Difference between revisions of "Arteritis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
'''''[[Polyarteritis nodosa]]''''' | '''''[[Polyarteritis nodosa]]''''' | ||
| − | + | ==Test yourself with the Vascular Pathology Flashcards== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[Vascular Pathology Flashcards]] | |
| + | |||
[[Category:Cardiovascular_System_-_Inflammatory_Pathology]][[Category:Cardiovascular_System_-_Vascular_Pathology]][[Category:Arterial_Pathology]] | [[Category:Cardiovascular_System_-_Inflammatory_Pathology]][[Category:Cardiovascular_System_-_Vascular_Pathology]][[Category:Arterial_Pathology]] | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 16:18, 15 February 2011
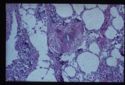
Presence of inflammatory cells within and around the vessel wall. Vasculitis often increases vessel permeability, presenting as oedema and haemorrhage. Petichial and ecchymotic haemorrhages within mucosae are characteristic.
Multiple aetiologies:
Infective
- Bacterial: Often toxin damage E.g. Salmonellosis, Erysipelas.
- Viral: Epitheliotropic viruses E.g. Equine arteritis, Canine distemper.
- Mycotic: Mucormycosis.
Parasitic
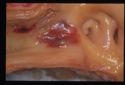
The main parasitic lesion of the arteries in th UK is Strongylus vulgaris of horses. Larvae and mmatures migrate along arterial walls, particularly cranial mesenteric and ilio-caecal arteries with occasional aberrent migration to the ascending aorta.