Difference between revisions of "Rhinitis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(New page: {{toplink |backcolour = D1EEEE |linkpage =Cardiorespiratory System - Pathology |linktext =Cardiorespiratory System |maplink = Cardiorespiratory System (Content Map) - Pathology |pagetype ...) |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
}} | }} | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | '''For an overview of respiratory infections see [[Respiratory System Inflammation - Pathology]]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ='''Rhinitis'''= | ||
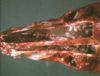
| + | [[Image:Mucoid rhinitis.jpg|right|thumb|100px|<small><center>Mucoid rhinitis (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Acute or chronic | ||
| + | *Aetiology | ||
| + | **Infectious | ||
| + | **Allergic | ||
| + | **Toxic | ||
| + | **Traumatic e.g. foreign bodies | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Serous cells usually first to respond to a noxious agent, releasing secretions into the mucocilliary blanket | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Serous rhinitis''' - typical mild 'runny nose' | ||
| + | **Loss of cilia and hydropic degeneration of epithelial cells | ||
| + | **Epithelium becomes susceptible to secondary bacterial infections, including overgrowth of resident nasopharyngeal flora | ||
| + | **Goblet cells become stimulated, changing the secretions into a thick opaque mucus -> | ||
| + | *'''Catarrhal rhinitis''' | ||
| + | **Contains mucus, emigrating leukocytes and few sloughed epithelial cells | ||
| + | *'''Mucopurulent''' and then '''purulent rhinitis''' | ||
| + | **When secondary bacterial infection is severe, migrating neutrophils pour into the exudate | ||
| + | **More severe damage to the nasal mucosa causes vascular permeability and seepage of large molecular weight proteins, including fibrinogen, into the exudate -> | ||
| + | *'''Fibrinopurulent''' and '''fibrinous rhinitis''' | ||
| + | *'''Fibronecrotic''' and '''ulcerative rhinitis''' are manifestations of very severe damage to the nasal mucosa | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ='''Chronic rhinitis'''= | ||
| + | *Happens when acute rhinitis fails to resolve - common | ||
| + | *Typically catarrhal or purulent | ||
| + | *In chronic purulent rhinitis | ||
| + | **Extensive fibrosis of the lamina propria | ||
| + | **Atrophy of nasal glands | ||
| + | **Squamous cell [[General Pathology - Disorders of Cell Growth#Metaplasia|metaplasia]] | ||
| + | *-> Impaired local defences | ||
| + | *Superficial fibrinous membrane can be peeled of without leaving dmaged tissue underneath | ||
| + | *Deeper fibronecrotic lesions associated with [[Fusobacterium|''Fusobacterium necrophorum'']] - yellowish fibronecrotic membrane, when removed, leaves ulcerated surface | ||
| + | *May manifest as [[Nasal cavity - hyperplastic and neoplastic#Nasal polyps|nasal polyps]], [[Nasal cavity - hyperplastic and neoplastic#Progressive ethmoidal haematoma|progressive haematoma]] in horses and [[Nasopharynx Hyperplastic and Neoplastic - Pathology#Nasopharyngeal polyp of cats|nasopharyngeal polyp]] of cats | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ='''Allergic rhinitis'''= | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Occurs in dogs, cats and horses, may occur seasonally in cattle, especially Channel Island breeds | ||
| + | *Similar inflammatory changes as above | ||
| + | *Due to hypersensitivity to inhaled allergens | ||
| + | *Eosinophils tend to be the dominant infiltrating leukocytes | ||
| + | *Grossly: | ||
| + | **Pale, thick, oedematous nasal mucosa | ||
| + | *Histologically: | ||
| + | **Hyperplastic, eroded nasal epithelium, eosinophil infiltrate | ||
| + | |||
| + | *If chronic -> '''Nasal granuloma''' | ||
| + | **Extends caudally, even to larynx and proximal trachea | ||
| + | **Grossly: | ||
| + | ***Granular hyperplastic epithelium with multiple nodules covered by normal epithelium | ||
| + | **Hisologically: | ||
| + | ***Centre of [[General Pathology - Chronic Inflammation#Granulation tissue|granulation tissue]] surrounded by oedematous lamina propria covered by hyperplastic epithelium | ||
| + | ***Goblet cell hyperplasia | ||
| + | ***Eosinophil infiltration | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <big>[[Paranasal Sinuses Inflammatory - Pathology#Sinusitis|'''Sinusitis''']] '''is a common sequel to rhinitis'''</big> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ='''Infectious causes of rhinitis'''= | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| cellpadding="10" cellspacing="0" border="1" | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology|'''VIRAL''']] | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Bacterial Infections - Pathology|'''BACTERIAL''']] | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Fungal Infections - Pathology|'''FUNGAL''']] | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Parasitic Infections - Pathology|'''PARASITIC''']] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Dogs''' | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Canine distemper|Canine distemper]] | ||
| + | | secondary | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Fungal Infections - Pathology#In Dogs|''A. fumigatus'']] | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Parasitic Infections - Pathology#In Dogs|''Linguatula serrata]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Parainfluenza- 2|Parainfluenza- 2]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Fungal Infections - Pathology#In Dogs|''C. neoformans'']] | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Parasitic Infections - Pathology#Capillaria aerophila|''Capillaria aerophila'']] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Canine herpes virus|Canine herpes virus]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Cats''' | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Feline viral rhinotracheitis|Feline viral rhinotracheitis]] | ||
| + | | secondary | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Fungal Infections - Pathology#In Cats|''Cryptococcus neoformans'']] | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Parasitic Infections - Pathology#In Cats|''Linguatula serrata]] sometimes | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Feline calicivirus|Feline calicivirus]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Fungal Infections - Pathology#In Cats|''Aspergillus fumigatus'']] | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Parasitic Infections - Pathology#Capillaria aerophila|''Capillaria aerophila'']] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Horses''' | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Equine rhinovirus|Equine rhinovirus]] | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Bacterial Infections - Pathology#Strangles|Strangles]] | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Fungal Infections - Pathology#In Horses|''Aspergillus'' spp.]] | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Parasitic Infections - Pathology#In Horses|''Parascaris equorum'']] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Equine influenza|Equine influenza]] | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Bacterial Infections - Pathology#Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus|''Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus'']] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Equine rhinopneumonitis|Equine rhinopneumonitis]] | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Bacterial Infections - Pathology#Glanders|Glanders]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Equine viral arteritis (EVA)|Equine viral arteritis]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Cattle''' | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis (IBR)|Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis]] | ||
| + | | secondary | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Parainfluenza- 3|Parainfluenza- 3]] | ||
| + | | subclinical [[Respiratory Bacterial Infections - Pathology#CAR bacillus|''CAR bacillus'']] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Bovine adenovirus|Bovine adenovirus]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Sheep''' | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Parainfluenza- 3|Parainfluenza- 3]] | ||
| + | | subclinical [[Respiratory Bacterial Infections - Pathology#CAR bacillus|''CAR bacillus'']] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Parasitic Infections - Pathology#Oestrus ovis|''Oestrus ovis'' larvae]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Pigs''' | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Inclusion body rhinitis|Inclusion body rhinitis]] | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Bacterial Infections - Pathology#Atrophic Rhinitis|Atrophic rhinitis]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Swine influenza|Swine influenza]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''For an overview of respiratory infections see [[Respiratory System Inflammation - Pathology]]''' | ||
Revision as of 21:33, 4 August 2008
|
|
For an overview of respiratory infections see Respiratory System Inflammation - Pathology
Rhinitis
- Acute or chronic
- Aetiology
- Infectious
- Allergic
- Toxic
- Traumatic e.g. foreign bodies
- Serous cells usually first to respond to a noxious agent, releasing secretions into the mucocilliary blanket
- Serous rhinitis - typical mild 'runny nose'
- Loss of cilia and hydropic degeneration of epithelial cells
- Epithelium becomes susceptible to secondary bacterial infections, including overgrowth of resident nasopharyngeal flora
- Goblet cells become stimulated, changing the secretions into a thick opaque mucus ->
- Catarrhal rhinitis
- Contains mucus, emigrating leukocytes and few sloughed epithelial cells
- Mucopurulent and then purulent rhinitis
- When secondary bacterial infection is severe, migrating neutrophils pour into the exudate
- More severe damage to the nasal mucosa causes vascular permeability and seepage of large molecular weight proteins, including fibrinogen, into the exudate ->
- Fibrinopurulent and fibrinous rhinitis
- Fibronecrotic and ulcerative rhinitis are manifestations of very severe damage to the nasal mucosa
Chronic rhinitis
- Happens when acute rhinitis fails to resolve - common
- Typically catarrhal or purulent
- In chronic purulent rhinitis
- Extensive fibrosis of the lamina propria
- Atrophy of nasal glands
- Squamous cell metaplasia
- -> Impaired local defences
- Superficial fibrinous membrane can be peeled of without leaving dmaged tissue underneath
- Deeper fibronecrotic lesions associated with Fusobacterium necrophorum - yellowish fibronecrotic membrane, when removed, leaves ulcerated surface
- May manifest as nasal polyps, progressive haematoma in horses and nasopharyngeal polyp of cats
Allergic rhinitis
- Occurs in dogs, cats and horses, may occur seasonally in cattle, especially Channel Island breeds
- Similar inflammatory changes as above
- Due to hypersensitivity to inhaled allergens
- Eosinophils tend to be the dominant infiltrating leukocytes
- Grossly:
- Pale, thick, oedematous nasal mucosa
- Histologically:
- Hyperplastic, eroded nasal epithelium, eosinophil infiltrate
- If chronic -> Nasal granuloma
- Extends caudally, even to larynx and proximal trachea
- Grossly:
- Granular hyperplastic epithelium with multiple nodules covered by normal epithelium
- Hisologically:
- Centre of granulation tissue surrounded by oedematous lamina propria covered by hyperplastic epithelium
- Goblet cell hyperplasia
- Eosinophil infiltration
Sinusitis is a common sequel to rhinitis
Infectious causes of rhinitis
| . | VIRAL | BACTERIAL | FUNGAL | PARASITIC |
| Dogs | Canine distemper | secondary | A. fumigatus | Linguatula serrata |
| . | Parainfluenza- 2 | . | C. neoformans | Capillaria aerophila |
| . | Canine herpes virus | . | . | . |
| Cats | Feline viral rhinotracheitis | secondary | Cryptococcus neoformans | Linguatula serrata sometimes |
| . | Feline calicivirus | . | Aspergillus fumigatus | Capillaria aerophila |
| Horses | Equine rhinovirus | Strangles | Aspergillus spp. | Parascaris equorum |
| . | Equine influenza | Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus | . | . |
| . | Equine rhinopneumonitis | Glanders | . | . |
| . | Equine viral arteritis | . | . | . |
| Cattle | Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis | secondary | . | . |
| . | Parainfluenza- 3 | subclinical CAR bacillus | . | . |
| . | Bovine adenovirus | . | . | . |
| Sheep | Parainfluenza- 3 | subclinical CAR bacillus | . | Oestrus ovis larvae |
| Pigs | Inclusion body rhinitis | Atrophic rhinitis | . | . |
| . | Swine influenza | . | . | . |
For an overview of respiratory infections see Respiratory System Inflammation - Pathology