Difference between revisions of "Ancylostoma caninum"
JamesSwann (talk | contribs) |
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| + | {{Taxobox | ||
| + | |name =''Ancylostoma caninum | ||
| + | |kingdom =Animalia | ||
| + | |phylum =[[Nematodes|Nematoda]] | ||
| + | |class =Secernentea | ||
| + | |sub-class = | ||
| + | |order =Strongylida | ||
| + | |super-family =[[Ancylostomatoidea]] | ||
| + | |family =Ancylostomatidae | ||
| + | |sub-family = | ||
| + | |genus =Ancylostoma | ||
| + | |species =''A. caninum'' | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Description== |
| − | + | [[File:Hookworms.jpg|thumb|Image of ''Ancylostoma caninum''<br><small>Copyright Joel Mills 2006 Wikimedia Commons]]</small> | |
| − | | | + | ''Ancylostoma caninum'' is a hookworm that belongs to the superfamily [[:Category:Ancylostomatoidea|Ancylostomatoidea]]. This superfamily contains exotic hookworms that infect both man and animals. ''A. caninum'' is rarely found in the UK but it is a major pathogen of dogs in many warmer and tropical regions of the world and it may be encountered in dogs that have travelled under the Pet Travel Scheme. The [[Ancylostomatoidea Life-Cycle|life-cycle of ''Ancylostoma caninum'']] is detailed elsewhere but it should be noted that L3 larvae of this species mainly enter by the transcutaneous route so that intestinal disease and blood loss are mainly seen in younger animals. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | Ancylostomatoidea | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |- | ||
| + | ==Identification== | ||
| + | [[File:Hookworm egg 1.jpg|thumb|Image of an egg of ''Ancylostoma caninum''<br><small>Copyright Joel Mills 2006 Wikimedia Commons]]</small> | ||
| + | ''A. caninum'' may be recognised on examination under a microscope by its large buccal cavity which contain three pairs of teeth along its anterior and ventral edges. Two smaller teeth are also present at the base of the cavity. | ||
| − | + | Like almost all hookworm eggs, those of ''A. caninum'' are oval in shape and around 50 um in diameter. The shell membrane is thin and transparent and, by the time the egg is passed in the faeces, it contains a segmented ovum at the 4 or 8 cell stage. In a tropical climate, the egg will hatch within 24 hours and only L1 larvae will then be detectable. | |
| − | '' | ||
==Pathogenesis== | ==Pathogenesis== | ||
| Line 44: | Line 36: | ||
==Zoonotic Potential== | ==Zoonotic Potential== | ||
| − | + | Hookworms are able to cause a disease called [[Cutaneous Larva Migrans]] in humans. | |
| + | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |literature search = [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?rowId=1&options1=AND&q1=title%3A%28%22Ancylostoma+caninum%22%29&occuring1=freetext&rowId=2&options2=AND&q2=&occuring2=freetext&rowId=3&options3=AND&q3=&occuring3=freetext&publishedstart=2000&publishedend=yyyy&calendarInput=yyyy-mm-dd&la=any&it=any&show=all&x=48&y=10 ''Ancylostoma caninum'' publications since 2000] | ||
| + | |Vetstream = [https://www.vetstream.com/canis/search?s=nematode Nematoda] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{review}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Webinars== | ||
| + | <rss max="10" highlight="none">https://www.thewebinarvet.com/parasitology/webinars/feed</rss> | ||
| + | [[Category:Ancylostomatoidea|C]][[Category:Dog_Nematodes]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Expert_Review]] |
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 17:32, 7 December 2022
| Ancylostoma caninum | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Nematoda |
| Class | Secernentea |
| Order | Strongylida |
| Super-family | Ancylostomatoidea |
| Family | Ancylostomatidae |
| Genus | Ancylostoma |
| Species | A. caninum |
Description
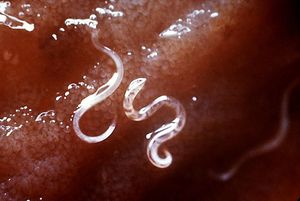
Ancylostoma caninum is a hookworm that belongs to the superfamily Ancylostomatoidea. This superfamily contains exotic hookworms that infect both man and animals. A. caninum is rarely found in the UK but it is a major pathogen of dogs in many warmer and tropical regions of the world and it may be encountered in dogs that have travelled under the Pet Travel Scheme. The life-cycle of Ancylostoma caninum is detailed elsewhere but it should be noted that L3 larvae of this species mainly enter by the transcutaneous route so that intestinal disease and blood loss are mainly seen in younger animals.
Identification
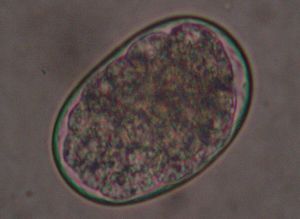
A. caninum may be recognised on examination under a microscope by its large buccal cavity which contain three pairs of teeth along its anterior and ventral edges. Two smaller teeth are also present at the base of the cavity.
Like almost all hookworm eggs, those of A. caninum are oval in shape and around 50 um in diameter. The shell membrane is thin and transparent and, by the time the egg is passed in the faeces, it contains a segmented ovum at the 4 or 8 cell stage. In a tropical climate, the egg will hatch within 24 hours and only L1 larvae will then be detectable.
Pathogenesis
A. caninum may cause disease in the following ways:
- The adult A. caninum is an avid blood-sucker, removing up to 0.1 ml of blood from the small intestinal wall every day. Heavy infections may occur when puppies ingest large numbers of L3 larvae from the milk of an infected dam or if they are exposed to a heavily contaminated environment and affected animals may show severe clinical signs, including:
- Severe acute anaemia which may occur in the prepatent period (before eggs are present in the faeces).
- Chronic anaemia that results in depletion of iron reserves, especially in older puppies.
- Severely affected animals may show poor growth and body condition.
- All hookworms may cause dermatitis, particularly in older animals which have developed some local cutaneous immunity and are able to kill invading larvae in the skin.
Control
Most conventional anthelmintic products licensed for use in dogs and cats (such as praziquantel and pyrantel) will clear infection by hookworms and it is a requirement of the Pet Travel Scheme that animals returning to the UK are treated with praziquantel 24-48 hours before entering the UK.
Zoonotic Potential
Hookworms are able to cause a disease called Cutaneous Larva Migrans in humans.
| Ancylostoma caninum Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |
 Search for recent publications via CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Ancylostoma caninum publications since 2000 |
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Webinars
Failed to load RSS feed from https://www.thewebinarvet.com/parasitology/webinars/feed: Error parsing XML for RSS