Difference between revisions of "Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Distal Tubule and Collecting Duct - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(New page: {{toplink |backcolour = C1F0F6 |linkpage =Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Nephron - Anatomy & Physiology |linktext =REABSORPTION AND SECRETION ALONG THE NEPHRON |maplink = Urinary Sys...) |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
}} | }} | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Distal Tubule== | ||
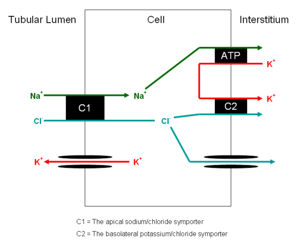
| + | [[Image:disttubexch.jpg|right|thumb|300px|<small><center>Exchange in the Principal Cells of the Distal Tubule</center></small>]] | ||
| + | * Important site of regulation of ions and water | ||
| + | * Less emphasis on bulk transport compared with proximal tubule | ||
| + | * More emphasis on fine management | ||
| + | * It is able to do this as it has high resistance epithelia. Allowing it to maintain substantial gradients across it | ||
| + | * Very important for the homeostasis of: | ||
| + | ** [[Sodium Homeostasis - Physiology#Distal Tubule and Collecting Ducts| Sodium]] | ||
| + | ** [[Potassium Homeostasis - Physiology#Distal Tubule| Potassium]] | ||
| + | ** [[Acid Base Balance By The Kidney - Anatomy & Physiology#Secretion of H+ in the Distal Tubule and Collecting Ducts| Acid Base]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | * There are two cell types present each with different functions. They are similar to the cells of the collecting ducts | ||
| + | ** Principal cells | ||
| + | *** Absorb sodium | ||
| + | *** Excrete potassium and hydrogen | ||
| + | *** Site of action of [[Aldosterone]] | ||
| + | ** Intercalated cells | ||
| + | *** ATP driven proton secretion | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Juxtaglomerular Apparatus== | ||
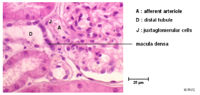
| + | [[Image:juxtaapp.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<small><center>Histology section showing the juxtaglomerular apparatus (© RVC 2008)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | * The terminal portion of the straight distal tubule contacts the afferent and efferent vessels supplying its own glomerulus | ||
| + | * These vessels are said to embrace the distal tubule | ||
| + | * Here a special apparatus called the Juxtaglomerular Apparatus has 3 different structures: | ||
| + | ** The tubular epithelial cells of the distal tubule which are in contact with the arterioles supplying the glomerulus of that nephron are called the '''macula densa'''. They play a vital role in the [[Autoregulation of GFR - Anatomy and Physiology#Tubuloglomerular Feedback (TGF)|regulation of the GFR]]. | ||
| + | ** The [[Juxtaglomerular Cells of The Distal Tubule - Renal Physiology | Juxtaglomerular Cells]] are smooth muscle cells which adjoin the macula densa in the capillary wall. | ||
| + | ** The Extraglomerular Mesangium has an unclear function | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Developmental== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Develops from metanephric tubule | ||
Revision as of 15:07, 3 September 2008
|
|
Distal Tubule
- Important site of regulation of ions and water
- Less emphasis on bulk transport compared with proximal tubule
- More emphasis on fine management
- It is able to do this as it has high resistance epithelia. Allowing it to maintain substantial gradients across it
- Very important for the homeostasis of:
- There are two cell types present each with different functions. They are similar to the cells of the collecting ducts
- Principal cells
- Absorb sodium
- Excrete potassium and hydrogen
- Site of action of Aldosterone
- Intercalated cells
- ATP driven proton secretion
- Principal cells
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
- The terminal portion of the straight distal tubule contacts the afferent and efferent vessels supplying its own glomerulus
- These vessels are said to embrace the distal tubule
- Here a special apparatus called the Juxtaglomerular Apparatus has 3 different structures:
- The tubular epithelial cells of the distal tubule which are in contact with the arterioles supplying the glomerulus of that nephron are called the macula densa. They play a vital role in the regulation of the GFR.
- The Juxtaglomerular Cells are smooth muscle cells which adjoin the macula densa in the capillary wall.
- The Extraglomerular Mesangium has an unclear function
Developmental
Develops from metanephric tubule