Difference between revisions of "Dermatophytosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m |
m |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
*Dermatophytes in [[Mycotic skin infections - Pathology#Dermatophytoses|dermatophytosis]] | *Dermatophytes in [[Mycotic skin infections - Pathology#Dermatophytoses|dermatophytosis]] | ||
| + | |||
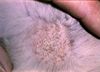
| + | [[Image: Microsporum canis lesions.jpg|100px|thumb|right|<small><center>''Microsporum canis'' alopecia and scaling lesions (Courtesy of Bristol BioMed Image Archive)</center></small>]] | ||
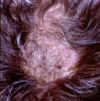
| + | [[Image: Ringworm dog.jpg|100px|thumb|right|<small><center>Ringworm in a dog (Courtesy of Bristol BioMed Image Archive)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | [[Image: Trichophyton mentagrophytes dog.jpg|100px|thumb|right|<small><center>Trichophyton mentagrophytes in a dog (Courtesy of Bristol BioMed Image Archive)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Caused by [[Fungi|dermatophytes]] | ||
| + | **''Microsporum'' - zoophilic | ||
| + | **''Trichophyton'' - geophilic | ||
| + | **''Epidermophyton'' - anthropophilic | ||
| + | *Common in many species, especially cats | ||
| + | *Hot, humid environment predisposes and viable fungi peripherally | ||
| + | *More common in young animals | ||
| + | *Produce proteolytic enzymes to penetrate surface lipid | ||
| + | *Fungal hyphae invade keratin -> break into arthrospores | ||
| + | *Epidermal hyperplasia ([[Skin Glossary - Pathology|hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis]]) and inflammation | ||
| + | *Superficial perivascular dermatitis -> exocytosis (migration through epidermal layers) -> intracorneal microabscesses | ||
| + | *Exocytosis -> folliculitis -> furunculosis | ||
| + | *Highly variable lesions | ||
| + | *Normal -> eruptive nodular -> pseudomycetoma -> onychomycosis | ||
| + | *Grossly: | ||
| + | **Circular or irregular lesion, may coalesce | ||
| + | **Scaly to crusty patches | ||
| + | **Alopecia due to broken hair shafts and hairs lost from inflammed follicles | ||
| + | **Follicular papules and pustules | ||
| + | **Peripheral red ring ('''ringworm''') due to dead fungi in areas of inflammation at centre of lesions and viable fungi peripherally | ||
| + | *Microscopically: | ||
| + | **Perifolliculitis, folliculitis or furunculosis | ||
| + | **Epidermal hyperplasia | ||
| + | **Intracorneal microabscesses | ||
| + | **Septate hyphae or spores may be found in stratum corneum and keratin of hair follicles | ||
Revision as of 16:58, 23 April 2009
| This article is still under construction. |
|
|
- Dermatophytes in dermatophytosis
- Caused by dermatophytes
- Microsporum - zoophilic
- Trichophyton - geophilic
- Epidermophyton - anthropophilic
- Common in many species, especially cats
- Hot, humid environment predisposes and viable fungi peripherally
- More common in young animals
- Produce proteolytic enzymes to penetrate surface lipid
- Fungal hyphae invade keratin -> break into arthrospores
- Epidermal hyperplasia (hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis) and inflammation
- Superficial perivascular dermatitis -> exocytosis (migration through epidermal layers) -> intracorneal microabscesses
- Exocytosis -> folliculitis -> furunculosis
- Highly variable lesions
- Normal -> eruptive nodular -> pseudomycetoma -> onychomycosis
- Grossly:
- Circular or irregular lesion, may coalesce
- Scaly to crusty patches
- Alopecia due to broken hair shafts and hairs lost from inflammed follicles
- Follicular papules and pustules
- Peripheral red ring (ringworm) due to dead fungi in areas of inflammation at centre of lesions and viable fungi peripherally
- Microscopically:
- Perifolliculitis, folliculitis or furunculosis
- Epidermal hyperplasia
- Intracorneal microabscesses
- Septate hyphae or spores may be found in stratum corneum and keratin of hair follicles