Difference between revisions of "Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Image:LH_Lymph_Node_Gross_Histology.jpg|thumb|150px|right|<p>'''Gross view'''</p><sup>©Nottingham Uni 2008</sup>]] | [[Image:LH_Lymph_Node_Gross_Histology.jpg|thumb|150px|right|<p>'''Gross view'''</p><sup>©Nottingham Uni 2008</sup>]] | ||
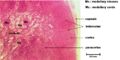
| − | <p>The body contains hundreds of lymph nodes of varying size and these are located along the routes of lymphatic vessels. Lymph nodes act as a filter for the lymph removing antigens and releasing immune-competent cells and immunoglobulins.</p> | + | <p>The body contains hundreds of lymph nodes of varying size (1-20mm) and these are located along the routes of lymphatic vessels. They are found throughout the body but are more concentrated in the axilla, groin and mesenteries. Lymph nodes act as a filter for the lymph removing antigens and releasing immune-competent cells and immunoglobulins.</p> |
==Development== | ==Development== | ||
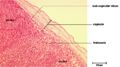
<p>Lymph nodes develop from lateral plate mesoderm in paired sacs from lymphatic vessels. These sacs undergo remodelling and endothelial and mesenchymal outgrowths form the meshwork of channels and spaces that produces the cortex-medulla structure. Lymphocytes then populate the cortex and medulla. The sub-capular sinus is a remainder of the lymphatic vessel.</p> | <p>Lymph nodes develop from lateral plate mesoderm in paired sacs from lymphatic vessels. These sacs undergo remodelling and endothelial and mesenchymal outgrowths form the meshwork of channels and spaces that produces the cortex-medulla structure. Lymphocytes then populate the cortex and medulla. The sub-capular sinus is a remainder of the lymphatic vessel.</p> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
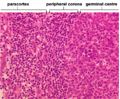
[[Image:LH_Lymph_Node_Follicles_Histology.jpg|thumb|150px|right|<p>'''Primary & secondary follicles'''</p><sup>©Nottingham Uni 2008</sup>]] | [[Image:LH_Lymph_Node_Follicles_Histology.jpg|thumb|150px|right|<p>'''Primary & secondary follicles'''</p><sup>©Nottingham Uni 2008</sup>]] | ||
[[Image:LH_Lymph_Node_Follicle_Histology.jpg|thumb|150px|right|<p>'''Secondary Follicle'''</p><sup>©RVC 2008</sup>]] | [[Image:LH_Lymph_Node_Follicle_Histology.jpg|thumb|150px|right|<p>'''Secondary Follicle'''</p><sup>©RVC 2008</sup>]] | ||
| − | <p>Grossly the lymph nodes | + | ===General=== |
| − | <p> The nodes are surrounded in a fibrous capsule that extends into the node as trabeculae. Below the capsule is the sub-capsular sinus. The nodes parenchyma contain a fine network of reticular fibres and cells | + | <p>Grossly the lymph nodes are round or bean shaped and have an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Microscopically the nodes have a follicles, paracortical zones and medullary cords and sinuses. At the hilum the medulla is present on the outer part of the node.</p> |
| − | <p>Lymph nodes have two types of follicles primary and secondary. Secondary follicles contain germinal centres (sites of B-cell proliferation) and have three layers. | + | ====Capsule and reticular framework==== |
| − | <p> High endothelial venules contain a large number of aquaporin-1 channels allowing for a | + | <p> The nodes are surrounded in a fibrous capsule that extends into the node as trabeculae, which provide an overall framework. Below the capsule is the sub-capsular sinus. The nodes parenchyma contain a fine network of reticular fibres and reticular cells. Reticular cells provide "scaffolding" for other cells as well as expressing surface complexes and substance to attract T,B and dendritic cells. |
| + | The cortex has aggregations of B cells (follicles) in its outer region and a paracortex consisting of a rim of T cells surrounding these follicles. Dendritic cells are also found in close association with the T cells. The medulla contains medullary cords of cells (B cells, plasma cells and some macrophages) and between these cords is the medullary sinus lined with endothelial cells and macrophages.</p> | ||
| + | ====Sinuses==== | ||
| + | <p>Three sinuses are present: | ||
| + | *Subcapsular/cortical | ||
| + | **Where afferent vessels drain | ||
| + | *Trabecular | ||
| + | **Drain lymph from subcapsular to medullary sinuses | ||
| + | *Medullary | ||
| + | Antigens and transformed cells that pass through the sinuses are filtered by macrophages and removed from the lymph.</p> | ||
| + | ====Follicles==== | ||
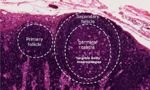
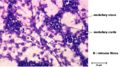
| + | <p>Lymph nodes have two types of follicles primary and secondary. Secondary follicles contain germinal centres (sites of B-cell proliferation) and have three layers. | ||
| + | *The central dark zone contains a high density of dividing centroblasts, B cells without surface Ig. These centroblasts migrate to the Basal light zone. | ||
| + | *In the basal light zone the B cells express surface Ig and become exposed to the follicular dendritic cells. | ||
| + | **Here there is a high rate of apoptosis but surviving cells migrate to the apical light zone. | ||
| + | *Apical light zone (mantle zone) which contains cells which are destined to become B memory (lymphoblasts) or plasma cells (plasmablasts). </p> | ||
| + | <p>Follicles in the cortex of a stimulated node are larger and have a pale germinal centre. Activated B cells differentiate into plasma and memory cells and plasma cells migrate migrate to the medullary cords and produce immunoglobulins.</p> | ||
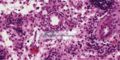
| + | ====High endothelial venules==== | ||
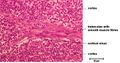
| + | <p> High endothelial venules (HEV)are composed of cuboidal/columnar epithelium and are the major route for lymphocytes to enter the node. HEV contain a large number of aquaporin-1 channels allowing for a large uptake of water which in turn drives lymph flow through the cortex, this fluid is returned direct to the bloodstream. The venules are the source of most of the nodes T and B cells and express selectins (receptors for lymphocytes primed with antigens).</p> | ||
===Pig Lymph Node=== | ===Pig Lymph Node=== | ||
<p> The structure of the pig lymph node is inverted compared with that of most mammals. | <p> The structure of the pig lymph node is inverted compared with that of most mammals. | ||
Revision as of 12:18, 21 July 2008
|
|
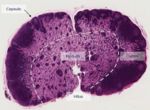
The body contains hundreds of lymph nodes of varying size (1-20mm) and these are located along the routes of lymphatic vessels. They are found throughout the body but are more concentrated in the axilla, groin and mesenteries. Lymph nodes act as a filter for the lymph removing antigens and releasing immune-competent cells and immunoglobulins.
Development
Lymph nodes develop from lateral plate mesoderm in paired sacs from lymphatic vessels. These sacs undergo remodelling and endothelial and mesenchymal outgrowths form the meshwork of channels and spaces that produces the cortex-medulla structure. Lymphocytes then populate the cortex and medulla. The sub-capular sinus is a remainder of the lymphatic vessel.
Structure
General
Grossly the lymph nodes are round or bean shaped and have an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Microscopically the nodes have a follicles, paracortical zones and medullary cords and sinuses. At the hilum the medulla is present on the outer part of the node.
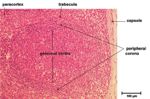
Capsule and reticular framework
The nodes are surrounded in a fibrous capsule that extends into the node as trabeculae, which provide an overall framework. Below the capsule is the sub-capsular sinus. The nodes parenchyma contain a fine network of reticular fibres and reticular cells. Reticular cells provide "scaffolding" for other cells as well as expressing surface complexes and substance to attract T,B and dendritic cells. The cortex has aggregations of B cells (follicles) in its outer region and a paracortex consisting of a rim of T cells surrounding these follicles. Dendritic cells are also found in close association with the T cells. The medulla contains medullary cords of cells (B cells, plasma cells and some macrophages) and between these cords is the medullary sinus lined with endothelial cells and macrophages.
Sinuses
Three sinuses are present:
- Subcapsular/cortical
- Where afferent vessels drain
- Trabecular
- Drain lymph from subcapsular to medullary sinuses
- Medullary
Antigens and transformed cells that pass through the sinuses are filtered by macrophages and removed from the lymph.
Follicles
Lymph nodes have two types of follicles primary and secondary. Secondary follicles contain germinal centres (sites of B-cell proliferation) and have three layers.
- The central dark zone contains a high density of dividing centroblasts, B cells without surface Ig. These centroblasts migrate to the Basal light zone.
- In the basal light zone the B cells express surface Ig and become exposed to the follicular dendritic cells.
- Here there is a high rate of apoptosis but surviving cells migrate to the apical light zone.
- Apical light zone (mantle zone) which contains cells which are destined to become B memory (lymphoblasts) or plasma cells (plasmablasts).
Follicles in the cortex of a stimulated node are larger and have a pale germinal centre. Activated B cells differentiate into plasma and memory cells and plasma cells migrate migrate to the medullary cords and produce immunoglobulins.
High endothelial venules
High endothelial venules (HEV)are composed of cuboidal/columnar epithelium and are the major route for lymphocytes to enter the node. HEV contain a large number of aquaporin-1 channels allowing for a large uptake of water which in turn drives lymph flow through the cortex, this fluid is returned direct to the bloodstream. The venules are the source of most of the nodes T and B cells and express selectins (receptors for lymphocytes primed with antigens).
Pig Lymph Node
The structure of the pig lymph node is inverted compared with that of most mammals.
- Most follicles are found deep in the paracortex
- The paracortex is surrounded by loose medullary tissue
- Afferent lymphatics enter at the hilus
- Connect with para-trabecular sinuses and exit from efferent lymphatics on the node surface.
- Blood vessels enter and leave at the hilus
Histology
- Images will be re-arranged
Functions
As the spleen removes antigens from the blood, lymph nodes remove antigens from tissue. Antigen presenting cells (B and T cells) migrate from peripheral tissue via afferent lymphatic vessels to the lymph nodes where they present their antigen to lymphocytes. B cells and T cells enter via the high endothelial venules by diapedesis and B cells migrate to the cortex while T cells to the deep cortex.
Antibodies and immunologically competent cells leave the lymph nodes via the efferent lymphatics.
In pathology
Lymph node pathology can be found here