Difference between revisions of "Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology"
| (19 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| Line 7: | Line 6: | ||
==Structure and Function== | ==Structure and Function== | ||
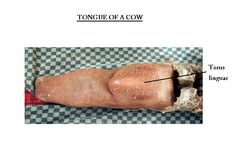
| − | The | + | The tounge is skeletal muscle dorsally. There is structural fat surrounded by a cartilagenous sheath forming lyssa (canids only) ventrally. There is an attached root and body with a free apex. The '''frenulum''' (fold of mucosa) attaches the body of the tongue to the floor of the [[Oral Cavity Overview - Anatomy & Physiology|oral cavity]]. The root of tongue is attached to the [[Hyoid Apparatus - Anatomy & Physiology|hyoid bone]]. In the horse and dog, the tongue is 'u' shaped, becoming broader towards the tip. The furrow in the centre of the canid tongue is called the '''median sulcus'''. In the ox, sheep and pig the tongue is 'v' shaped with a pointed apex. The '''torus linguae''' is a swelling across the tongue laterally which pushes food against the [[Hard Palate|hard palate]]. |
[[Image:Tongue Anatomy Cow2.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Tongue Anatomy (Cow) - Copyright Nottingham 2008]] | [[Image:Tongue Anatomy Cow2.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Tongue Anatomy (Cow) - Copyright Nottingham 2008]] | ||
==Muscles== | ==Muscles== | ||
| − | |||
===Intrinsic Muscles=== | ===Intrinsic Muscles=== | ||
| − | Intrinsic muscles include the dorsal and ventral longitudinal muscles and the transverse and vertical bundles. | + | Intrinsic muscles include; the dorsal and ventral longitudinal muscles and the transverse and vertical bundles. |
===Extrinsic Muscles=== | ===Extrinsic Muscles=== | ||
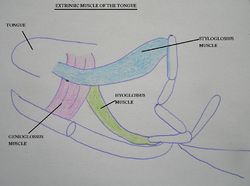
| − | The extrinsic muscles include | + | The extrinsic muscles include; |
'''Styloglossus''' | '''Styloglossus''' | ||
| − | + | The origin is the [[Hyoid Apparatus - Anatomy & Physiology|hyoid apparatus]] (stylohyoid). It retracts and elevates the tongue. | |
| + | [[Image:Tongue Venous Drainage.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Venous Drainage of the Tongue - Copyright Prof. Pat Mccarthy]] | ||
'''Genioglossus''' | '''Genioglossus''' | ||
| − | The origin is | + | The origin is the incisive part of the [[Skull and Facial Muscles - Anatomy & Physiology#Mandible (mandibula)|mandible]]. It protrudes and depressed the tongue. |
'''Hyoglossus''' | '''Hyoglossus''' | ||
| − | The origin is | + | The origin is the [[Hyoid Apparatus - Anatomy & Physiology|hyoid apparatus]] (basihyoid). It retracts and depresses the tongue. |
'''Geniohyoideus''' | '''Geniohyoideus''' | ||
| − | + | The origin is the incisive part of the [[Skull and Facial Muscles - Anatomy & Physiology#Mandible (mandibula)|mandible]] and the insertion site is the body of the [[Hyoid Apparatus - Anatomy & Physiology|hyoid]]. It lies below the tongue (not within it) and draws the [[Hyoid Apparatus - Anatomy & Physiology|hyoid]], and therefore the tongue forward. | |
[[Image:Tongue Muscles Drawing.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Drawing of the Extrinsic Muscles of the Tongue - Copyright nabrown]] | [[Image:Tongue Muscles Drawing.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Drawing of the Extrinsic Muscles of the Tongue - Copyright nabrown]] | ||
| Line 41: | Line 40: | ||
==Innervation== | ==Innervation== | ||
| − | All muscles moving the tongue are innervated by the hypoglossal nerve ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN XII]]). The rostral 2/3 of the tongue is innervated by the | + | All muscles moving the tongue are innervated by the hypoglossal nerve ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN XII]]). The rostral 2/3 of the tongue is innervated by the lingual branch of the trigeminal ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN V]]) which is sensory supplying temperature, touch and pain. The chorda tympani of the facial ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN VII]]) supplies the taste. The caudal 1/3 of the tongue is innervated by the glossopharyngeal ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN IX]]) providing motor function for taste. |
==Vasculature== | ==Vasculature== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 48: | ||
[[Image:Tongue Histology Cat.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Tongue Histology (Cat) - Copyright RVC 2008]] | [[Image:Tongue Histology Cat.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Tongue Histology (Cat) - Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
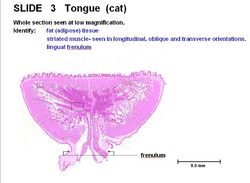
| − | The | + | The tounge consists of stratified squamous epithelium. There are [[Lingual Gland - Anatomy & Physiology|lingual]] glands and a mucosal covering tightly adheres to the contact surface. The degree of keratinisation depends on the diet. There is less keratinisation on the ventral surface and sides of tongue. It is covered by papillae (taste buds)for protection and taste. Papillae are specialised projections of the mucosa. Some papillae have taste buds, others are mechanical to roughen the surface of the tongue. |
==Types of Papillae== | ==Types of Papillae== | ||
| Line 59: | Line 58: | ||
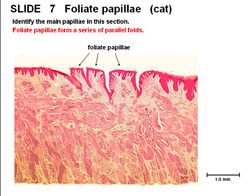
===Foliate=== | ===Foliate=== | ||
| − | + | 8 to 12 papillae in parallel folds, one either side of the tongue midline. Consists of a stratified squamous epithelium, present in the caudal 1/3 of the tongue. There are taste buds, glands and lymphatics present. | |
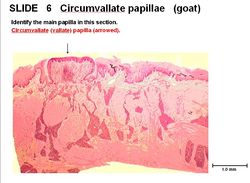
===Vallate=== | ===Vallate=== | ||
[[Image:Circumvallate Papillae.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Circumvallate Papillae (Goat) - Copyright RVC 2008]] | [[Image:Circumvallate Papillae.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Circumvallate Papillae (Goat) - Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
| − | There are | + | There are 3 to 6, often secondary papillae in taste buds. There are broad glands in the caudal 1/3 of tongue. Taste buds and lymphatics are present. |
===Fungiform=== | ===Fungiform=== | ||
| − | + | Red dots on tongue surface. Consists of keratinised, stratified squamous epithelium and blood vessels. Involved in loss of heat via panting in dogs. Present in the rostral 2/3 of the tongue, taste buds are present. | |
[[Image:Filoform Papillae Histology.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Filoform Papillae Histology (Cat) - Copyright RVC 2008]] | [[Image:Filoform Papillae Histology.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Filoform Papillae Histology (Cat) - Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
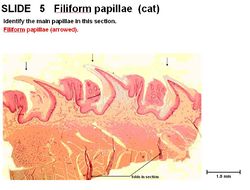
===Filiform=== | ===Filiform=== | ||
| − | + | The most numerous. They point caudally. There are no taste buds, glands or lymphatics. They are the smallest and consist of a thick keratin on stratified squamous epithelium. They are very prominent in cat and are present in the rostral 2/3 of the tongue. | |
==[[Gustatory System - Anatomy & Physiology|Taste Buds]]== | ==[[Gustatory System - Anatomy & Physiology|Taste Buds]]== | ||
| − | Also found on the [[Soft Palate|soft palate]] and | + | *Also found on the [[Soft Palate|soft palate]] and [[Pharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|pharynx]] (but sparsely distributed) |
| + | |||
| + | *Constant cell turnover | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Flat, thick cells | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Taste hairs (microvilli) pointing though taste pore | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Nerves transduce chemical signals into nervous signals | ||
==Species Differences== | ==Species Differences== | ||
| − | [[Image:Pig Tongue.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:Pig Tongue.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Pig Tongue'' <br> Pollo 2007, WikiMedia Commons]] |
===Canine=== | ===Canine=== | ||
| − | + | *Stretch receptors in the tongue | |
| + | |||
| + | *Uses the tongue to lose heat by panting | ||
===Ruminant=== | ===Ruminant=== | ||
| − | + | *Tongue is heavily keratinised with long papillae for eating (protective surface) | |
| + | |||
| + | *Ox has lenticular papillae which are hard and horny due to heavy keratinisation | ||
===Feline=== | ===Feline=== | ||
| − | + | *Long papillae for grooming so tongue is rough | |
===Porcine=== | ===Porcine=== | ||
| − | Most of the papillae are soft, long and directed caudally | + | *Most of the papillae are soft, long and directed caudally |
===[[Avian Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|Avian]] === | ===[[Avian Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|Avian]] === | ||
| − | + | *There is a bone present | |
| + | |||
| + | *It is mainly used for manipulation of food rather than vocalisation like in mammals | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Parrots use the tongue to produce human sounds (see [[Syrinx - Anatomy & Physiology#Species differences|here]]) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Test yourself with the Tongue & Facial Muscle Flashcards== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology - Flashcards#Tongue Flashcards|Tongue Flashcards]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Facial_Muscles_-_Musculoskeletal_-_Flashcards|Facial Muscles Flashcards]] | ||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
| − | + | [[Tongue - Pathology|Pathology of the tongue]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| + | [[Category:To Do - A&P]] | ||
Revision as of 21:43, 27 December 2010
Introduction
The tongue (lingua) occupies the ventral aspect of the oral cavity and oropharynx. It is involved with grooming, lapping, prehension and manipulating food in the oral cavity. It is also involved in the deglutition reflex and vocalisation. The tongue is capable of vigorous and precise movements due to the apex being free of attachments to the oral cavity.
Structure and Function
The tounge is skeletal muscle dorsally. There is structural fat surrounded by a cartilagenous sheath forming lyssa (canids only) ventrally. There is an attached root and body with a free apex. The frenulum (fold of mucosa) attaches the body of the tongue to the floor of the oral cavity. The root of tongue is attached to the hyoid bone. In the horse and dog, the tongue is 'u' shaped, becoming broader towards the tip. The furrow in the centre of the canid tongue is called the median sulcus. In the ox, sheep and pig the tongue is 'v' shaped with a pointed apex. The torus linguae is a swelling across the tongue laterally which pushes food against the hard palate.
Muscles
Intrinsic Muscles
Intrinsic muscles include; the dorsal and ventral longitudinal muscles and the transverse and vertical bundles.
Extrinsic Muscles
The extrinsic muscles include;
Styloglossus
The origin is the hyoid apparatus (stylohyoid). It retracts and elevates the tongue.
Genioglossus
The origin is the incisive part of the mandible. It protrudes and depressed the tongue.
Hyoglossus
The origin is the hyoid apparatus (basihyoid). It retracts and depresses the tongue.
Geniohyoideus
The origin is the incisive part of the mandible and the insertion site is the body of the hyoid. It lies below the tongue (not within it) and draws the hyoid, and therefore the tongue forward.
Innervation
All muscles moving the tongue are innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII). The rostral 2/3 of the tongue is innervated by the lingual branch of the trigeminal (CN V) which is sensory supplying temperature, touch and pain. The chorda tympani of the facial (CN VII) supplies the taste. The caudal 1/3 of the tongue is innervated by the glossopharyngeal (CN IX) providing motor function for taste.
Vasculature
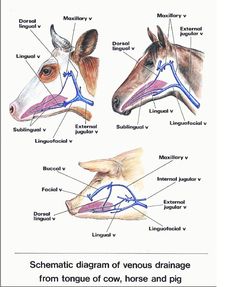
The main blood supply to the tongue is via the lingual artery, a branch of the external carotid artery. A secondary blood supply to the tongue is provided via the tonsillar branch of the facial artery and the ascending pharyngeal artery.
Histology
The tounge consists of stratified squamous epithelium. There are lingual glands and a mucosal covering tightly adheres to the contact surface. The degree of keratinisation depends on the diet. There is less keratinisation on the ventral surface and sides of tongue. It is covered by papillae (taste buds)for protection and taste. Papillae are specialised projections of the mucosa. Some papillae have taste buds, others are mechanical to roughen the surface of the tongue.
Types of Papillae
Conical
Conical papillae are not found in horses. They are present in the caudal 1/3 of the tongue. They point caudally and have no taste buds. There is a thick epithelium.
Foliate
8 to 12 papillae in parallel folds, one either side of the tongue midline. Consists of a stratified squamous epithelium, present in the caudal 1/3 of the tongue. There are taste buds, glands and lymphatics present.
Vallate
There are 3 to 6, often secondary papillae in taste buds. There are broad glands in the caudal 1/3 of tongue. Taste buds and lymphatics are present.
Fungiform
Red dots on tongue surface. Consists of keratinised, stratified squamous epithelium and blood vessels. Involved in loss of heat via panting in dogs. Present in the rostral 2/3 of the tongue, taste buds are present.
Filiform
The most numerous. They point caudally. There are no taste buds, glands or lymphatics. They are the smallest and consist of a thick keratin on stratified squamous epithelium. They are very prominent in cat and are present in the rostral 2/3 of the tongue.
Taste Buds
- Also found on the soft palate and pharynx (but sparsely distributed)
- Constant cell turnover
- Flat, thick cells
- Taste hairs (microvilli) pointing though taste pore
- Nerves transduce chemical signals into nervous signals
Species Differences
Canine
- Stretch receptors in the tongue
- Uses the tongue to lose heat by panting
Ruminant
- Tongue is heavily keratinised with long papillae for eating (protective surface)
- Ox has lenticular papillae which are hard and horny due to heavy keratinisation
Feline
- Long papillae for grooming so tongue is rough
Porcine
- Most of the papillae are soft, long and directed caudally
Avian
- There is a bone present
- It is mainly used for manipulation of food rather than vocalisation like in mammals
- Parrots use the tongue to produce human sounds (see here)