Difference between revisions of "Muscles Degenerative - Pathology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Redirected page to Category:Muscles - Degenerative Pathology) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | # | + | ==Degeneration== |
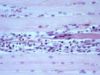
| + | [[Image:Degenerate muscle fibres.jpg|right|thumb|100px|<small><center>Degenerate muscle fibres (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Different types of degeneration | ||
| + | *May, or may not, be reversible | ||
| + | *Cloudy swelling, hydropic, vacuolar, granular and fatty change | ||
| + | *Occur following many different types of insult and are usually '''segmental''' | ||
| + | *If regeneration does not occur after formation of small vacuoles, [[Muscles Degenerative - Pathology#Necrosis|necrosis]] follows | ||
| + | **Vacuolation -> floccular degeneration -> granular degeneration -> [[Hyaline Degeneration|hyaline]] and [[Zenker Degeneration - Pathology|Zenker’s degeneration]] | ||
| + | *[[Hydropic Degeneration#Vacuolar Degeneration|'''Vacuolar degeneration''']]: | ||
| + | **Due to swelling of organelles or due to glycogen or fat accumulation | ||
| + | **May be caused by hypokalaemia, hyperkalaemia or necrosis | ||
| + | *Histologically: | ||
| + | **Swollen | ||
| + | **Hypereosinophilic | ||
| + | **Lost cross striations | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Muscle Calcification]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Muscle Ossification]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Muscle Pigmentation]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==[[Muscle Necrosis]]== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==[[Muscle Atrophy]]== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==[[Toxic Myopathy]]== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==[[Endocrine Myopathy]]== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Nutritional myopathy== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[White Muscle Disease|White muscle disease]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Exertional myopathies== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Caused by intensive and exhaustive activity of major muscle masses | ||
| + | *Glycogen used up -> local heat and lactic acid -> muscle degeneration | ||
| + | *Other forms include '''capture myopathy''', racing greyhounds, sheep chased by dogs | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Equine Rhabdomyolysis]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Porcine Stress Syndrome]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Neuromuscular junction diseases== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Aquired myasthenia gravis=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *See [[Myasthenia Gravis|congenital MG]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Botulism]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Circulatory disturbances== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Muscle Congestion]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Muscle Ischaemia]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Trauma== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Due to: | ||
| + | **Direct transection of myofibres | ||
| + | **Compression of myofibres | ||
| + | **Secondary from haemorrhage (bruising) | ||
| + | ***May increase muscle pressure -> [[Muscles Degenerative - Pathology#Ischaemia|ischaemia]] -> [[Muscles Degenerative - Pathology#Necrosis|necrosis]] | ||
| + | **Partial rupture - ''e.g.'' of diaphragm in road traffic accident | ||
| + | **Complete rupture - ''e.g.'' quadriceps of racing greyhounds | ||
| + | **Myorrhexis (tearing) - ''e.g.'' slippery floor causing 'splits' in cattle -> adductor muscle tear | ||
| + | *Healing is by [[Muscle Regeneration|regeneration]] | ||
| + | *Fibrosis (scarring) will compromise function | ||
| + | *During [[Bones Fractures - Pathology|fractures]], fragments may cause further trauma if moved | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Muscles - Degenerative Pathology]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Musculoskeletal System - Pathology]] | ||
Revision as of 18:10, 3 March 2011
Degeneration
- Different types of degeneration
- May, or may not, be reversible
- Cloudy swelling, hydropic, vacuolar, granular and fatty change
- Occur following many different types of insult and are usually segmental
- If regeneration does not occur after formation of small vacuoles, necrosis follows
- Vacuolation -> floccular degeneration -> granular degeneration -> hyaline and Zenker’s degeneration
- Vacuolar degeneration:
- Due to swelling of organelles or due to glycogen or fat accumulation
- May be caused by hypokalaemia, hyperkalaemia or necrosis
- Histologically:
- Swollen
- Hypereosinophilic
- Lost cross striations
Muscle Calcification
Muscle Ossification
Muscle Pigmentation
Muscle Necrosis
Muscle Atrophy
Toxic Myopathy
Endocrine Myopathy
Nutritional myopathy
White muscle disease
Exertional myopathies
- Caused by intensive and exhaustive activity of major muscle masses
- Glycogen used up -> local heat and lactic acid -> muscle degeneration
- Other forms include capture myopathy, racing greyhounds, sheep chased by dogs
Equine Rhabdomyolysis
Porcine Stress Syndrome
Neuromuscular junction diseases
Aquired myasthenia gravis
- See congenital MG
Botulism
Circulatory disturbances
Muscle Congestion
Muscle Ischaemia
Trauma
- Due to:
- Direct transection of myofibres
- Compression of myofibres
- Secondary from haemorrhage (bruising)
- Partial rupture - e.g. of diaphragm in road traffic accident
- Complete rupture - e.g. quadriceps of racing greyhounds
- Myorrhexis (tearing) - e.g. slippery floor causing 'splits' in cattle -> adductor muscle tear
- Healing is by regeneration
- Fibrosis (scarring) will compromise function
- During fractures, fragments may cause further trauma if moved