Difference between revisions of "Q Fever"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Taxobox | ||
| + | |name = Coxiella burnetii | ||
| + | |kingdom = | ||
| + | |sub-kingdom = | ||
| + | |phylum = Proteobacteria | ||
| + | |super-class = | ||
| + | |class = Zymobacteria | ||
| + | |sub-class = Alphaproteobacteria | ||
| + | |super-order = | ||
| + | |order = Legionellales | ||
| + | |sub-order = | ||
| + | |super-family = | ||
| + | |family = Coxiellaceae | ||
| + | |sub-family = | ||
| + | |genus = Coxiella | ||
| + | |species = ''C. burnetii'' | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
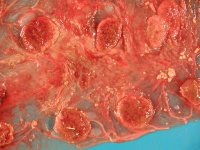
[[File:Q Fever.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Goat placenta from Q fever abortion. Note the thickened intracotyledonary areas and tan exudate. The cotyledons have tan necrotic margins and congested, red centres. Copyright CFSPH Iowa State.]] | [[File:Q Fever.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Goat placenta from Q fever abortion. Note the thickened intracotyledonary areas and tan exudate. The cotyledons have tan necrotic margins and congested, red centres. Copyright CFSPH Iowa State.]] | ||
Revision as of 11:33, 8 June 2011
| Coxiella burnetii | |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Proteobacteria |
| Class | Zymobacteria |
| Sub-class | Alphaproteobacteria |
| Order | Legionellales |
| Family | Coxiellaceae |
| Genus | Coxiella |
| Species | C. burnetii |
Q fever
- Caused by Coxiella burnetti
- Influenza-like disease of humans in contact with farm animals
- Transmitted to humans by inhalation from parturient sheep, goats and cattle
- Organisms replicate in female genital tract and mammary glands of ruminants
- Shedding occurs in uterine discharges, foetal fluid and milk
- Infections in animals usually subclinical
- Sporadic abortions occur in sheep, goats, cattle, cats
- Infertility may result in ruminants, as well as placentitis or endometritis
- Hepatitis, myocarditis and interstitial pneumonia may occur in affected foetuses
- Diagnosis: MZN-stained smears of placental tissue and uterine discharges; immunofluorescence; PCR; culture; serology
- Control: disposal of infected placenta and separation of pregnant ruminants; inactivated vaccines
Coxiella burnetti (rickettsia)
Infection by inhalation, ingestion or tick bites. Leads to late abortion or birth of weak lambs/kids. See a thickened leathery placenta covered in exudate. ZN stains can be use to demonstrate organisms.