Difference between revisions of "Equine Urinary System - Horse Anatomy"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
===Innervation=== | ===Innervation=== | ||
The bladder receives sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve supply. | The bladder receives sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve supply. | ||
| − | *Parasympathetic supply: This comes from S1-S3, synapses within the '''pelvic plexus''', continues as the '''pudendal nerve''' and is excitatory to the destrusor muscle. Parasympathetic dominance allows emptying of the bladder. | + | *'''Parasympathetic supply''': This comes from S1-S3, synapses within the '''pelvic plexus''', continues as the '''pudendal nerve''' and is excitatory to the destrusor muscle via release of Acetylcholine which binds muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Parasympathetic dominance allows emptying of the bladder. |
| − | *Sympathetic Supply: This comes from L1-L4, synapses within the '''caudal mesenteric ganglion''' before entering the '''pelvic plexus. | + | *'''Sympathetic Supply''': This comes from L1-L4, synapses within the '''caudal mesenteric ganglion''' before entering the '''pelvic plexus'''. Postganglionic fibres continue as the '''hypogastric nerves''', which terminate on beta 2 receptors within the detrusor muscle. It has inhibitory action on muscular contraction, therefore enabling bladder filling. |
==Urethra== | ==Urethra== | ||
| Line 111: | Line 111: | ||
===Muscles of the Urethra=== | ===Muscles of the Urethra=== | ||
The '''''urethralis''''' muscle runs the entire length of the urethra and forms the '''external urethral sphincter'''. Unlike the [[Urinary Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology#Internal Urethral Sphincter|internal sphincter]], the external sphincter is composed of striated muscle fibres which are under the voluntary control of the somatic nervous system. | The '''''urethralis''''' muscle runs the entire length of the urethra and forms the '''external urethral sphincter'''. Unlike the [[Urinary Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology#Internal Urethral Sphincter|internal sphincter]], the external sphincter is composed of striated muscle fibres which are under the voluntary control of the somatic nervous system. | ||
| − | === | + | ===Innervation of the External Urethral Sphincter=== |
| − | + | The ''urethralis'' muscle receives somatic innervation originating from S1-S3 and continuing via the '''pudendal nerve'''. This releases the neurotransmitter Acetylcholine, which binds to nicotinic Acetylcholine receptors and mediates skeletal muscle contraction of the external urethral sphincter. This is important in urine retention. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Vascular Supply=== | ===Vascular Supply=== | ||
Blood Supply comes from the '''Urethral Artery''', which is a branch of the '''vaginal artery''' which in turn is a branch of the '''internal pudendal''' which is a branch of the '''internal iliac'''. | Blood Supply comes from the '''Urethral Artery''', which is a branch of the '''vaginal artery''' which in turn is a branch of the '''internal pudendal''' which is a branch of the '''internal iliac'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:To Do - AP Review]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:25, 28 November 2012
| This article is still under construction. |
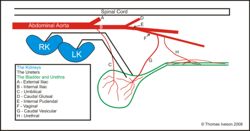
Kidneys
The kidneys of the horse are both enclosed in a fat capsule. Dorsally they rest against the psoas muscle and against the diaphragm. The left kidney is bean-shaped and the right kidney is heart-shaped. The right kidney lies cranial to the left kidney.
The right kidney is to be found ventrally to, and between, the last 2 ribs and first lumbar transverse process. Cranially it touches the liver and caudally it is attached to the pancreas and the base of caecum. The duodenum winds around its lateral and then ventral surfaces. Medially is the caudal vena cava and adrenal gland.
The left kidney is between the last rib and 3rd transverse process. Its ventral surface is almost completely covered by the peritoneum and contacts the small intestine and and small colon. The spleen contacts it cranioventrally. Medially is the left [[Equine Endocrine System - Horse Anatomy#Adrenal Glands|adrenal gland] and aorta.
The Basic Components of the Kidney
Outer fibrous capsule
A tough outer capsule surrounds the parenchyma and this prevents the kidney expanding.
Renal Cortex
The renal cortex is the outermost layer of parenchyma, it lies just beneath the renal capsule. The renal cortex is comprised of two parts, peripheral zone and the inner juxtamedullary zone. The cortex contains the following parts of the nephron:
Renal Medulla
The renal medulla is the inner layer of renal parenchyma. In the horse, medullary pyramids and their papillae are completely fused to form a renal crest; hence they are said to have a unilobar type of kidney. The medulla can be split into two parts, the outer and the inner. Different parts of the nephron reside in these areas.
Outer Medulla
The outer medulla can be further divided into the outer and inner stripe.
- Outer Stripe: This section located just inside the cortex contains the following parts of the nephron:
- The Inner Stripe: Located inside of the outer stripe this section contains the following parts:
The outer stripe contains the straight proximal tubules and the inner does not. However the inner contains thin ascending limbs and the outer does not. This difference makes up the anatomical demarcation between the two stripes.
Inner Medulla
The inner medulla only contains the following parts:
Renal Pelvis
The renal crest opens into the renal pelvis. The renal pelvis is an expansion where the proximal ureter begins. The renal pelvis is located within the renal sinus. The renal sinus is located within an indentation on the medial side of the kidney. The renal sinus is a potential space, which is occupied by the ureter, branches of the renal artery and vein, lymphatics and nerves that enter the kidney at the hilus. In the horse, the renal pelvis consists of a central cavity and two large terminal recesses. The terminal recess is a long tube-like structure that collects urine from the poles of the kidneys into the renal pelvis. Most of the papillary ducts open into the terminal recesses. The renal pelvis is lined with transitional epithelium and contains mucous glands in the horse; giving urine a frothy appearence.
Vascular Supply
The kidney receives approximately 25% of cardiac output. Each kidney is supplied by a renal artery, which is a branch of the abdominal aorta. The renal artery subsequently divides at the hilus of each kidney into interlobar arteries, which run to the corticomedullary junction. Here they branch into arcuate arteries. The arcuate arteries then give rise to interlobular arteries which radiate into the renal cortex. The interlobular arteries become the afferent arteriole and subsequently the capillary loops of the glomerulus. These capillary loops then unite to become the efferent arteriole, which supplies a capillary network around the nephrons. This capillary network drains blood from the renal cortex into the interlobular veins, arcuate veins, then interlobar veins. The interlobar veins drain into the renal veins, which subsequently drain into the caudal vena cava.
The renal capsule is supplied by capillary branches of the interlobular arteries. Venous drainage of the capsule is provided by the stellate veins, which subsequently drain into the interlobular veins.
The vasa recta form a series of straight capillaries that lie parallel to the loop of Henle within the renal medulla. The vasa recta branch off the efferent arterioles of juxtamedullary nephrons. Blood flow within the vasa recta is very slow, allowing the countercurrent exchange mechanism to occur within the loop of Henle by mainaining a meduallary concentration gradient. The maintenance of this concentration gradient is one of the components responsible for the kidney's ability to produce concentrated urine.
Innervation
The kidney receives sympathetic and parasympathetic fibres from the solar plexus. These fibres travel with renal arteries. Sympathetic fibres synapse in coeliac ganglion and cranial mesenteric ganglion.
Lymphatic Drainage
Lymphatic vessels are satellite to the blood vessels. The drain first to the renal lymph nodes, before terminating in the lumbar lymph nodes.
Ureters
The ureters convey urine from the renal pelvis to the bladder. There are two of them, one for each kidney. The ureters run retroperitoneally along the roof of the abdominal cavity and then enters the pelvis. Once entering the pelvis it moves medially in the broad ligament of the female or the genital fold of the male. It ends at its junction on the dorsolateral surface of the bladder within the lateral ligament. The ureter then runs intramurally (within the bladder wall) before opening into the bladder lumen at slit-like openings known as ostia.
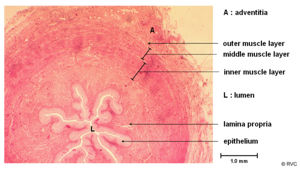
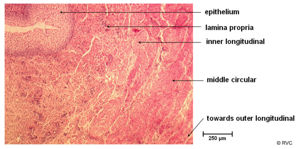
Wall
The wall of the ureters has an internal mucosa layer formed from transitional epithelium. This provides protection against the urine. The middle layer is a muscularis layer. This is well developed for peristalsis, though can enter into spasm on irritation. The outer layer is composed of adventitia. In the horse, the wall in the proximal urethra contains mucous-producing glands.
Junction with the Bladder
The ureter enters the bladder obliquely near the neck of the bladder and runs between the muscular layers and mucosa. They open through 2 slits on a raised hillock.
Movement of Urine
The movement of urine along the ureters is achieved by peristalsis which is powered by locally regulated smooth muscle. This maintains a low pressure in the renal pelvis.
Vascular Supply
The renal pelvis and proximal ureter is supplied by the renal artery. The distal ureter is supplied by the cranial vesicular artery and the vaginal artery (in the female) and prostatic artery (in the male).
Lymphatic Drainage
- Lumbar lymph nodes
- Medial iliac lymph nodes
Innervation
The ureter receivs parasympathetic and sympathetic innervation.
Bladder
The bladder is where urine is stored before being expelled by the body through the micturition reflex. Without a bladder urinary continence would be impossible.
The bladder is a hollow, muscular organ. It is divided for descriptive purposes into three parts:
- Cranial Pole
- Intermediate body
- Caudal neck
Its wall comprises a muscle layer covered in transitional epithelium. Its size and posistion are determined by how full it is. When empty the mucosa of the bladder wall is wrinkled and thicker. The bladder rests on the pubic bones, entirely within the pelvis and is largely retroperitoneal. When full and distended, the mucosal folds disappear and the wall appears thinner, it then becomes intraperitoneal. There are two folds (plicae uretericae) that do not disappear, even when the bladder is distended; these extend from the ureteral opening to the neck of the bladder before folding to become the urethral crest.
The trigone of the bladder gets its name as it looks like a triangle without a base. The trigone is bounded by the plicae uretericae. It is believed to have increased sensitivty and is of different embryological origin to the rest of tissue. More details can be found here.
Muscles of the Bladder
The three muscular components of the bladder described below play a pivotal part in the micturition reflex.
Detrusor Muscle
This network of smooth muscle fibres lie in three sheets within the bladder wall and are supplied by both parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves. It is responsible for storage and expression of urine from the bladder.
Vascular Supply
The main blood supply to the bladder is via the caudal vesical arteries. These are branches of the vaginal artery (in the female) and the prostatic artery (in the male). A minor supply to the cranial bladder is provided by the reduced umbillical arteries.
Lymphatics
Lymphatics of the bladder drain into the iliosacral lymph nodes
Innervation
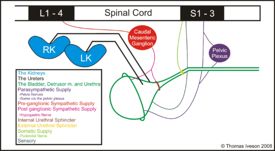
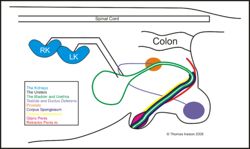
The bladder receives sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve supply.
- Parasympathetic supply: This comes from S1-S3, synapses within the pelvic plexus, continues as the pudendal nerve and is excitatory to the destrusor muscle via release of Acetylcholine which binds muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Parasympathetic dominance allows emptying of the bladder.
- Sympathetic Supply: This comes from L1-L4, synapses within the caudal mesenteric ganglion before entering the pelvic plexus. Postganglionic fibres continue as the hypogastric nerves, which terminate on beta 2 receptors within the detrusor muscle. It has inhibitory action on muscular contraction, therefore enabling bladder filling.
Urethra
This muscular tube is the connection between the bladder and the external environment and plays a vital role in conscious urinary continence.
The Layers of the Urethra
The layers of the walls of the urethra are largely similar to those of the bladder apart from one significant difference; in both the male and the female the urethral submucosa has a network of veins which may contribute to continence by forming a kind of erectile tissue.
Female
The urethra empties at the external urethral orifice on the ventral wall of the vagina. This is often at the vestibulo-vaginal junction. Only urine passes through the female urethra. In the horse, the urethra is short and wide.
Male
The urethra empties at tip of penis. The male urethra carries urine, semen and seminal secretions from the accessory sex glands. The uretha is divided into 3 parts:
- Pre-prostatic - bladder neck to seminal hillock
- Prostatic portion - openings of deferant, vesicular and prostatic ducts
- Penile portion - ischial arch to penile tip
The combination of the pre-prostatic and prostatic portions are called the pelvic portion.
Muscles of the Urethra
The urethralis muscle runs the entire length of the urethra and forms the external urethral sphincter. Unlike the internal sphincter, the external sphincter is composed of striated muscle fibres which are under the voluntary control of the somatic nervous system.
Innervation of the External Urethral Sphincter
The urethralis muscle receives somatic innervation originating from S1-S3 and continuing via the pudendal nerve. This releases the neurotransmitter Acetylcholine, which binds to nicotinic Acetylcholine receptors and mediates skeletal muscle contraction of the external urethral sphincter. This is important in urine retention.
Vascular Supply
Blood Supply comes from the Urethral Artery, which is a branch of the vaginal artery which in turn is a branch of the internal pudendal which is a branch of the internal iliac.