Hard Palate
Revision as of 12:11, 3 September 2010 by Bara (talk | contribs) (moved Hard Palate - Anatomy & Physiology to Hard Palate)
Introduction
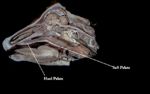
The hard palate (palatum durum) forms the rostral roof of the oral cavity. It merges caudally with the soft palate where a connective tissue aponeurosis replaces the bone.
Structure and Function
- Bony shelf of palatine processes of the incisive, maxillary and palatine bones. Failure of the palatine bones to fuse results in cleft palate.
- 6-8 fixed transverse ridges to direct food caudally
- Flat
- Incisive papilla (small median swelling) behind incisive teeth
- Smaller papillae ducts branching to nasal cavity and vomeronasal organ
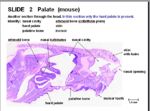
Histology
- Thick mucosa
- keratinised stratified squamous epithelium
Species Differences
Herbivores
- More heavily keratinised
Feline
- Short hard palate