Odontodystrophy
Also known as: Enamel Hypoplasia
Introduction
See Enamel Dysplasia
Clinical Signs
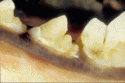
In ruminants, one will see a chalky mottling and yellow brown pitting of the tooth, due to enamel hypoplasia. There is usually no difficulty in mastication detected and the animal is clinically well.
In dogs, enamel hypoplasia may result in severe discoloration or pitting of a tooth or teeth due to the effect on enamel formation.
Diagnosis
Clinical signs are diagnostic, plus history e.g. of CDV in dogs, fluoride in cattle.
Treatment and Control
There is no treatment for this condition. Control measures are prevention of the causes of the disease, e.g. vaccination against CDV and prevention of fluoride poisoning in cattle.
If only a single tooth is affected, restorative treatment can be performed using dental composites or a metal-alloy jacket crown.
| Odontodystrophy Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Veterinary Dentistry Q&A 13 |
References
Tutt, C., Deeprose, J. and Crossley, D. (2007) BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Dentistry (3rd Edition), British Small Animal Veterinary Association.
Williams, A (2008) Alimentary System Study Guide, Royal Veterinary College.
Verstraete, F. (1999) Self-assessment colour review in Veterinary Dentistry Manson Publishing
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt6989130c086cc9_20272110 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt6989130c16fba9_95570755 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt6989130c207597_63353448
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |