Difference between revisions of "Hindbrain - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
===Cerebellum=== | ===Cerebellum=== | ||
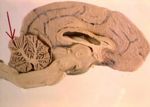
| + | [[Image:braincerebellumarrow.jpg|thumb|right|150px|The location of the cerebellum. Image courtesy of BioMed Archive]] | ||
| + | |||
* The cerebellum: | * The cerebellum: | ||
** Inhibits upper motor neurons | ** Inhibits upper motor neurons | ||
Revision as of 15:35, 14 August 2009
| This article is still under construction. |
|
|
Introduction
Includes development and overview of the system (Paragraph format)
Structure and Function
| Structures Present | Function | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon) | Myelencephalon - Medulla Oblongata
Metencephalon - Pons and Cerebellum |
Medulla Oblongata - Cranial nerves, hearing, visceral fibres
Cerebellum - Posture, balance etc |
Medulla Oblongata
Pons
Cerebellum
- The cerebellum:
- Inhibits upper motor neurons
- Co-ordinates movement
Consequences of Cerebellar Pathology
- Cerebellar pathology can result in:
- Hypermetria
- Unconsious proprioceptive deficits
- Increased motor tone on the side of the lesion (in assymetrical damage).
- This gives head tilting AWAY from the damage.
- "A paradoxical vestibular sign".
- This gives head tilting AWAY from the damage.
- Damage to the cerebellum does NOT cause weakness.
Species Differences
- The size of the brain differs between species, but otherwise the structure is quite constant.