Difference between revisions of "Intussusception"
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
Intussusception results from vigorous contractions due to intestinal irritation, which force a segment of an intestine to teloscope into the lumen of a more relaxed adjacent segment. A normograde intussusception is the most common, but retrograde intussusception has also been reported. Intussusception normally occurs due to gastrointestinal disease, although it is often hard to identify the cause. Parasites, infectious enteritis, metabolic disorders, foreign bodies, history of recent intestinal surgery, intestinal masses have all been known to associate with intussusception. Chronic intussusception can occur with little haemodynamic changes. | Intussusception results from vigorous contractions due to intestinal irritation, which force a segment of an intestine to teloscope into the lumen of a more relaxed adjacent segment. A normograde intussusception is the most common, but retrograde intussusception has also been reported. Intussusception normally occurs due to gastrointestinal disease, although it is often hard to identify the cause. Parasites, infectious enteritis, metabolic disorders, foreign bodies, history of recent intestinal surgery, intestinal masses have all been known to associate with intussusception. Chronic intussusception can occur with little haemodynamic changes. | ||
| − | Intussusceptions can occur along any length of the intestine, however, [[Colon - Anatomy & Physiology #Structure|ileocolic]] and jejunojejunal intussusceptions are the most common. More caudal intussusception can cause it to protrude from the rectum. This has to be distinguished from a rectal prolapse. In intussusception, it is possible to pass a probe next to the anus, but not in [[Rectal Prolapse | + | Intussusceptions can occur along any length of the intestine, however, [[Colon - Anatomy & Physiology #Structure|ileocolic]] and jejunojejunal intussusceptions are the most common. More caudal intussusception can cause it to protrude from the rectum. This has to be distinguished from a rectal prolapse. In intussusception, it is possible to pass a probe next to the anus, but not in [[Rectal Prolapse|rectal proplapse]]. |
Initially, a partial obstruction results. Overtime, this progresses to a complete obstruction, with obstruction of venous return, arterial occlusion and avulsion of vessels. The intestinal walls become oedematous, ischaemic and turgid, resulting in devitalisation if not treated. Adhesion can occur in long standing cases due to fibrin deposition. | Initially, a partial obstruction results. Overtime, this progresses to a complete obstruction, with obstruction of venous return, arterial occlusion and avulsion of vessels. The intestinal walls become oedematous, ischaemic and turgid, resulting in devitalisation if not treated. Adhesion can occur in long standing cases due to fibrin deposition. | ||
Revision as of 13:05, 28 June 2010
- Telescoping of one segment of the bowel into another.
- Occurs in all species.
- Particularly in young dogs.
- Can occur in the small intestine, caecum or colon.
Clinical
- Intussusception is a less acute type of obstruction.
- Produces intermittent diarrhoea.
- Animals go downhill in a few days.
- Palpation of abdomen may allow a "Cumberland sausage" effect to be felt.
- NB abdominal palpation in small animal, rectal palpation in large animal.
Pathogenesis
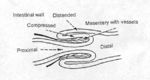
- Proximal intestine invaginates into lower part of intestine.
- Takes mesenteric attachment with it.
- Compression of the mesenteric vessels obstructs venous drainage of the gut, resulting in venous congestion.
- Swelling (oedema/congestion) arises.
- Inflammatory exudate from serous surface.
- Fibrinous adhesions form between surfaces making structure irreducible.
- Inflammatory exudate from serous surface.
- Swelling (oedema/congestion) arises.
- May progress to necrosis and gangrene of the tissue.
- There is often functional obstruction to bowel.
- May rupture, leading to peritonitis and death.
- Associated with anything that raises peristalsis e.g. change in diet, bacterial infection.
- Foreign body
- Intramural abscess/tumour
- Heavy parasitism
- Previous intestinal surgery
- Enteritis
- Other motility disorders.
- Change in diet
- Bacterial infection
Pathology
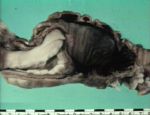
- When operate or at post mortem see large sausage shaped distension of length of intestine.
- Intussusception may occur post mortem
- There are no associated changes
- The condition is easilt reducible.
From Clinical
Signalment
- Occur most commonly in dogs
- 75% of cases affect animals under one year of age
- Breed predisposition:
Description
Intussusception is the invagination of a segment an intestine into the lumen of the adjoining intestine. The intussusceptum is the invaginated segment and the intussuscipien is the enveloping segment. Intussusception most commonly affects young animals. In order animals, it may be occur due to neoplasia or agonal changes.
Intussusception results from vigorous contractions due to intestinal irritation, which force a segment of an intestine to teloscope into the lumen of a more relaxed adjacent segment. A normograde intussusception is the most common, but retrograde intussusception has also been reported. Intussusception normally occurs due to gastrointestinal disease, although it is often hard to identify the cause. Parasites, infectious enteritis, metabolic disorders, foreign bodies, history of recent intestinal surgery, intestinal masses have all been known to associate with intussusception. Chronic intussusception can occur with little haemodynamic changes.
Intussusceptions can occur along any length of the intestine, however, ileocolic and jejunojejunal intussusceptions are the most common. More caudal intussusception can cause it to protrude from the rectum. This has to be distinguished from a rectal prolapse. In intussusception, it is possible to pass a probe next to the anus, but not in rectal proplapse.
Initially, a partial obstruction results. Overtime, this progresses to a complete obstruction, with obstruction of venous return, arterial occlusion and avulsion of vessels. The intestinal walls become oedematous, ischaemic and turgid, resulting in devitalisation if not treated. Adhesion can occur in long standing cases due to fibrin deposition.
Diagnosis
Clinical Signs
Acute Intussusception
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea; bloody mucoid faeces
- Abdominal pain
- Palpable sausage-shaped mass in the abdomen
- Tenesmus; in cases of ileocaecocolic intussusception
- Haematochezia; in cases of ileocaecocolic intussusception
Chronic Intussusception
- Intermittent diarrhoea
- Depression, anorexia and emaciation
Diagnostic Imaging
Radiography
- Plain abdominal radiography may reveal obstruction in the intestines. This, however, may not be present in cases of partial, chronic or intermittent intussusception. Jejunojejunal intussusception is reported to show signs of obstruction more commonly compared to ileocolic intussusception. A mass may be seen on radiograph.
- A barium enema or upper gastrointestinal contrast study can be useful in identifying the site of obstruction. This should be used with care as leakage of contrast into the abdominal cavity will result in peritonitis.
Ultrasonography
Abdominal ultrasound is a good diagnostic tool for intussusception. On a transverse section, a hyperechoic target mass in the centre with multiple hyperechoic and hypoechoic concentric ring is seen. On a longitudinal section, multiple hyperechoic and hypoechoic lines are seen. The intestines may also be hypomotile and proximal fluid accumulation can occur.
Colonoscopy
This can be used to identify ileocolic or caecocolic intussusception.
Treatment
Medical
This may be used in causes where the intussusception can be reduced manually through the skin.
Surgery
Fluid therapy and correction of any electrolyte and acid-base derangements should be carried out as soon as possible. Surgery is usually required to manually reduce or resect and anastomosis or both. This decision depends on the viability of the intestines, as determined by the colour, vascular supply and presence or absence of peristalsis. Risks of complications include dehiscence of site of anastomosis, peritonitis, recurrence (11-20%, most common within 1-5 days post surgery), ileus, intestinal obstruction and short bowel syndrome. Recurrence can be treated with motility altering drugs or intestinal pexy or plication. It is important to preserve as much of the intestine as possible to avoid short bowel syndrome.
Prognosis
This depends on the location, completeness and period of the intusussception. The prognosis is good in animals treated with early surgical intervention and aggressive supportive care. The prognosis is worse for animals with perforated intestine and peritonitis.
References
- Barreau, P. (2008) Intussusception: Diagnosis and Treatment 33rd WSAVA Congress
- Ettinger, S.J. and Feldman, E. C. (2000) Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine Diseases of the Dog and Cat Volume 2 (Fifth Edition) W.B. Saunders Company.
- Fossum, T. W. et. al. (2007) Small Animal Surgery (Third Edition) Mosby Elsevier
- Hall, E.J, Simpson, J.W. and Williams, D.A. (2005) BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Gastroenterology (2nd Edition) BSAVA
- Nelson, R.W. and Couto, C.G. (2009) Small Animal Internal Medicine (Fourth Edition) Mosby Elsevier.