Difference between revisions of "Lymphoma"
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
Hayes A. (2006) Feline lymphoma 1. Principles of diagnosis and management, In Practice, 28, pp 516-524 | Hayes A. (2006) Feline lymphoma 1. Principles of diagnosis and management, In Practice, 28, pp 516-524 | ||
| + | |||
Head K. W, Else R. W, Dubielzig R.R, (2002) Tumours of the Alimentary Tract, in Tumours in Domestic Animals, 4th edition, Ed Menten D. J, Iowa State Press, Blackwell Publishing, Iowa, pp 471-472 | Head K. W, Else R. W, Dubielzig R.R, (2002) Tumours of the Alimentary Tract, in Tumours in Domestic Animals, 4th edition, Ed Menten D. J, Iowa State Press, Blackwell Publishing, Iowa, pp 471-472 | ||
| + | |||
Morris J, Dobson J (2001) Gastrointestinal Tract, in Small Animal Oncology, Blackwell Science, pp 228-239 | Morris J, Dobson J (2001) Gastrointestinal Tract, in Small Animal Oncology, Blackwell Science, pp 228-239 | ||
| + | |||
Selting K. A, (2007), Intestinal Tumours, Cancer of the Gastrointestinal Tract, in Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, fourth edition, Eds Withrow S.J, Vail D.M, Missouri, Saunders Elsevier, pp 491-501 | Selting K. A, (2007), Intestinal Tumours, Cancer of the Gastrointestinal Tract, in Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, fourth edition, Eds Withrow S.J, Vail D.M, Missouri, Saunders Elsevier, pp 491-501 | ||
| + | |||
White, R. A. S, (2003), Tumours of the intestines, in BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Oncology, second edition, Eds Dobson J. M, Lascelles B. D. X, Gloucester, British Small Animal Veterinary Association, pp 229-233 | White, R. A. S, (2003), Tumours of the intestines, in BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Oncology, second edition, Eds Dobson J. M, Lascelles B. D. X, Gloucester, British Small Animal Veterinary Association, pp 229-233 | ||
Revision as of 17:57, 16 August 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
Description
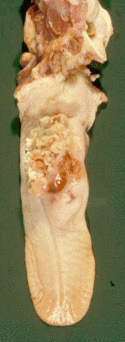
- Localised lymphoma: can be intramural or extend intraluminally. The lesion may be focal or multifocal. The tumour can be of a variety of shapes namely nodular, plaque-like or circumferential. Circumferential transmural or intramural tumours often bulge outward since the diseased muscle atrophies so that rows of lymphocytes remain supported by parallel bands of reticulum fibers only. The circumferential intramural form is the most frequently seen in the feline intestine.
- Diffuse lymphoma: with these tumours there is a granular or cobblestone appearance to the mucosa. The mesenteric lymph nodes are often affected.
- In cats the most frequent sites are the jejunum, ileocaecocolic junction, duodenum, colon and stomach (in decreasing order of frequency).
- In dogs focal lesions most frequently occur in the small intestine. Multifocal tumours are rarer and affect various sites.
- At the time of diagnosis in cats tumour nodules are often already apparent in the liver, kidney, spleen and abdominal and sternal lymph nodes. Differentiating AL and multicentric lymphoma may be difficult at this point.
- In most cats AL is not associated with FeLV and aetiololgy is idiopathic.
Signalment
Affected cats are usually over 5 years old and oriental breeds may be predisposed.
Affected dogs have a wide age range, most are middle-aged however young animals can be affected. There may be a male predilection.
Gastric
- Diffuse infiltration of lymphocytes.
- Seen primarlity in dogs and cattle, but also in the pig and cat.
Intestinal
- Lymphoma occurs in both the small and large intestines.
- Is a relatively common neoplasm of the cat and dog.
- Causes a diffuse spread of neoplastic lymphocytes through the mucosa and the rest of the wall.
- Leads to malabsorption and therefore diarrhoea and the development of a protein losing enteropathy.
Alimentary Lymphoma
Intestinal tumours are uncommon accounting for less than 10% of all tumours in dogs and cats and 22% of gastrointestinal tumours in dogs and 35% in cats. Intestinal tumours in dogs and cats are usually malignant, alimentary lymphoma (AL) being the most common type of intestinal malignancy in cats and the second most frequent malignancy to affect the intestine in dogs. Primary AL may be differentiated from widespread multicentric lymphoma by the fact that the lymph nodes are not affected with AL. AL must also be distinguished from localised lymphoma that affects the mesenteric lymph node only with no intestinal involvement, which should be classified in the miscellaneous lymphoma group.
Diagnosis
Clinical Signs
The following may be seen:
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Weight loss
- Anorexia
- Tenesmus
- Dyschezia
- (Peritonitis - following complete intestinal obstruction and rupture)
Physical Examination
- An abdominal mass may be palpable
- Bowel loops may feel thickened
- Enlarged mesenteric lymph nodes may be palpable
Haematology and Biochemistry
Haematological analysis should always be performed with suspected lymphoma for staging purposes and for the recording of base-line parameters prior to the initiation of any treatment to assess the severity of any future myelosuppression. Potential abnormalities include:
- For those with bone marrow involvement:
- Lymphocytosis
- Thrombocytopenia
- Neutropenia
- Presence of immature lymphoid precursors
- Affected cats are not usually leukemic
- Hypoproteinaemia
- Elevated hepatic enzymes
- Elevated BUN/creatinine
FeLV/FIV
All cats with suspected lymphoma should be tested for FeLV and FIV, usually performed via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) available in general practice in kit form (CITE test). Virus isolation would be required for a definitive result, however this is not only more time-consuming but is more expensive. An ELISA is also frequently used for the diagnosis of FIV.
Paraneoplastic Syndromes
- Dogs may present with hypercalcaemia, affected cats are not usually hypercalcaemic
- (Hypergammaglobulinaemia)
Radiography
A mass may be visible via plain or contrast abdominal radiography. Both abdominal and thoracic imaging is required in assessing the surrounding structures.
Ultrasonography
Superior to radiography in assessing infiltration or abnormalities of tissue architecture and assessing the surrounding structures for metastasis. Guided aspirates or biopsies may also be taken at this time, including lymph node sampling, to evaluate degree of systemic involvement.
Bone Marrow Aspirate/Biopsy
Should be taken ideally for all cases as part of the staging procedure.
Staging
A group staging system is used for lymphoma(Owen, 1980):
- Stage I - Involvement limited to a single node or lymphoid tissue in a single organ (excluding bone marrow)
- Stage II - Involvement of many lymph nodes in a regional area (+/- tonsils)
- Stage III - Generalised lymph node involvement
- Stage IV - Liver and/or spleen involvement (+ stage III)
- Stage V - Manifestations in the blood and involvement of bone marrow and/or other organ systems (+/-stages I-IV)
Each stage is then subclassifed as a) without systemic signs or b) with systemic signs.
Treatment
Surgery
Firstly, celiotomy is required for many cases of AL to obtain biopsy material. For solitary masses without systemic disease resection and anastomosis of the intestine is advised (single modality treatment). Local resection in cats has occasionally been curative. However, surgery alone may be insufficient for long-term control of the disease and if not all the tumour is able to be resected, or should relapse occur, or if there is systemic progression, chemotherapy will be required(multimodal treatment).
Radiotherapy
Lymphoma is highly radiosensitive and in theory should be efficient in treating all forms of lymphoma, however, surrounding tissues often have a low tolerance.
Chemotherapy
- Combination chemotherapy is the most frequent method of treatment
- Commonly used protocols include:
- COP - Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine, Prednisolone. Frequently used in cats and can be used for induction therapy (8weeks) as well as a long term maintenance protocol
- COAP - Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine, Prednisolone, Cytosine arabinoside
- CHOP - Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine, Prednisolone, Doxorubicin, (potentiated sulphonamides)
- Corticosteroids must not be administered prior to initiation of chemotherapy as they can cause resistance to cytotoxics and hence reduce the rate of response and the survival time.
- The aim is to induce remission and then continue with a maintenance regime, adjusting the dose as required with rescue therapy should relapse occur.
- Response to treatment can be monitored via reduction in tumour mass and size of lymph nodes.
- Haematological values should be frequently monitored to assess degree of effects of drugs.
Supportive Therapy
For those receiving chemotherapy:
- High quality, palatable diet
- Appetite stimulation in cats e.g Cyproheptadine (Periactin)
- Antiemetics
- Assisted (tube) feeding
- Fluid therapy
- Laxatives
- Analgesia
- Treatment for and monitoring of:
- Azotaemia
- Neutropenia/sepsis
- Hypercalcaemia
- Pyrexia
Prognosis
- Mean survival times for dogs and cats:
- Without therapy: 6-8 weeks.
- For those receiving cortocosteroids only: 3 months.
- For those receiving chemotherapy: 6-9 months.
- Local canine lymphoma responds better to chemotherapy than the diffuse form of disease.
- Immunophenotype (T cell versus B cell lymphoma)does not appear to be associated with prognosis in cats as it can be in dogs. Factors indicating a better prognosis (overall survival) in cats include:
- Early presentation
- A complete initial response to treatment
- A clinically well patient(‘substage a’ disease)
- Whether doxorubicin is included in the treatment protocol may also affect prognosis
- In cats, response rate to induction chemotherapy is 26-79%
- Thus there is an apparently a poorer response rate in cats compared with dogs, however, 30-40% of cats that do have complete remission will maintain complete remission for two years or more and long-term maintenance chemotherapy can frequently be stopped and many will then live free of disease. Hence, dogs may have higher remission rates but are less likely than cats to be able to maintain remission without chemotherapy.
References
Hayes A. (2006) Feline lymphoma 1. Principles of diagnosis and management, In Practice, 28, pp 516-524
Head K. W, Else R. W, Dubielzig R.R, (2002) Tumours of the Alimentary Tract, in Tumours in Domestic Animals, 4th edition, Ed Menten D. J, Iowa State Press, Blackwell Publishing, Iowa, pp 471-472
Morris J, Dobson J (2001) Gastrointestinal Tract, in Small Animal Oncology, Blackwell Science, pp 228-239
Selting K. A, (2007), Intestinal Tumours, Cancer of the Gastrointestinal Tract, in Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, fourth edition, Eds Withrow S.J, Vail D.M, Missouri, Saunders Elsevier, pp 491-501
White, R. A. S, (2003), Tumours of the intestines, in BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Oncology, second edition, Eds Dobson J. M, Lascelles B. D. X, Gloucester, British Small Animal Veterinary Association, pp 229-233