Difference between revisions of "Sarcoptes"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{review}} | {{review}} | ||
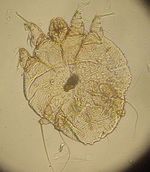
| − | [[Image:Sarcoptes scabei.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcoptes scabei'' - | + | [[Image:Sarcoptes scabei.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcoptes scabei'' - Kalumet 2004,Wikimedia Commons]] |
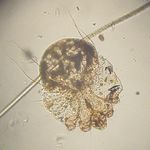
[[Image:Sarcoptes scabei 2.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcoptes scabei'' - Joel Mills 2006,Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Sarcoptes scabei 2.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcoptes scabei'' - Joel Mills 2006,Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
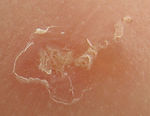
[[Image:Scabies human skin pruritus.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Scabies on human skin resulting in pruritus - Geary 2006,Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Scabies human skin pruritus.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Scabies on human skin resulting in pruritus - Geary 2006,Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
Revision as of 13:23, 20 July 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Sarcoptes mites are burrowing mites of dogs and foxes. They Cause Sarcoptic Mange. The mites prefer hairless skin and so begin on the hocks, elbows and pinnae. The mites are usually spread by direct host to host contact.
Identification
Sarcoptes mites are small, round mites. They have short legs that project only a short distance from the body margin. They have dorsal spines arranged in rows and a terminal anus. The male mites are about 250μm in length and the females are about 400-430μm in length.
Life cycle
Sarcoptes mites have a 3 week life cycle. The female lays eggs in the epidermis in an egg laying pocket. The female feeds on liquid oozing from damaged tissue. The eggs then hatch in 1 week and 6 legged larvae are released. They crawl to skin surface and then burrow back into the epidermis into moulting pockets. The larvae moult to become 8 legged nymphs. The nymphs moult twice before becoming adults. Adult males then emerge and look for females to mate.
Diagnosis
Mite infection can be diagnosed with a skin scrape of a 'non-scratched' region. The presence of one Sarcoptes mite is diagnostic.