Difference between revisions of "Sarcoptic Mange"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
'''[[Sarcoptic Mange - Pig|In Pigs]]''' | '''[[Sarcoptic Mange - Pig|In Pigs]]''' | ||
| − | + | '''[[Sarcoptic Mange - Cattle|In Cattle]]''' | |
| − | '''Cattle''' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 22:33, 30 March 2010
Transmission
- Close contact
- Adults and larvae can be transferred from one skin surface to another
Pathogenesis
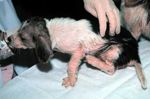
- Erythema with papule formation
- Scale and crust formation
- Alopecia
- Intense pruritus for 1 week
- Self-inflicted trauma
- Scab formation
- Wrinkling and thickening of skin
- Hypersensitivity may develop
- Rash develops
Sarcoptes scabiei
- Causes scabies
- Strains of S. scabiei can be passed between different animals and cause clinical signs although the infection is likely to resolve spontaneously and be unlikely to establish
Diagnosis
- Skin scraping until capillary blood appears
- Adults, eggs, immature mites and faecal pellets can be seen microscopically
- Place material on a microscope slide
- Add 10% KOH
- Warm slide over bunsen flame
Treatment
- Acaricide
- For more information on acaricides click here
- Treat both infected and in-contact animals
- Older products have to be given in repeat treatments
- Avermectins are effective in farm animals
- Selamectin is available as a good spot-on for dogs
Sheep
- Notifiable in UK
- Lesions on hairy parts of face
- E.g. Face, ears, axillae and groin
- Causes considerable hide damage in local African breeds of long haired sheep
Horses
- Notifiable in UK
- Lesions begin on head, neck and shoulders then spread to rest of body