Difference between revisions of "Hypoadrenocorticism"
JamesSwann (talk | contribs) |
JamesSwann (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{unfinished}} | |
| + | |||
| + | {| cellpadding="10" cellspacing="0" border="1" | ||
| + | | Also known as: | ||
| + | | '''Addison's disease''' | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Description== | ||
| + | Addison's disease occurs due to a failure to produce adequate amounts of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid hormones from the adrenal cortex. The majority of cases are '''primary''' and occur due to an autoimmune response directed at the endocrine cells of the adrenal glands, resulting in adrenocortical atrophy. This is an example of a [[Type IV Hypersensitivity - WikiBlood|type IV (delayed type) hypersensitivity response]]. Smaller numbers of primary cases are caused by haemorrhage, necrosis or neoplasia within the adrenal glands. '''Secondary''' hypoadrenocorticism occurs due to a reduction in the secretion of ACTH from the anterior pituitary gland. | ||
| − | |||
===Primary Hypoadrenocorticism=== | ===Primary Hypoadrenocorticism=== | ||
| − | [[Image:Adrenal atrophy.jpg | + | [[Image:Adrenal atrophy.jpg|thumb|125px|Image of an adrenal gland undergoing atrophy.<br><small>Copyright A. Jefferies 2008</small>]] |
| − | + | There are several possible causes of primary hypoadrenocorticism, including: | |
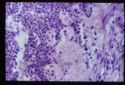
| − | *'''Adrenal atrophy''' | + | *'''Adrenal atrophy''' is thought to be an autoimmune disease caused by a type IV immune response. Affected animals have an increased risk of developing other immune-mediated diseases, including [[Immune Mediated Haemolytic Anaemia|immune-mediated haemolytic anaemia]]. Grossly, the adrenal glands are small, difficult to locate and they are dark brown on cut sections. Histological analysis reveals the presence of an infiltrate of lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages. |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:Adrenal necrosis.jpg|thumb|125px|Image of an adrenal gland undergoing necrosis<br><small>Copyright A. Jefferies 2008</small>]] | |
| − | + | [[Image:Adrenal necrosis2.jpg|thumb|125px|Image of an adrenal gland undergoing necrosis<br><small>Copyright A. Jefferies 2008</small>]] | |
| − | [[Image:Adrenal necrosis2.jpg | ||
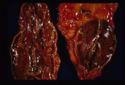
| − | * | + | *'''Adrenal necrosis''' may be caused by certain infections or it may be a sequel to other metabolic diseases. In horses, [[Salmonella|'''salmonellosis''']] may cause adrenal necrosis in horses but, in small animals, necrosis is more likely to occur due to myoarteritis in uraemic animals resulting in ischaemia of the adrenal gland. Idiopathic necrosis may occur with no apparent cause. Grossly, the glands contain areas of red haemorrhage with yellow necrotic foci. |
| − | |||
| − | *'''Bilateral adrenalectomy | + | *'''Bilateral adrenalectomy''' or '''mitotane therapy''' may cause iatrogenic hypoadrenocorticism. Mitotane, which is used in the treatment of hyperadrenocorticism (Cushing's disease) selectively destroys the zona fasciculata and reticularis while sparing the essential zona glomerulosa. Iatrogenic Addison's disease is a common sequel of its use. |
===Secondary Hypoadrenocortisism=== | ===Secondary Hypoadrenocortisism=== | ||
| − | |||
Deficient pituitary secretion of ACTH. Often '''iatrogenic''' due to withdrawal of glucocorticoid treatment. Prolonged high dose treatment induce adrenal atrophy due to the effect of negative feedback on the pituitary. The withdrawal of drug must be gradual to allow to adrenal gland to return to function over a period of time. | Deficient pituitary secretion of ACTH. Often '''iatrogenic''' due to withdrawal of glucocorticoid treatment. Prolonged high dose treatment induce adrenal atrophy due to the effect of negative feedback on the pituitary. The withdrawal of drug must be gradual to allow to adrenal gland to return to function over a period of time. | ||
Usually little effect on mineralocorticoids as ACTH has little trophic effect on their production. | Usually little effect on mineralocorticoids as ACTH has little trophic effect on their production. | ||
===Pathophysiology=== | ===Pathophysiology=== | ||
| + | The glucococorticoid hormone '''cortisol''' enables animals to cope with stress while the minerlaocorticoid '''aldosterone''' plays a critical role in the regulation of sodium and potassium concentrations and of extracellular fluid volume. Aldosterone normally acts to increase sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion in the kidney so deficient aldosterone secretion will result in '''hyponatraemia''', '''hypochloraemia''' and '''hyperkalaemia'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Deficiency of cortisol results in '''hypoglycaemia''' (as cortisol usually antagonises the action of insulin), increased circulating levels of [[Lymphocytosis|lymphocytes]] and [[Eosinophilia|eosinophils]] and increased skin pigmentation. This latter syndrome occurs as low levels of glucocorticoids allow increased ACTH production as negative feedback on the pituitary is removed or decreased. As ACTH is released, so is MSH (Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone), increasing the pigmentation of the skin in chronic cases of hypoadrenocorticism. | ||
| − | + | ==Diagnosis== | |
| − | + | ===Clinical Signs=== | |
| − | + | Addison's disease may present acutely as an '''Addisonian crisis''' or it may cause chronic disease over several months before it is diagnosed. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*Acute necrosis will present as an acute syndrome with hypovolaemic shock, [[Control of Feeding - Anatomy & Physiology#The Vomit Reflex|vomiting]] and collapse. | *Acute necrosis will present as an acute syndrome with hypovolaemic shock, [[Control of Feeding - Anatomy & Physiology#The Vomit Reflex|vomiting]] and collapse. | ||
*Chronic damage to the adrenal gland will result in dehydration, [[Diarrhoea|diarrhoea]], anorexia and weakness. | *Chronic damage to the adrenal gland will result in dehydration, [[Diarrhoea|diarrhoea]], anorexia and weakness. | ||
| − | + | ===Laboratory Tests=== | |
| − | |||
*'''Haematology''': | *'''Haematology''': | ||
**Haemoconcentration in acute crisis; due to rapid dehydration. | **Haemoconcentration in acute crisis; due to rapid dehydration. | ||
| Line 47: | Line 46: | ||
*'''Electrolyte imbalance''': as above. | *'''Electrolyte imbalance''': as above. | ||
*'''Pre-renal azotaemia''': elevated urea and creatinine. | *'''Pre-renal azotaemia''': elevated urea and creatinine. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Other Tests=== | ||
*'''ACTH stimulation test''': Positive test is low initial cortisol with no response to ACTH. | *'''ACTH stimulation test''': Positive test is low initial cortisol with no response to ACTH. | ||
*'''ECG change''': Due to hyperkalaemia. In severe cases may see P-wave absence and sino-atrial standstill. | *'''ECG change''': Due to hyperkalaemia. In severe cases may see P-wave absence and sino-atrial standstill. | ||
| − | + | ===Diagnostic Imaging=== | |
| + | |||
| + | ==Treatment== | ||
*Acute crisis: Rapid i/v saline and i/v glucocorticoids. | *Acute crisis: Rapid i/v saline and i/v glucocorticoids. | ||
*Chronic form: '''Fludrocortisone acteta''' to replace mineralocorticoids. Add table salt to food and give glucocorticoids in times of stress E.g. transport. | *Chronic form: '''Fludrocortisone acteta''' to replace mineralocorticoids. Add table salt to food and give glucocorticoids in times of stress E.g. transport. | ||
| − | + | ==Prognosis== | |
Revision as of 08:58, 17 August 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
| Also known as: | Addison's disease |
Description
Addison's disease occurs due to a failure to produce adequate amounts of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid hormones from the adrenal cortex. The majority of cases are primary and occur due to an autoimmune response directed at the endocrine cells of the adrenal glands, resulting in adrenocortical atrophy. This is an example of a type IV (delayed type) hypersensitivity response. Smaller numbers of primary cases are caused by haemorrhage, necrosis or neoplasia within the adrenal glands. Secondary hypoadrenocorticism occurs due to a reduction in the secretion of ACTH from the anterior pituitary gland.
Primary Hypoadrenocorticism
There are several possible causes of primary hypoadrenocorticism, including:
- Adrenal atrophy is thought to be an autoimmune disease caused by a type IV immune response. Affected animals have an increased risk of developing other immune-mediated diseases, including immune-mediated haemolytic anaemia. Grossly, the adrenal glands are small, difficult to locate and they are dark brown on cut sections. Histological analysis reveals the presence of an infiltrate of lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages.
- Adrenal necrosis may be caused by certain infections or it may be a sequel to other metabolic diseases. In horses, salmonellosis may cause adrenal necrosis in horses but, in small animals, necrosis is more likely to occur due to myoarteritis in uraemic animals resulting in ischaemia of the adrenal gland. Idiopathic necrosis may occur with no apparent cause. Grossly, the glands contain areas of red haemorrhage with yellow necrotic foci.
- Bilateral adrenalectomy or mitotane therapy may cause iatrogenic hypoadrenocorticism. Mitotane, which is used in the treatment of hyperadrenocorticism (Cushing's disease) selectively destroys the zona fasciculata and reticularis while sparing the essential zona glomerulosa. Iatrogenic Addison's disease is a common sequel of its use.
Secondary Hypoadrenocortisism
Deficient pituitary secretion of ACTH. Often iatrogenic due to withdrawal of glucocorticoid treatment. Prolonged high dose treatment induce adrenal atrophy due to the effect of negative feedback on the pituitary. The withdrawal of drug must be gradual to allow to adrenal gland to return to function over a period of time. Usually little effect on mineralocorticoids as ACTH has little trophic effect on their production.
Pathophysiology
The glucococorticoid hormone cortisol enables animals to cope with stress while the minerlaocorticoid aldosterone plays a critical role in the regulation of sodium and potassium concentrations and of extracellular fluid volume. Aldosterone normally acts to increase sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion in the kidney so deficient aldosterone secretion will result in hyponatraemia, hypochloraemia and hyperkalaemia.
Deficiency of cortisol results in hypoglycaemia (as cortisol usually antagonises the action of insulin), increased circulating levels of lymphocytes and eosinophils and increased skin pigmentation. This latter syndrome occurs as low levels of glucocorticoids allow increased ACTH production as negative feedback on the pituitary is removed or decreased. As ACTH is released, so is MSH (Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone), increasing the pigmentation of the skin in chronic cases of hypoadrenocorticism.
Diagnosis
Clinical Signs
Addison's disease may present acutely as an Addisonian crisis or it may cause chronic disease over several months before it is diagnosed.
- Acute necrosis will present as an acute syndrome with hypovolaemic shock, vomiting and collapse.
- Chronic damage to the adrenal gland will result in dehydration, diarrhoea, anorexia and weakness.
Laboratory Tests
- Haematology:
- Haemoconcentration in acute crisis; due to rapid dehydration.
- Non-regenerative anaemia in chronic form; glucocorticoid deficiency decreases erythropoeisis.
- Electrolyte imbalance: as above.
- Pre-renal azotaemia: elevated urea and creatinine.
Other Tests
- ACTH stimulation test: Positive test is low initial cortisol with no response to ACTH.
- ECG change: Due to hyperkalaemia. In severe cases may see P-wave absence and sino-atrial standstill.
Diagnostic Imaging
Treatment
- Acute crisis: Rapid i/v saline and i/v glucocorticoids.
- Chronic form: Fludrocortisone acteta to replace mineralocorticoids. Add table salt to food and give glucocorticoids in times of stress E.g. transport.