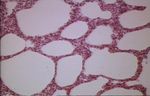
Interstitial Pneumonia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
- Lung inflammation that occurs primarily in alveolar walls rather than in alveolar spaces
- Can be widely distributed but is often most severe in caudal lung lobes
- Diffuse or patchy damage to alveolar septa, may be acute or chronic
- Lesions in most cases result from blood-borne insult and are more likely to involve the dorsocaudal regions, although the damage is often diffuse
- No concentrated inflammatory response in the airway, only secondary to damage of alveolar walls
- As part of systemic infection
- Canine distemper (in alveolar macrophages as inclusions)
- Salmonellosis
- Toxoplasmosis (in alveolar wall)
- Acute interstitial pneumonia is characterised by exudation into the alveolar lumen and in cattle is associated with interstitial emphysema
Examples: