Respiratory Fungal Infections - Pathology
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
|
|
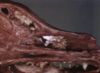
Aspergillus fumigatus
- Aspergillus fumigatus
- Most commonly in dogs but also other species
- Causes rhinitis, often also involves the frontal sinus
- Chronic necrotising inflammation with friable exudate containing necrotic tissue and fungal hyphae
- Result in severe neutrophilic rhinitis/sinusitis
- These lesions can be aggressive causing destruction of turbinates and nasal septum
- Can occur secondary to areas of mucosal compromise eg: adjacent to a space-occupying lesion
- Can cause pulmonary aspergillosis especially in birds, but also other animals
- Initiated by inhalation of spores,the most likely source of which is mouldy feed and bedding
- Given the wide exposure that occurs, it is thought that immunodeficiency may contribute to colonisation with this organism
- Gross lesions :
- Multiple discrete grey/ white nodules which develop around fungal colonies
- Blood vessels can become involved in the lesions -> invasion, haemorrhage or thrombosis
- Histologically:
- Granulomatous chronic lesions
- Macrophages and epithelioid cells
- Fibrous capsule
- In horses:
- Nasal aspergillosis
- Guttural pouch infections in horses - fungal plaques form on the adventitia of the carotid arteries can lead to catastrophic haemorrhage following erosion of carotid arteries!
- Often present with epistaxis
- May present with neurological dysfunction
- Rarely extends to other resions: cranium, middle ear, atlanto-occipital joint
- May extend to sinuses
Cryptococcus neoformans
- Cryptococcus neoformans
- Causes a granulomatous rhinitis, gelatinous exudate, granulomatous pneumonia
- Nodules or destructive masses which often result in facial swelling
- In severe cases, extension from nasal cavity to involve skin and oral mucosa can occur
- Can invade through adjacent structures, eg: through the cribiform plate into the brain! These cases therefore can present as a primary neurological disease.
- Microscopic:
- Large number of fungi and only few macrophages, lymphocytes and giant cells
Blastomycosis
- Caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis
- Occurs mainly in the Americas, Middle East and Africa, occasionally in Europe
- Mainly in young dogs, occasionally other species
- Can involve almost any tissue after spread from lungs
- Gross lesions:
- Microscopic lesions:
- Yeast fungi with thich walls in nodules with macrophages, neutrophils and giant cells
Histoplasmosis
- Caused by Histoplasma capsulatum
- Gross lesions in lungs:
- Firm encapsulated granulomas (granulomatous pneumonia)
- Microscopic lesions:
- Macrophages with inracytoplasmic yeasts
- Also in other tissues
Pneumocystis carinii
- Important cause of pneumonia in humans associated with immunodeficiency states
- It has been occasionally reported in young or immunosuppressed animals (e.g. Arabian foals with congenital immunodeficiency)
- Grossly:
- Diffuse interstitial pneumonia
- Patches of firmness or consolidation
- Histologically:
- Alveoli are filled with pale staining acidophilic material (= trophozoite and cyst forms of the organism)
- It is thought that as P. carinii is often present as a latent infection, alveolar macrophages normally control the organism - a process which fails in immunodeficient states