Bones - Dog Anatomy
Introduction
The information below will highlight the bone anatomy of the domestic dog which will include the major and selected important minor aspects of anatomy. Very detailed anatomy of individual bones is not covered below due to space restrictions.
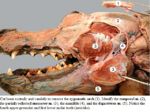
The anatomical information included below is commonly split into separate areas; the head (displayed in yellow on the right), the neck (displayed in pink), the trunk (displayed in dark blue) and the forelimbs / hindlimbs (displayed in light blue). The limbs will be further sub-divided into proximal and distal anatomy. The following information will use this concept to facilitate easier understanding of the individual areas of anatomy.
Anatomy of the Head
Anatomically the head encompasses all bones cranial to the cervical vertebrae of the neck and is shown in yellow in the diagram above. The conformation of the canine head is extremely variable due to selective breeding over many generations. The key characteristics of the head that create this variability include the ear shape and size, eye position and the length of the nose.
The head consists of a number of complex bones of varying types and size which will be both described in text and where possible will also be shown photographically. The head is mainly comprised of the skull, mandible, ossicles and hyoid apparatus. Asscessory cartilage is also present within the external ear, larynx and nose.
Skull

The shape and size of the skull varies widely between different breeds of dog. Dogs have different skull lengths depending on breed. Mesocephalic dogs have average conformation whilst dolichocephalic dogs have longer skull lengths and brachycephalic dogs have shorter skull lengths. The skull protects the brain and head against injury and supports the structures of the face. The skull is comprised of many individual bones that are normally fused together in adults to form a strong single structure. The process of bone fusion is called endochondral ossification and represents the process where the various plates of cartilage within the skull are converted to bone. In young animals each bone within the head is seperated by narrow fibrous tissues or 'sutures' and it is these sutures that allow provision for growth. The sections below will highlight these major bone structures of the skull.
Occipital Bone (os occipitale)
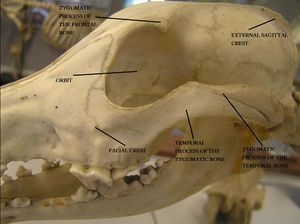
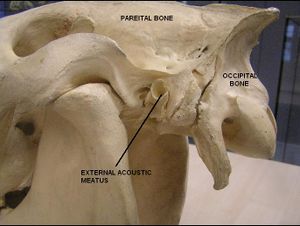
The occipital bone is the most caudal bone of the skull and the external occipital protuberance is the most caudal element found medially within the bone. This protuberance provides the attachment for the nuchal ligament. The occipital bone has nuchal crests laterally and a sagittal crest medially and dorsally to the external occipital protuberance. The sagittal crest is prominent and can be palpated in most canines unless they are very well muscled. These elements together form the nuchal wall and the foramen magnum. The pars basilaris element is the caudal base of the cranium, although rostral to foramen magnum and joined by a cartilagenous suture to basisphenoid bone. It has muscular tubercules on ventral surface where the flexors of the head and neck attach and a caudocranial fossa encloses the pons and medulla oblongata. The squamous part (pars squamosa) is dorsal to lateral parts and occipital condyles. The nuchal crest is often used as a landmark for collection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Occipital condyles are present which articulate with the atlas to form the atlanto-occipital joint. The paracondylar process provide muscle attachment sites for muscles of the head. The hypoglossal canal is also within this structure.
Sphenoid Bone (os sphenoidale)
The sphenoid bone forms the base of the neurocranium and is composed of a body and wings. The bones are separated by cartilage which ossifies with age. The presphenoid (os praespenoidale) is rostral and has a caudal fossa which is a hollow body with sphenoid sinuses located inside. Within the sinuses are the optic chiasma and optic canal. The basisphenoid (os basispenoidalis) is caudal and has a median cranial fossa. The wings oppose the temporal bone, maxilla, orbit and the brain. The wings also form the oval foramen. The pterygoid processes are also present.
Temporal Bone (os temporale)
The temporal bone is composed of squamous, petrosal and tympanic parts and forms the lateral wall of the cranial cavity. It articulates with the frontal, parietal and sphenoid bones. The squamous element joins the temporal process of the zygomatic bone to form the zygomatic arch and forms the articulating surface of the temporomandibular joint. An articular tubercle and mandibular fossa are present. Occipital process and retrotympanic processes surround the external acoustic meatus whilst the petrosal part encloses the inner ear internally via the internal acoustic meatus. Ventrally this structure forms the mastoid process. The styloid process attaches the hyoid apparatus and a stylomastoid foramen is also present. The tympanic part is the ventral section of the temporal bone containing the tympanic bulla. The tympanic membrane separates tympanic cavity from external acoustic meatus and encloses the auditory ossicle dorsally. The musculotubal canal contains tensors of the soft palate.
Frontal Bone (os frontale)
The frontal bone is a paired structure joined by the interfrontal suture between the cranium and the face and enclosing the frontal sinuses. The nasal and lacrimal bones border the frontal squama section and form the zygomatic process laterally and part of the orbit dorsally. The temporal line extends into the external sagittal crest. The nasal section is the rostral part of the frontal bone and the orbital part is perforated by the ethmoidal foramen. Medially the dorsal oblique muscle of the eyeball attaches. The temporal part provides the muscle attachments for the temporalis muscle.
Parietal Bone (os parietale)
The parietal bone is a paired structure and forms the dorsolateral wall of the cranium with the cccipital bone caudally and the frontal bone rostrally. It is composed of a parietal plane, temporal plane and a nuchal plane (in the ox). Internally the grooves and ridges correspond with the gyri and sulci of the brain. There is also an interparietal bone between the occipital bone and the parietal bone which fuses with age.
Ethmoid Bone (os ethmoidale)
The ethmoid bone forms part of the cranial and facial parts of the skull and is located deep in the orbit. External lamina consist of the roof plate, floor plate and paired orbital plates. The ethmoid bone is separated from the cranial cavity by the cribiform plate. Numerous small foramina exist where the olfactory nerve (CN I) passes through. The perpendicular plate splits the ethmoid into two halves and the ethmoid larbyrinth protrudes from the ethmoid tubes. The tubes are composed of two rows of ethmoturbinates and air filled ethmoidal meatuses. Secondary ethmoturbinates may also be present. Ethmoturbinates are divided into endoturbinates and ectoturbinates. The first endoturbinate forms the dorsal nasal conchae and the second endoturbinate froms the middle nasal conchae. The endoturbinates form 3 nasal meatuses; the dorsal nasal meatus, the middle nasal meatus and the ventral nasal meatus.
Nasal Bone (os nasale)
The nasal bone is a paired structure and forms the roof of the nasal cavity. Dorsal nasal conchae attach to the ethmoidal crest on the internal surface. A rostral suture forms the apex and between the nasal and incisive bones is the nasoincisive notch.
Lacrimal Bone (os lacrimale)
The lacrimal bone forms part of the lateral wall of the face and orbit and is situated near the medial canthus. It articulates with the frontal bone, zygomatic bone and maxilla. It also articulates with the palatine bone in canines. It is composed of an orbital and facial part separated by supra- and infraorbital margins. The nasolacrimal duct is present by the margin of the orbital surface. The ventral oblique muscle attaches caudal to the margin of the orbital surface. The nasal surface forms the boundaries of the maxillary and frontal sinuses.
Zygomatic Bone (os zygomaticum)
The zygomatic bone is lateral and ventral to the lacrimal bone and forms the orbit and zygomatic arch. The supraorbital margin is formed by the zygomatic process of the temporal bone and the frontal process of the zygomatic bone. The facial crest is present on lateral surface.
Incisive Bone (os incisivium)
The incisive bone is a paired structure composed of body, nasal, palatine and alveolar parts. It joins with the maxilla to form the interalveolar margin. It also forms the rostral part of the facial section of the skull, the roof of the hard palate and the opening to the nasal cavity. The alveolar process forms conical sockets for the incisor teeth.
Palatine Bone (os palatinum)
The palatine bone is a paired structure between the maxilla, sphenoid and pterygoid bones. It is composed of a horizontal plate (forms part of the hard palate), perpendicular plate (forms the dorsal and lateral walls of the nasopharyngeal meatus) and the choanae. The nasal crest present on the horizontal plate. The palatine sinus is present on horizontal plate.
Vomer
The vomer is unpaired and extends from the choanae of the palatine bone to the floor of the nasal cavity. It attaches to the median nuchal crest and has a septal sulcus which surrounds nasal cavity.
Pterygoid Bone (os pterygoideum)
The pterygoid bone is a paired structure bordered by the palatine and sphenoid bones. It forms the dorsal and lateral walls of the nasopharyngeal cavity. The pterygoid hamulus is formed by the pterygoid bone.
Maxilla
The maxilla forms most of the facial part of the skull, including the lateral walls of the face, nasal cavity, oral cavity and hard palate. It also forms the ventral nasal conchae and articulates with all of the facial bones as it is the largest bone of the face. The maxillary body encloses the maxillary sinuses and forms the external surface of the face. It also forms the facial crest. The infraorbital foramen is palpable. The conchal crest is on nasal surface where the ventral nasal conchae attaches. The lacrimal canal opens into the lacrimal foramen on the nasal surface. The pterygopalatine surfaces are the caudal part of the maxilla which terminate in the maxillary tubercle where the sphenopalatine, maxillary and caudal palatine foramen are present. The alveolar processes present are separated by interalveolar septa. The palatine process forms the hard palate with the palatine bone. The palatine fissure is formed at the articulation with the incisive bone. The nasal surface of palatine process forms the nasal crest and encloses part of the palatine sinuses. The oral surface has numerous palatine foramina present.
Mandible (mandibula)
The mandible can be divided into the body and the ramus. The body of the mandible supports the incisor teeth (rostrally) and cheek teeth (caudally). The section of the body which does not support any teeth is called the interalveolar margin or diastema. The mandibule also contains the mandibular canal and the mental foramen. The facial notch is on the ventral surface where the parotid duct (in herbivores) and facial vessels run. The ramus extends from the caudal end of the body dorsally towards the zygomatic arch. The masseter muscle attaches to the lateral surface at the masseteric fossa. The medial pterygoid attaches to the medial surface at the pterygoid fossa. The angle of the mandible terminates dorsally in the condylar process and the coronoid process which are separated by the mandibular notch. The temporal muscle inserts onto the coronoid head. The condylar process articulates with the mandibular process of the skull (see here).
Major Skull Foramen and Canals
The jugular foramen is located either side of basilar part of occipital bone, adjacent to tympanic bulla and contains the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), vagus nerve (CN X) and accessory nerve (CN XI). The jugular foramen also contains the internal carotid artery. The foramen magnum is formed by the occipital bones and is the spinal cord's passage to the neck and body. The alar ligaments run through the foramen magnum together with vertebral arteries, spinal arteries and tectoral membranes. The hypoglossal canal is between paracondylar and condylar processes on lateral part of occipital bone. The hypoglossal nerve (CN XII), condylar artery and condylar vein all pass through. The optic chiasma runs in a transverse depression behind the sphenoid rostrum on presphenoid bone and facilitates the path of the optic nerve (CN II).
The optic canal passes from the optic chiasma over wings of the presphenoid bones and facilitates the path of the optic nerve (CN II). The oval foramen is found within the caudal wing of the basisphenoid bones and the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3) passes through it. The alar canal is formed by the rostral border of the basisphenoid bone at the base of the pterygoid processes. It is composed of the caudal alar foramen, rostral alar foramen and the small alar foramen. The maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V2) passes through together with the temporal artery.
The stylomastoid foramen is situated on the petrosal part of the temporal bone and allows the facial nerve (CN VII) to pass through. The ethmoidal foramen perforates the orbital part of the frontal bone allowing the olfactory nerve (CN I) and ethmoidal artery and vein to pass through.
The orbital fissure is on the presphenoid bone and allows the opthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V1), occulomotor nerve (CN III), trochlear nerve (CN IV) and the abducens nerve (CN VI) to pass through. The supraorbital foramen is on the frontal bone and allows the opthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V1) to pass through together with the frontal artery and vein. The infraorbital foramen is on the maxilla and allows the maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V2) to pass through together with the infraorbital artery and vein. The mental foramen is on rostral end of the mandible and allows the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3) and the mental artery and vein to pass. The palatine canal runs through horizontal plate of palatine bone and allows the palatine artery, palatine vein and palatine nerves to pass through. The internal acoustic meatus is made up of the medial surface of the petrosal part of the temporal bone and is the facial opening for the facial nerve (CN VII). It is also the cochlear opening, dorsal vestibule opening and the ventral vestibule opening for the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII).
Facial Muscles
For further generalised information on canine muscles please see the Canine Muscles page. The major facial muscles are covered in the following sections of anatomy and physiology, although these pages are not canine specific:
Muscles involved in Deglutition
Trunk
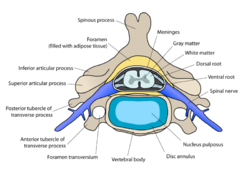
The trunk is in broad terms the body of the animal and is what would remain if the head and limbs were removed. It can be seperated in four parts, the cervical vertebrae, thorax, lumbar region and pelvis. Anatomically these structures are highly distinguishable and each area has a distinctive shape, size and physiological role. The vertebrae within the trunk consist of a body, which encloses the vertebral foramen (through which the spinal cord and meninges run), a spinous process, and a transverse process, as well as articular processes by which they join together. The form of the spinous process varies with respect to species and region.
Joints of the Spinal Column
Within the spinal column there are two types of joints: cartilaginous and synovial. Cartilaginous joints provide direct connections between vertebral bodies. The bodies of adjacent vertebrae are connected by thick, flexible intervertebral discs, consisting of two parts; the nucleus pulposus and the annulus fibrosis. The nucleus pulposus has a slightly eccentric shape and is a notochord derivative. It is contained under pressure and prone to escape during spinal trauma. The annulus fibrosis has encircling bundles of fibrous tissue surrounding the nucleus pulposus that pass obliquely from one vertebra to another with changing orientation. These are not prone to damage. The second type of spinal column joint is the synovial joint. These are found between facets on vertebral arches and there are various conformational differences between the regions of the head and pelvis.
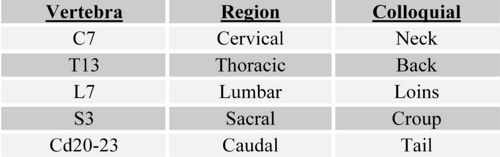
Cervical Region
Canines have seven cervical vertebrae, as do almost all other mammals. The first two cervical vertebrae are known as the atlas and the axis respectively, and have altered conformations to the other five vertebrae to allow movement of the head. The atlas has no conventional body, instead it is composed of two lateral masses joined by dorsal and ventral arches. The atlas and axis are fused in embryonic life. The wing of the atlas is the transverse process of this vertebra and allows the spinal column to articulate with the skull, by providing a resting place for the occipital condyles. The axis is the longest vertebra. The Atlanto-occipital joint is between the condyles of the skull and corresponding cavities of the atlas. It functions as a ginglymus where movement is restricted to flexion/extension in the sagittal plane (eg nodding). The Atlantoaxial joint is where the ventral arch of atlas and the body of the axis face into a single synovial cavity with limited areas of contact. Movement is rotational about a longitudinal axis (eg. head shaking). The nuchal ligament connects the spinous process of the axis to the spinous process of the first thoracic vertebra (T1). The last (C7) cervical vertebra has a taller spinous process than those preceding it, and articulates with the first pair of ribs. The remaining cervical vertebrae become progressively shorter caudally and the spinous process is initially small and is only more developed in C7. Each vertebrae has a transverse foramen which facilitates the passage of vertebral vessels and nerves.
Thoracic Vertebrae
Canines and most mammals have thirteen thoracic vertebrae. Thoracic vertebrae articulate with one another and with the ribs using both cartilaginous and synovial joints (see section above). Thoracic vertebrae are generally very similar throughout the length with only small differences occurring gradually between those vertebrae both cranially and caudally. have short vertebral bodies with flattened extremities, costal facets, short transverse processes and prominent spinous processes. They reach a maximum height, a few vertebrae behind the cervicothoracic junction (constituting the withers of the horse) and then decline. The orientation of spinous processes shifts from caudo- to craniodorsal.
Lumbar Vertebrae
The lumbar vertebrae are longer and more uniform in shape than the thoracic vertebrae. They are also shorter in height, with long, flattened transverse processes that project laterally.
Sacral Vertebrae
The sacrum is a single bone formed by the fusion of several vertebrae that articulates with the pelvic girdle. It allows the thrust of the hindlimbs to be transmitted to the trunk. The sacrum narrows caudally and is curved to present a concave surface to the pelvic cavity.
Caudal Vertebrae
The number of caudal vertebrae varies greatly even within species. There is a progressive simplification of their form.
Forelimb
Structures of the Proximal Forelimb and Shoulder
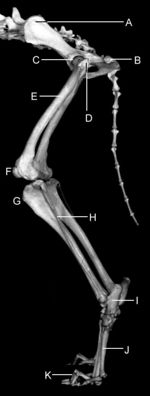
Scapula
The Scapula forms the basis of the shoulder region, providing points of attachment of extrinsic and intrinsic muscles. It is held in place by a synsarcosis of muscles and does not form a conventional articulation with the trunk. The spine culminates in the acromion. The scapular cartilage is comprised of only a very narrow rim.
Clavicle
In the cat, a remnant of bone may remain embedded in the fibrous intersection in the brachiocephalicus, which may prove misleading in radiographic images.
Humerus
The Humerus is the long bone of the forearm, articulating with the scapula to form the shoulder and the radius and ulna to form the elbow. In situ, it lies obliquely along the ventral thorax and is more horizontal in larger species. The greater tubercle is not separated into two parts like in other species. In dogs and cats, it articulates with the ulna medially via a trochlea and the radius laterally via a capitulum.
Radius
A radial tuberosity provides a site of attachment for brachialis and biceps brachii mm. This roughened area is very variable in size in dogs and can be non-existent.
Ulna
The ulna shaft tapers distally, lying oblique to the radius, i.e. the proximal end lies medial and the distal end lateral to the radius. There is a distinct gap between it and the radius, which is filled by the pronator quadratus muscle. The distal styloid process is blunt and articulates with the ulnar carpal bone, accessory carpal bone and ulnar notch of the radius.
Joints of the Proximal Forelimb
Shoulder Joint
The joint capsule barely extends past the areas of articulation, except where it continues distally into the intertubercular groove of the humerus. This provides cushioning and synovial support for the bicipital tendon. The bicipital tendon and the joint capsule pouch are held in place by the transverse humeral retinaculum, which lies between the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus.
Elbow Joint
The radius articulates with the capitulum and lateral trochlear surface of the humeral condyle. Whilst the medial part articulates with the trochlear notch of the ulna. To allow the radius to rotate slightly the radial head has a marginal band of cartilage making the articular circumference. It faces the radial notch of the ulna between the medial and lateral coronoid processes. The joint capsule runs from just proximal to the articular surface of the condyle of the humerus to the periphery of the olecranon fossa; it pouches between the ulna and radius, and under the tendinous attachments of some muscles.
Collateral ligaments are paired and lie medially and laterally. They both attach proximally to the epicondyle and distally to the tuberosities of the radius and ulna.
Annular ligament of the radius attaches to the sides of the coronoid process of the ulna. This runs deep to the collateral ligaments and forms a ring for the radial head to turn in during pronation and supination.
The radius and ulna are joined mid-shaft by the interosseous ligament, the remainder is filled by the interosseous membrane.
Structures of the Distal Forelimb
Carpal Bones
Carpal bones comprise two rows:
Proximally - the radial and intermediate bones are fused to form the radial carpal bone. The accessory carpal bone articulates with both the ulnar carpal bone and the distal ulna.
Distally - bones I-IV are present.
Metacarpal Bones
These are covered in detail in the canine phalanges section.
Joints of the Distal Forelimb
Carpal Joint
The synovial membranes form three compartments corresponding to each joint. The proximal is the largest whilst the middle carpal and carpometacarpal sacs communicate and extend into the intermetacarpal articulations. The fibrous joint capsule is common to all three joints and attaches to the individual bones and various intercarpal ligaments. The extensor retinaculum is fibrous collagenous tissue on the dorsal aspect that allows passage of the extensor tendons. On the palmar aspect lies the palmar carpal fibrocartilage, that provides attachment for some metacarpal bones. Paired collateral ligaments bridge the sides of the three main articulations.
The flexor retinaculum is the carpal fascia on the palmar aspect, and lies between the accessory carpal bone and the medial aspect of the carpus. This with the joint capsule and medial surface of the accessory carpal bone, makes up the carpal canal. It houses just the deep digital flexor tendon in the dog. The intermetacarpal joints, are tight joints between the proximal ends of the metacarpals. The joint capsules are continuous with that of the carpal joint. They are held together by the interosseous metacarpal ligaments.
Hindlimb
Pelvic Girdle and Hip
The pelvis encircles the pelvic cavity and has several functions including protecting the pelvic viscera, and the reproductive and urinary organs. The pelvis is also essential in locomotion and posture. The pelvis also contains the pelvic canal which, dependant on size, can cause problems during parturition.
Bones
The pelvic girdle is formed by two hip bones which are joined ventrally at the cartilagenous pelvic symphysis and articulate dorsally with the sacrum. The three components of each hip bone are the ilium, pubis and ischium.
The bone that articulates with the hip bones to form the hip joint is the femur.
Canine Bone Specifics
The ilium is large and prominent in canines. In the dog the tuber coxae has two prominences; the cranial and caudal ventral iliac spines and although not usually visible, both are readily palpable. The sacral tuber has two prominences; the cranial and caudal dorsal iliac spines. The iliac crest is wide and convex and the ileal wing is orientated in an almost sagittal manner and both are easily palpable.
Within the the ischium, the canine ischial tuberosity is linear in shape.
The femoral head of the canine femur is circular and is situated in the centre of the head. There is a distinct neck connecting the femoral head to the shaft and the greater trochanter is level with the femoral head.
Joints and Synovial Structures
Sacroiliac Joint
In dogs, the short branch of the dorsal sacroiliac ligaments connects the sacral tuberosity to the mamillary processes of the sacrum. The sacrotuberous ligament consists of a fibrous cord between the ischial tuberosity and the transverse process of the last sacral vertebrae. (This ligament is absent in the cat.)
Coxafemoral/Hip Joint
The dog has the greatest range of movement in this joint compared to other domestic species. It has the ability to flex, extend, rotate, adduct and abduct its whole limb because of this.
Distal Limb
Bones
Metacarpals and Metatarsals
The arrangement of the metatarsals are similar to those of the metacarpals in that they are rod shaped bones, numbered from I to V. The 1st is the most medial and is very small, the 3rd and 4th are the longest. The proximal base of each articulates with it's corresponding carpal bone and the adjacent metacarpal. The distal end is its head, which is transversely cylindrical and articulates with the proximal phalanx. Metacarpals II - V possess a sagittal ridge on their palmar aspects.
Phalanges
The proximal phalanx of the main digits (II - V) have a concave articular surface and the palmar border has a groove to accomodate the articular surface of the metacarpus when the joint is fixed. The distal head has two convex areas separated by a groove. The middle phalanx is roughly two-thirds the length of the proximal phalanx and its base has a sagittal ridge on the articular surface which articulates with the groove of the proximal phalanx. The head resembles that of the proximal phalanx. The distal phalanx is made up of a cone-shaped ungual process with a distinct collar called the 'ungual crest'. The deep ungual groove distal to the crest provides attachment for the proximal border of the claw and articulates with the middle phalanx via a small sagittal crest. A bony sesamoid bone is found on the dorsal aspect of the metacarpophalangeal joint. The 'dew claw' (metacarpal I) is normally present in the forelimb but often not in the hindlimb. It normally only consists of two phalanges that resemble the proximal and distal ones.
Joints
Metacarpophalangeal Joint
The metacarpophalangeal joint is able to undergo flexion and extension movements. Each joint (except the first digit) has a pair of sesamoid bones associated with the palmar aspect of the joint which articulate with a concave area of the proximal phalanx. The joint capsule runs between the four bones of the joint extending dorsally under the extensor tendon and part also intermingling with an expanding area of the common digital extensor tendon. Distally it binds to the articular cartilage of the proximal phalanx and on the palmar aspect its dorsal attachment is level with the proximal end of the sesamoid bones. The collateral ligaments bind the the metacarpal bone to the proximal phalanx, with a deep branch attaching to the sesamoid bone. The palmar/intersesamoidean ligament is a mass of fibrocartilage that embeds the sesamoid bones. The palmar aspect of this ligament forms a groove for the deep flexor tendon to run in. The collateral sesamoid ligaments connect the outer aspect of the sesamoids to the proximal phalanx whilst the distal sesamoid ligaments, although not well developed in the dog, connect the distal surface of the sesamoids to the palmar aspect of the phalanx. These ligaments include the cruciate and short ligaments. The superficial transverse metacarpal ligaments surround the flexor tendons and their sheaths at the point of the sesamoid ligaments and the distal annular ligaments cross the surface of the flexor tendons and sheaths at the level of the proximal and middle phalanx.
Proximal Interphalangeal Joint
The proximal interphalangeal joint provides flexion and extension movements. The joint capsule attaches near the articular surfaces of the proximal and middle phalanges and extends slightly in a pouch dorsally and more extensively on the palmar aspect. The dorsal capsule is reinforced by a fibrocartilaginous nodule; the extensor tendon attaches to the capsule here. The collateral ligaments connect the distal end of the proximal phalanx to the proximal end of the middle phalanx and lie in a vertical direction rather than along the bone axis.
Distal Interphalangeal Joint
The distal interphalangeal joint allows extension and slight flexion movements. The joint capsule attaches to the articular periphery of the bones and has a small fibrocartilagenous bead in the palmar aspect. The collateral ligaments connect the distal part of the middle phalanx to the sides of the ungual crest of the distal phalanx. The dorsal ligament connects the proximal dorsal border of the extensor process of the distal phalanx. These are paired in dogs and function is to keep the claw raised until contraction of the deep digital flexor acts to overcome their tension.