Pituitary Gland Flash Cards - Anatomy & Physiology
Revision as of 16:45, 3 September 2008 by A.allison (talk | contribs) (New page: {{toplink |backcolour = FAFAD2 |linkpage =Endocrine System - Anatomy & Physiology |linktext =Endocrine System |maplink = Endocrine System (Content Map) - Anatomy & Physiology |pagetype =An...)
|
|
Pituitary Gland
| Question | Answer | Article |
|---|---|---|
| Describe the location of the Pituitary Gland. |
|
Answer article |
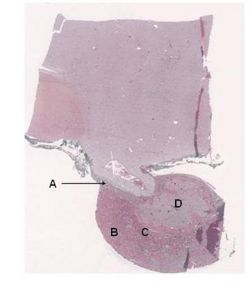
| Label the diagram: |
|
Answer article |
| Which sections of the Pituitary Gland labelled above make up the Adenohypophysis and Neurohypophysis: |
|
Answer article |
| What is the blood supply to the Pituitary Gland: |
|
Answer article |
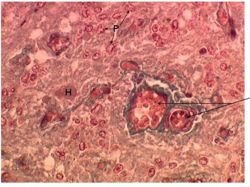
| What part of the Pituitary Gland does this histological section represent: |
|
Answer Article |
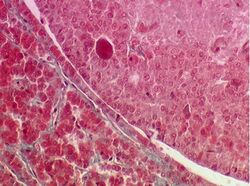
| Which parts of the Pituitary Gland does this histological section represent: |
|
Answer Article |
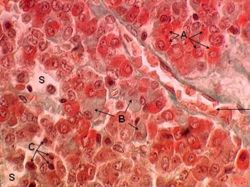
| What part of the Pituitary Gland does this histological section represent: |
|
Answer Article |
| What are the cell types within the Pars Distalis and what hormones do they produce? |
|
Answer article |
| What is secreted by the Posterior Pituitary Gland and what are their actions: |
|
Answer article |
| Decribe how Milk Let-Down is initiated: |
|
Answer article |