Difference between revisions of "Rumination"
m (moved Rumination - Anatomy & Physiology to Rumination over redirect) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{OpenPagesTop}} | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
The function of rumination is to decrease particle size, increase surface area for microbial digestion, break down impervious plant coatings and mix food. It introduces saliva as an aid to maintaining rumen pH. Coarseness of the ration influences the amount of time spent in rumination. Cattle ruminate for up to 10 hours per day. For example cattle fed hay diet spend roughly 8 hours per day ruminating; cattle fed ground dried grass diet spend roughly 5-9 hours per day ruminating and on concentrate diet spend roughly 2.5 hours per day ruminating. (Cattle claw health has been linked to the time cattle spend grazing versus ruminating). | The function of rumination is to decrease particle size, increase surface area for microbial digestion, break down impervious plant coatings and mix food. It introduces saliva as an aid to maintaining rumen pH. Coarseness of the ration influences the amount of time spent in rumination. Cattle ruminate for up to 10 hours per day. For example cattle fed hay diet spend roughly 8 hours per day ruminating; cattle fed ground dried grass diet spend roughly 5-9 hours per day ruminating and on concentrate diet spend roughly 2.5 hours per day ruminating. (Cattle claw health has been linked to the time cattle spend grazing versus ruminating). | ||
| − | + | {{OpenPages}} | |
[[Category:Stomach - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Stomach - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
[[Category:A&P Done]] | [[Category:A&P Done]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Alimentary Anatomy - Cattle]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:37, 8 February 2013
Introduction
Rumination is the process of digestion in the ruminant. It involves three simplified processes. the first is regurgitation . The second is re-mastication, which increases the surface area of food particles for digestion through further mechanical breakdown, and the third is reinsalivation. Reinsalivation increases the volume of saliva produced (whilst chewing) and allows minerals to be recycled. Saliva is an important buffer in relation to rumen pH.
Process
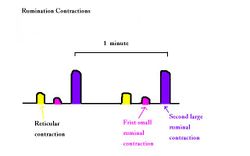
The reflex is initiated by mechanical stimulation of the receptors in the mucosa of the reticulum, ruminoreticular fold and cardiac area of the rumen. Frequency of contractions depends on the animal's feeding activity and diet contents. E.g. Cattle fed on hay or straw have the most frequent contractions at 79-100 per hour during feeding, 55-76 per hour during rumination. On the other hand, cattle that are resting (not feeding or ruminating) only have contractions at 47-80 per hour. Discrete reticular contraction precedes biphasic ruminal contraction (see ruminoreticular contractions).
Regurgitation depends upon the coordination of the stomach movements with the thoracic wall and throat: inspiration against a closed glottis creating a negative pressure in the thorax - allowing ingesta to be drawn into the oesophagus. Ingesta is carried to the oral cavity via an antiperistaltic wave. The process is controlled by rumination centres in the hypothalamus. Fibre increases stomach motility (type and length of fibre is important). An increase in volatile fatty acids decreases stomach motility.
Function
The function of rumination is to decrease particle size, increase surface area for microbial digestion, break down impervious plant coatings and mix food. It introduces saliva as an aid to maintaining rumen pH. Coarseness of the ration influences the amount of time spent in rumination. Cattle ruminate for up to 10 hours per day. For example cattle fed hay diet spend roughly 8 hours per day ruminating; cattle fed ground dried grass diet spend roughly 5-9 hours per day ruminating and on concentrate diet spend roughly 2.5 hours per day ruminating. (Cattle claw health has been linked to the time cattle spend grazing versus ruminating).
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt697bc72b2a9bd3_39496714 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt697bc72b326884_52250761 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt697bc72b3710f7_76295607
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |