Anus - Anatomy & Physiology
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
|
|
Introduction
The anus is the terminal portion of the alimentary tract which communicates with the external environment. Two sphincters control it's aperture. It allows faeces and gas to leave the body. Defeacation is the process where faeces are expelled from the rectum through the anus.
Structure
- There are two anal sphincters:
- Internal anal sphincter, formed by thickening of the circular smooth muscle of the gut and under autonomic control.
- External anal sphincter, formed from striated skeletal muscle and under voluntary control.
Function
- To transmit faeces from the rectum to the external environment.
- Anal sphincters give control over the regularity of defeaction, and this may be consciously controlled in some species.
- The anal canal lubricates the passage of faeces.
Histology
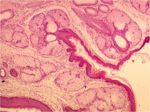
- At the anus, the columnar intestinal epithelium is replaced by the stratified squamous keratinised epithelium of the skin.
- The anal canal joins the bowel to the exterior and is the last 2-3cm of the alimentary tract.
- This is a short passage derived from the proctodeum (formed by invagination of the surface ectoderm).
- Sebaceous and large apocrine sweat glands both occur in this region in association with the anal sphincters.
- Before joining the anal canal, the rectum becomes dilated to form the rectal ampulla.
- At the rectoanal junction, the lumen is constricted by longitudinal folds in the mucosa.
- These are normally pressed together to occlude the lumen.
- As the muscosa changes from columnar to cutaneous, three zones are created:
- Columnar
- Has many longitudinal folds.
- Divided from the rectum by the anorectal line.
- This is a line where the mucosa is stratified squamous epithelium containing lots of lymphoid tissue.
- Intermediate
- Divided from the cutaneous zone by the anocutaneous line.
- Cutaneous
- Skin.
- Stratified squamous keratinised epithelium.
- Surrounds the anus.
- Excretory ducts of the anal sacs open into this region.
- Columnar
Species Differences
Carnivore
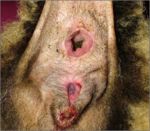
- The dog and cat posses two anal sacs. In the dog, these are the size of a hazlenut.
- Located ventrolaterally between the internal and external anal sphincters.
- They are large, coiled apocrine tubules that have many tubuloalveolar glands in their walls.
- These tubuloalveolar glandsw produce a fatty secretion.
- The fundus of the sac secretes a potent smelling fluid that drains through a single duct to an opening near the anocutaneous juncntion.
- The anal sacs get compressed during defecation, which causes the fluid to be expressed. The scent of the fluid is thought to act as a territorial marker.
- Anal sacs are clinically important as they are commonly diseased in dogs - frequently, they become enlarged due to accumulated secretion.
- The dog has perianal glands that lie in the skin surrounding the anus.
- They are modified sebaceous glands.
Equine
Porcine
- Also have anal sacs.