Difference between revisions of "Tick Life Cycle"
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| − | |||
[[Image:Ticks mating.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Ixodes ricinus'' mating - Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Ticks mating.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Ixodes ricinus'' mating - Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
[[Image:Ixodidae life cycle.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Life cycle of Ixodidae family ticks - CDC, Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Ixodidae life cycle.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Life cycle of Ixodidae family ticks - CDC, Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| Line 14: | Line 13: | ||
===Two-host ticks=== | ===Two-host ticks=== | ||
| − | :: In these species both the larvae and nymphs feed and develop on the same host. The nymphs will leave the host once they have taken a meal and develop into adults which will feed on a new host. The genus [[ | + | :: In these species both the larvae and nymphs feed and develop on the same host. The nymphs will leave the host once they have taken a meal and develop into adults which will feed on a new host. The genus [[Hyalomma spp.|''Hyalomma'']] is an example of two host ticks. |
===Three-host ticks=== | ===Three-host ticks=== | ||
| Line 21: | Line 20: | ||
==Soft Ticks== | ==Soft Ticks== | ||
The soft ticks life cycle almost always involves multiple hosts. They feed once as larvae before moulting to become a nymph, this is followed by several more nymphal stages each involving a blood meal before moulting. Moulting takes place off the host, therefore it is common for each feed to take place on a different host. As adults the females lay multiple small batches of eggs off the host after each feed. The amount of time the soft ticks take for each blood meal is considerably shorter than that of the hard ticks and so they do not engorge to as great an extent. | The soft ticks life cycle almost always involves multiple hosts. They feed once as larvae before moulting to become a nymph, this is followed by several more nymphal stages each involving a blood meal before moulting. Moulting takes place off the host, therefore it is common for each feed to take place on a different host. As adults the females lay multiple small batches of eggs off the host after each feed. The amount of time the soft ticks take for each blood meal is considerably shorter than that of the hard ticks and so they do not engorge to as great an extent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |flashcards = [[Ticks_Flashcards|Ticks Flashcards]] | ||
| + | |literature search = [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title:(%22tick%22)+AND+title:(%22life+cycle%22)&fq=subject_facet:%22Acari%22 Tick life cycle publications] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{review}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:Ticks|A]] | [[Category:Ticks|A]] | ||
| − | + | ||
[[Category:Expert_Review]] | [[Category:Expert_Review]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:02, 19 July 2012
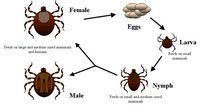
Overview
Ticks are temporary ectoparasites meaning that they only spend a short period of their lives on the host species, the rest of the time is spent free living in the environment. Tick life cycles consist of 3 stages; larva, nymph and adult. Between each life stage the tick must take at least one blood meal in order to develop to the next stage or to produce eggs. Hard ticks take a single large blood meal at each life stage whereas soft ticks feed in smaller meals more frequently and can do so on many hosts.
Hard ticks
Hard ticks can be classified by the number of host species they parasitise during their life cycle.
One-host ticks
- These ticks will feed at each stage and develop on the same host. This group includes the genus Boophillus.
Two-host ticks
- In these species both the larvae and nymphs feed and develop on the same host. The nymphs will leave the host once they have taken a meal and develop into adults which will feed on a new host. The genus Hyalomma is an example of two host ticks.
Three-host ticks
- Each stage of the three host ticks life cycle will feed on a different host species. In general the size of the host will increase with each feed as the size of the tick increases. The Ixodes genus of ticks are three host feeders.
Soft Ticks
The soft ticks life cycle almost always involves multiple hosts. They feed once as larvae before moulting to become a nymph, this is followed by several more nymphal stages each involving a blood meal before moulting. Moulting takes place off the host, therefore it is common for each feed to take place on a different host. As adults the females lay multiple small batches of eggs off the host after each feed. The amount of time the soft ticks take for each blood meal is considerably shorter than that of the hard ticks and so they do not engorge to as great an extent.
| Tick Life Cycle Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Ticks Flashcards |
 Search for recent publications via CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Tick life cycle publications |
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a0916e074030_73712867 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a0916e13d6a7_59882768 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a0916e1e4b81_54635107
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |