Giardiasis
| This article is still under construction. |
Description
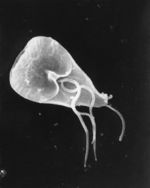
Giardia is a binucleate, flagellate protozoa that causes enteric infection giardiasis in dogs and occasionally cats. Transmission is via cysts that are shed in the faeces, and may be direct or indirect. Indirect water-borne transmission is the most common modality and is favoured by cool, moist conditions that prolong cyst survival. Once cysts are ingested, motile trophozoites are released and attach to the cells of the small intestinal mucosa via an adhesive disc. Multiplication by binary fission can then occur, and trophozoites encyst to a stage adapted for survival in the external environment. Cysts are seen in the faeces from day 3 post-infection, and can survive in the environment for several months. Animals that mount an immune response to Giardia can eliminate infection; however, the immunity acquired does not necessarily prevent re-infection after a short period.
Giardiasis is a condition of significant zoonotic concern. Although the cat protozoa G. felis seems to be species-specific, dogs can host both the canine-specific G. canis and G. lamblia, which has zoonotic genotypes. It is not known how important dogs are as a reservoir for human Giardia infection, or how frequently zoonotic transmission occurs. In man, Giardia may cause acute diarrhoea, particualrly in immunocompromised individuals. Subclinical infections also occur.
Signalment
Dogs are more commonly affected than cats. There are no age, breed or sex predispositions for Giardia infection, but puppies and kittens are more likely to contract clinical disease than adult animals.
Diagnosis
Clinical Sgns
Clinical signs are more likely to be seen in younger animals; older hosts are usually infected asymptomatically. Signs can be acute, transient, intermittent or chronic, can chronic infection can lead to debilitation. Malabsorbtion syndrome with soft, frothy, greasy, voluminous, malodourous faeces can occur.
Affected animals may show no clinical signs or, alternatively, may suffer from actue diarrhoea or chronic loose, foul smelling faeces typical of steatorrhea. Frequency of defaecation is normally increased. The clinical signs of giardiasis normally include diarrhoea, but vomiting and possibly weight loss, together with the presence of foul smelling faeces may be seen in some cases.
Laboratory Tests
- Faecal examination
- Cysts need to be distinguished from pollen grains and yeasts
- Cyst excretion is intermittent
- Faeces need to be collected over a 3 day period
- Cysts are heavy
- Needs higher density flotation fluids
- Do not float well in saturated sodium chloride solution
- Immunoassays
- Detect cyst antigen in faeces
Treatment
- Sanitation and hygiene
- Minimise risk of human infection
- Boil (or sterilise through other means) drinking water in regions of the world where drinking water may be contaminated
- Avoid uncooked foodstuffs
- Contaminated by washing
Prognosis
Links
References
- Drug Treatments
- Metronidazole
- Flagyl, Torgyl
- Fenbendazole
- Panacur
- Metronidazole
- Vaccination
- Killed trophozoites
- Available in the USA for cats and dogs
- Decreases the excretion and viability of cysts
- Decreases environmental pressure