Female Reproductive Tract - Horse Anatomy
| This article is still under construction. |
Ovaries
The ovary is the female Gonad homologous to the male Testes.The structures found within the ovary are undergoing constant changes throughout the oestrus cycle from the Follicles containing Oocytes, to the formation of Corpus Haemorrhagicum, Corpus Luteum, and finally Corpus Albicans. The ovaries of the mare are two kidney-shaped structures situated ventral to the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae, supported by the mesovarium. During the non-breeding season they measure 2-4cm in length and 2-3cm in width. During the sexually active stage, they are 6-8cm in length and 3-4cm in width.
In the mare, the structure of the ovary is reversed compared to other species. The cortex is in the centre and is enclosed by a dense, richly vascularised connective tissue layer, which is analagous to the medulla of other domestic mammals.
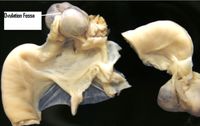
Tunica Albiguinea
The connective tissue layer covering the ovarian cortex. The whole ovary is contained within the tunica albiguinea except the ovulation fossa. Overlying this structure is a single layered germinal epithelium.
Cortex
Contains Follicles in various stages of development as well as the Corpus Luteum (includes Corpus Haemorrhagicum and Corpus Albicans). The cortex reaches the surface of the ovary at the ovulation fossa, a deep indentation at the free margin. This is where mature follicles rupture in ovulation, as opposed to at various points on the surface in other domestic mammals. Follicles can be identified by transrectal palpation, but Corpora Lutea cannot. Identification of Corpora Lutea requires ultrasonography.
Medulla
The Medulla is made up of dense connective tissue. This is where all of the lymphatics, nerves and vasculature of the ovary are found.
Histology
Stroma
The body of the ovary (ovarian stroma) consists of:
- Spindle-shaped cells
- Fine collagen fibres
- Ground substance
Stromal cells resemble fibroblasts, but some contain lipid droplets. Bundles of smooth muscle cells are scattered throughout the stroma.
Cortex
Contains:
- Follicles containing oocytes in various stages of development
- Atretic Follicles
- Corpora lutea
- Corpora albicans
The superficial cortex is more fibrotic than the deep, and is called the tunica albuginea. On the surface of the ovary is the germinal epithelium. This is a continuation of the peritoneum.
Medulla
The medulla is highly vascular. It contains hilus cells, which are similar to the Leydig cells of the testes.
Vasculature
Arterial Supply
- The ovarian artery (a branch of the Aorta) and ovarian branches of the uterine artery form anastomoses in the mesovarium and the broad ligament. From this arterial plexus ~10 coiled helicine arteries enter the hilus of the ovary. Smaller branches form a plexus at the corticomedullary junction, giving rise to straight cortical arterioles, which radiate into the cortex. Here they branch and anastomose to form vascular arcades, which give rise to a rich capillary network around follicles.
Venous Drainage
Venous drainage follows the course of the arterial system. Medullary veins are large and tortuous. The ovarian artery is closely associated with the uterine vein. This is important for the transfer of luteolytic PGF2α from the uterus to the ovary.