Difference between revisions of "Odontoblasts - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(New page: {{toplink |backcolour =BCED91 |linkpage =Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology |linktext =Alimentary System |maplink = Alimentary (Concept Map)- Anatomy & Physiology |pagetype =Anatomy |sublin...) |
m (Text replace - '|maplink = Alimentary (Concept Map)- Anatomy & Physiology' to '|maplink = ') |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|linkpage =Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology | |linkpage =Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
|linktext =Alimentary System | |linktext =Alimentary System | ||
| − | |maplink = | + | |maplink = |
|pagetype =Anatomy | |pagetype =Anatomy | ||
|sublink1=Oral Cavity - Teeth & Gingiva - Anatomy & Physiology#Anatomy of the Enamel Organ | |sublink1=Oral Cavity - Teeth & Gingiva - Anatomy & Physiology#Anatomy of the Enamel Organ | ||
Revision as of 00:06, 3 July 2010
|
|
Introduction
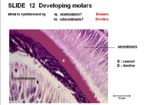
Odontoblasts are cells in the enamel organ which forms the tooth. They secrete dentine.
Properties
- Derived from mesenchyme
- Single layer of elongated columnar cells
- At dental-pulp border
- Outer layer of the dental papilla
- The first layer of dentine is formed on the enamel organ. As production increases, the odontoblasts are displaced from the enamel
- It is a major part of the tooth structure and is produced continually by the odontoblasts.
- Rate of dentine synthesis is increased during repair as it is innervated (but still acellular).