Difference between revisions of "Intestinal Arterial Thromboembolism"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
* E.g. '''equine''' [[Salmonellosis|'''salmonellosis''']]. | * E.g. '''equine''' [[Salmonellosis|'''salmonellosis''']]. | ||
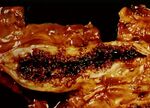
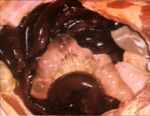
[[Image:Infaction of the small bowel.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Infarction of the small bowel (Courtesy of Bristol BioMed Image Archive)]] | [[Image:Infaction of the small bowel.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Infarction of the small bowel (Courtesy of Bristol BioMed Image Archive)]] | ||
| + | ==== Verminous endarteritis ==== | ||
| + | *Caused by larvae of [[Strongylus vulgaris|''S. vulgaris'']] within the cranial mesenteric artery | ||
| + | *Also called "verminous aneurism" (misnomer as aneurism = dilatation/thinning of blood vessel wall; also, aneurisms are rare) | ||
| + | *Wall of artery grossly thickened (organising thrombi, inflammatory responses) | ||
| + | *Can be detected on rectal palpation | ||
| + | *Many cases asymptomatic | ||
| + | *May get embolism → infarction of areas of intestinal wall → colic or chronic ulceration (note: generally good collateral circulation; therefore colic is not inevitable) | ||
| + | *Aberrant larvae may cause thrombosis in other arteries; e.g. iliac, cerebral, coronary | ||
| + | *Avermectin/milbemycins or fenbendazole are used to control migrating ''S. vulgaris'' larvae | ||
| + | |||
===Small Animals=== | ===Small Animals=== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 41: | ||
[[Category:Intestine_-_Vascular_Disturbances]] | [[Category:Intestine_-_Vascular_Disturbances]] | ||
| − | [[Category:Intestinal Diseases - Dog]][[Category:Vascular Diseases - Dog]][[Category:Intestinal Diseases - Cat]] | + | [[Category:Intestinal Diseases - Dog]][[Category:Vascular Diseases - Dog]][[Category:Intestinal Diseases - Cat]][[Category:Vascular Diseases - Cat]] |
[[Category:To_Do_-_Clinical]] | [[Category:To_Do_-_Clinical]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Vascular Diseases - Horse]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Small Intestinal Diseases - Horse]] |
| + | [[Category:Cardiology Section]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:45, 15 October 2013
- Non-strangulation infarction.
- There is often a functional obstruction at point of infarction.
- Relatively rare as the bowel has a good anastomosing blood supply.
Horses
- E.g. Strongylus vulgaris larvae migrating in cranial mesenteric artery in horse
- Cause arteritis with thickening of wall
- Due to fibrin and debris deposition and hypersensitivity reaction
- Leads to vasoconstriction
- May occlude lumen and encourage thromboemboli.
- Can cause ischaemic necrosis of a segment of small intestine
- Is less common now that Strongylus vulgaris infections are declining.
- Cause arteritis with thickening of wall
- E.g. equine salmonellosis.
Verminous endarteritis
- Caused by larvae of S. vulgaris within the cranial mesenteric artery
- Also called "verminous aneurism" (misnomer as aneurism = dilatation/thinning of blood vessel wall; also, aneurisms are rare)
- Wall of artery grossly thickened (organising thrombi, inflammatory responses)
- Can be detected on rectal palpation
- Many cases asymptomatic
- May get embolism → infarction of areas of intestinal wall → colic or chronic ulceration (note: generally good collateral circulation; therefore colic is not inevitable)
- Aberrant larvae may cause thrombosis in other arteries; e.g. iliac, cerebral, coronary
- Avermectin/milbemycins or fenbendazole are used to control migrating S. vulgaris larvae
Small Animals
- Especially dogs
- Road traffic accidents produce and infact in the gut.
- Renal disease also causes infarction.
- Particularly nephrotic syndrome.
- Anticoagulant proteins are lost in the urine, leading to a prothrombic state in the ciruclation.
Pathology
- Similar to that caused by venous congestion.
- See sharply delineated dark areas in bowel that are flaccid with loss of tone.
- These become necrotic followed later by peritonitis.