Difference between revisions of "Giardia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Taxobox |
| − | + | |name =Giardia | |
| − | + | |kingdom =Protista | |
| − | | | + | |sub-kingdom =Biciliata |
| − | | | + | |phylum =Metamonada |
| − | | | + | |super-class =Eopharyngea |
| − | | | + | |class =Trepomonadea |
| − | | | + | |sub-class =Diplozoa |
| − | | | + | |super-order = |
| + | |order =Giardiida | ||
| + | |sub-order = | ||
| + | |super-family = | ||
| + | |family =Diplomonadidae | ||
| + | |sub-family = | ||
| + | |genus =Giardia | ||
| + | |species = | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Giardia lamblia life cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Giardia lamblia life cycle'' - Wikimedia Commons]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Image:Giardia lamblia life cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Giardia lamblia'' | ||
[[Image:Giardia lamblia.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Giardia lamblia'' - Janice Carr]] | [[Image:Giardia lamblia.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Giardia lamblia'' - Janice Carr]] | ||
[[Image:Giardia.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Giardia'' - Joaquim Castellà Veterinary Parasitology Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona]] | [[Image:Giardia.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Giardia'' - Joaquim Castellà Veterinary Parasitology Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona]] | ||
[[Image:Giardia cyst.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Giardia'' cyst - Courtesy of the Laboratory of Parasitology, University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine]] | [[Image:Giardia cyst.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Giardia'' cyst - Courtesy of the Laboratory of Parasitology, University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine]] | ||
| − | + | ==Overview== | |
| + | These protozoan parasite are found in humans as well as wild and domestic animals. They are a common cause of severe [[Diarrhoea|diarrhoea]] as part of the clinical symptoms [[Giardiasis|giardiasis]]. | ||
| − | + | ==Recognition== | |
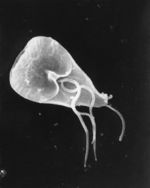
| − | + | ''Giardia spp.'' are flagellate protozoa with 8 flagella, 6 of which emerge from the body and are used in motility. They are 15-20μm long, pear shaped with a flat ventral surface. The most unique feature of this protozoa is the presence of a large adhesive disk in the flat surface that is used for attaching to the intestinal mucosa. | |
| − | + | ==Life Cycle== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*Simple and direct | *Simple and direct | ||
| Line 49: | Line 45: | ||
==Pathogenesis== | ==Pathogenesis== | ||
| − | *Commonest cause of protozoal [[ | + | *Commonest cause of protozoal [[Diarrhoea|diarrhoea]] of man in the UK |
*Common in domesticated animals | *Common in domesticated animals | ||
| Line 68: | Line 64: | ||
***Some subspecies are zoonotic | ***Some subspecies are zoonotic | ||
| − | + | {{Learning | |
| − | + | |flashcards = [[Giardia_Flashcards|Giardia Flashcards]] | |
| − | + | |Vetstream = [https://www.vetstream.com/canis/search?s=protozoa Protozoa] | |
| − | + | }} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | = | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{unfinished}} | |
| + | [[Category:Miscellaneous_Protozoa]] | ||
| + | [[Category:To_Do_-_Parasites]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:57, 4 June 2016
| Giardia | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Protista |
| Sub-kingdom | Biciliata |
| Phylum | Metamonada |
| Super-class | Eopharyngea |
| Class | Trepomonadea |
| Sub-class | Diplozoa |
| Order | Giardiida |
| Family | Diplomonadidae |
| Genus | Giardia |
Overview
These protozoan parasite are found in humans as well as wild and domestic animals. They are a common cause of severe diarrhoea as part of the clinical symptoms giardiasis.
Recognition
Giardia spp. are flagellate protozoa with 8 flagella, 6 of which emerge from the body and are used in motility. They are 15-20μm long, pear shaped with a flat ventral surface. The most unique feature of this protozoa is the presence of a large adhesive disk in the flat surface that is used for attaching to the intestinal mucosa.
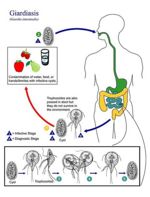
Life Cycle
- Simple and direct
- Trophozoites attach to intestinal wall
- Reproduce by binary fission
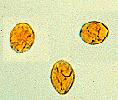
- Form cysts of 10μm
- Multi-nucleate cysts formed intermittently
- Immediately infective when passed in faeces
- Prepatent period of 5-6 days
Pathogenesis
- Commonest cause of protozoal diarrhoea of man in the UK
- Common in domesticated animals
- Infections often asymptomatic in domestic animals
- Can cause villous atrophy leading to malabsorption
- Infection can persist for weeks to months if not treated
Epidemiology
- Infection via direct oral-faecal route or through contaminated water source (water-borne)
- Wild animals may act as a source of infection for humans
- E.g. Beavers
- Divided into 7 species
- G. duodenalis most commonly infects humans
- Some subspecies are zoonotic
- G. duodenalis most commonly infects humans
| Giardia Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Giardia Flashcards |
| This article is still under construction. |