Difference between revisions of "Insecta"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
| − | ==Life | + | ==[[Insect Life Cycles]]== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<big> | <big> | ||
Revision as of 23:08, 19 May 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Classification
The phylum arthropoda is divided into several subphylums including Chelicerata (which includes the arachnids), Myriapoda, Hexapoda (which includes the insecta), Crustacea and Trilobitomorpha. These are then divided into many classes. The two of major veterinary importance are the insecta and arachnida classes.
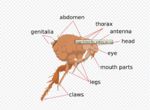
Insect Structure and Function
Insect Life Cycles