.L, Pinalto, G, Schultz, K.T (1999) Induction and maintenance of gastric ulceration in horses in simulated race training. Equine Vet J Suppl, 29:40-44
- ↑ MacAllister, C.G, Sangiah, S (1993) Effect of ranitidine (in healing of experimentally induced gastric ulcers in ponies. Am J Vet Res, 54:1103-1107. In: Vatistas, N.J, Sifferman, R.L, Holste, J, Cox, J.L, Pinalto, G, Schultz, K.T (1999) Induction and maintenance of gastric ulceration in horses in simulated race training. Equine Vet J Suppl, 29:40-44
- ↑ Vatistas N.J, Snyder, J.R, Carlson, G.P, Johnson, B, Arther, R.M, Thurmiind, M, Lloyd, K.C.K (1994) Epidemiology study of gastric ulcerarion in the Thoroughbred race horse: 202 horses. Proc Am Ass Equine Pract, 39:125-126. In: Vatistas, N.J, Sifferman, R.L, Holste, J, Cox, J.L, Pinalto, G, Schultz, K.T (1999) Induction and maintenance of gastric ulceration in horses in simulated race training. Equine Vet J Suppl, 29:40-44
- ↑ Murray, M.J, Schusser, G.F, Pipers, F.S, Gro:ss, S.J (1996) Factors associated with gastric lesions in Thoroughbred racehorses. Equine Vet J, 28:368-374. In: Vatistas, N.J, Sifferman, R.L, Holste, J, Cox, J.L, Pinalto, G, Schultz, K.T (1999) Induction and maintenance of gastric ulceration in horses in simulated race training. Equine Vet J Suppl, 29:40-44
- ↑ McClure, S.R, Glickman, L.T, Glickman, N.W (1999) Prevalence of gastric ulcers in show horses. J Am Vet Med Ass 215:1130-1133. In: In: Jonsson, H, Egenvall, A (2006) Prevalence of gastric ulceration in Swedish Standardbreds in race training. Equine Vet J, 38(3):209-213.
- ↑ Vatistas, N.J, Snyder, J.R, Carlson, G, Johnson, B, Arthur, R.M, Thurmond, M, Zhou, H, Lloyd, L.K (1999) Cross-sectional study of gastric ulcers of the squamous mucosa in Thoroughbred racehorses. Equine Vet J Suppl, 29:34-39. In: Jonsson, H, Egenvall, A (2006) Prevalence of gastric ulceration in Swedish Standardbreds in race training. Equine Vet J, 38(3):209-213.
- ↑ 60.0 60.1 60.2 60.3 60.4 60.5 60.6 60.7 60.8 Orsini, J (2000) Tutorial Article Gastric ulceration in the mature horse: a review. Equine Vet Educ, 12(1):24-27.
- ↑ Videla, R, Andrews, F.M (2009) New perspectives in equine gastric ulcer syndrome. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract, 25(2):283-301.
- ↑ Dukti, S.A, Perkins, S, Murphy, J, Barr, B, Boston, R, Southwood, L.L, Bernard, W (2006) Prevalence of gastric squamous ulceration in horses with abdominal pain. Equine Vet J, 38:347-349.
- ↑ Franklin, S.H, Brazil, T.J, Allen, K.J (2008) Poor performance associated with equine gastric ulceration syndrome in four Thoroughbred racehorses. Equine Vet Educ, 20:119-124. In: Nadeau, J.A, Andrews, F.M (2009) Science: Overviews Equine gastric ulcer syndrome: The continuing conundrum. Equine Vet J, 41(7):611-615.
- ↑ Nieto, J.E, Snyder, J.R, Vatistas, N.J, Jones, J.H (2009) Effect of gastric ulceration on physiologic responses to exercise in horses. Am J Vet Res, 70(6):787-95.
- ↑ MacAllister, C.G, Andrews F.M, Deegan E, Ruoff, W, Olovson, S.G (1997) A scoring system for gastric ulcers in horses. Equine Vet J, 29:430-433.
- ↑ Andrews, F.M, Reinmeyers, C.R, McCracken, M.D, Blackford, J.T, Nadeau, J.A, Saabye, L, Sotell, M, Saxton, A (2002) Comparison of endoscopic, necropsy and histology scoring of equine gastric ulcers. Equine Vet J,34(5):475-478.
- ↑ Rodrigues, N.L, Dore, M, Doucet, M.Y (2009) Validation of a transendoscopic glandular and nonglandular gastric biopsy technique in horses. Equine Vet J, 41(7):631-5.
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 Martineau, H, Thompson, H, Taylor, D (2009) Pathology of gastritis and gastric ulceration in the horse. Part 2: a scoring system. Equine Vet J,41(7):646-51.
- ↑ Carter, S, Pellegrini, F.A (2006) The use of novel antibody tools to detect the presence of blood in equine feces. Company Bulletin Freedom Health LLC 1-3. In: Nadeau, J.A, Andrews, F.M (2009) Science: Overviews Equine gastric ulcer syndrome: The continuing conundrum. Equine Vet J, 41(7):611-615.
- ↑ Pellegrini, F.L, Carter, S.D (2007) An equine necroscopic study to determine the sensitivity and specificity of a dual antibody test. Company Bulletin Freedom Health LLC 1-2. In: Nadeau, J.A, Andrews, F.M (2009) Science: Overviews Equine gastric ulcer syndrome: The continuing conundrum. Equine Vet J, 41(7):611-615.
- ↑ O'Connor, M.S, Steiner, J.M, Roussel, A.J, et al. (2004) Evaluation of urine sucrose concentration for detection of gastric ucleration in horses. Am J Vet Res, 65:31-39. In: Sanchez, L.C (2010) 'Diseases Of The Stomach' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 15.
- ↑ Hewetson, M, Cohen, N.D, Love, S, et al. (2006) Sucrose concentration in bood: a new method for assessment of gastric permeability in horses with gastric ulceration. J Vet Intern Med, 20:388-394. In: Sanchez, L.C (2010) 'Diseases Of The Stomach' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 15.
- ↑ Taharaguchi, S, Nagano, A, Okai, K, et al. (2007) Detection of an isoform of alpha(1)-antitrypsin in serum samples from foals with gastric ulcers. Vet Rec, 161:338-342. In: Sanchez, L.C (2010) 'Diseases Of The Stomach' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 15.
- ↑ 74.0 74.1 Vatistas, N.J, Snyder, J.R, Nieto, J, Thompson, D, Pollmeier, M, Holstes, J (1999) Acceptability of a paste formulation and efficacy of high dose omeprazole in healing gastric ulcers in horses maintained in race training. Equine Vet J Suppl, 29:71-76.
- ↑ Javsicas, L.H, Sanchez, L.C (2008) The effect of omeprazole paste on intragastric pH in clinically ill neonatal foals. Equine Vet J, 40(1):41-4.
- ↑ MacAllister, C.G, Sifferman, R.L, McClure, S.R et al. (1999) Effects of omeprazole paste on healing of spontaneous gastric ulcers in horses and foals: a field trial. Equine Vet J Suppl, 77-80. In: Sanchez, L.C (2010) 'Diseases Of The Stomach' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 15.
- ↑ Murray, M.J (1994) Gastric ulcers in adult horses. Comp Cont Educ Pract Vet, 16:792-794,797. In: Orsini, J (2000) Tutorial Article Gastric ulceration in the mature horse: a review. Equine Vet Educ, 12(1):24-27.
- ↑ Leandro, G, Pilotto, A, Franceschi, M et al. (2001) Prevention of acute NSAID-related gastroduodenal damage: a meta-analysis fo controlled clinical trials. Dig Dis Sci, 46:1924-1936. In: Sanchez, L.C (2010) 'Diseases Of The Stomach' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 15.
- ↑ Sangiah, S, MacAllister, C.C, Amouzadeh, H.R (1989) Effects of misoprostol and omeprazole on basal gastric pH and free acid content in horses. Res Vet Sci, 47:350-354. In: Sanchez, L.C (2010) 'Diseases Of The Stomach' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 15.
- ↑ Tomlinson, J.E, Blikslager, A.T (2005) Effects of cyclooxygenase inhibitors flunixin and deracoxib on permeability of ischaemic-injured equine jejunum. Equine Vet J, 37:75-80. In: Sanchez, L.C (2010) 'Diseases Of The Stomach' in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 15.
- ↑ Videla, R, Andrews, F.M (2009) New perspectives in equine gastric ulcer syndrome.Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract, 25(2):283-301.
- ↑ 82.0 82.1 Andrews, F.M, Frank, N, Sommardahl, C.S, Buchanan, B.R, Elliott, S.B, Allen, V.A (2006) Effects of intravenously administrated omeprazole on gastric juice pH and gastric ulcer scores in adult horses. J Vet Intern Med, 20(5):1202-6.