Difference between revisions of "Toroviruses"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Also known as: '''''Torovirus Infections — Berne Virus — BEV — Breda Virus — BRV — Bovine Torovirus — BoTV — Equine Torovirus — ETV — Prototype Berne Virus — Porcine Torovirus'''''. | ||
{{Taxobox | {{Taxobox | ||
| − | |name = | + | |name = Toroviruses |
|kingdom = Virus | |kingdom = Virus | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
|sub-order = | |sub-order = | ||
|super-family = | |super-family = | ||
| − | |family = Coronaviridae | + | |family = [[:Category:Coronaviridae|Coronaviridae]] |
|sub-family = | |sub-family = | ||
|genus = Torovirus | |genus = Torovirus | ||
|species = Toroviruses | |species = Toroviruses | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
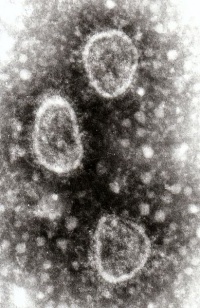
| − | Toroviruses are relatively new viruses belonging to the family Coronaviridae. | + | [[File:Torovirus.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Electron Micrograph of Torovirus particles]] |
| − | + | Toroviruses are relatively new viruses belonging to the family [[:Category:Coronaviridae|Coronaviridae]]. They are enveloped positive sense single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) viruses that are pleomorphic, 120-140 nm in diameter and are relatively stable in acid or alkaline environment between pH 2.5-10. Toroviruses have been isolated from horses (Equine torovirus, ETV, prototype Berne virus) and calves with diarrhoea (bovine torovirus, BoTV, prototype Breda virus). | |
==Signalment== | ==Signalment== | ||
| − | + | Hosts include cattle, zebu, goats, horses, sheep, pigs, lagomorphs, rodents, domestic cats and humans. | |
==Clinical Signs== | ==Clinical Signs== | ||
| − | The disease causes diarrhoea, pyrexia, dehydration, lethargy and depression in all ages of cattle. In calves it causes anorexia, mucoid faeces and the following neurological signs; generalised weakness, paralysis, inability to stand, trembling and sudden death. It can also cause respiratory problems such as laryngitis, tracheitis and pneumonia. | + | The disease causes diarrhoea, pyrexia, dehydration, lethargy and depression in all ages of cattle. In calves it causes anorexia, mucoid faeces and the following neurological signs; generalised weakness, paralysis, inability to stand, trembling and sudden death. It can also cause respiratory problems such as laryngitis, tracheitis and pneumonia. Young, colostrum-deprived calves are particularly at risk. |
| − | In cats, diarrhoea and protruding | + | In cats, diarrhoea and protruding nictitating membranes have been associated with feline torovirus infections. |
| − | Pigs can shed the torovirus without showing any symptoms of disease <ref name=" Kroneman et al., 1998">Kroneman, A., Cornelissen, L.A.H.M., Horzinek, M.C., Groot, R.J.de., Egberink, H.F., (1998) | + | Pigs can shed the torovirus without showing any symptoms of disease <ref name=" Kroneman et al., 1998">Kroneman, A., Cornelissen, L.A.H.M., Horzinek, M.C., Groot, R.J.de., Egberink, H.F., (1998) '''Identification and characterization of a porcine torovirus'''. ''Journal of Virology'', 72(5):3507-3511; 35 ref.</ref>. |
==Epidemiology== | ==Epidemiology== | ||
| − | Toroviruses are found in many species but little is known about the transmission or interspecies transmission of the virus. | + | Toroviruses are found in many species but little is known about the transmission or interspecies transmission of the virus. It is presumed that they are spread via the faecal-oral route and through subclinical or chronically infected cattle <ref name=" Koopmans and Horzinek, 1994"> Koopmans, M., Horzinek, M.C., (1994) '''Toroviruses of animals and humans: a review'''. ''Advances in Virus Research'', 43:233-273; many ref. </ref>. |
| − | The Berne virus (BEV) has been found in horses; whereas the Breda virus (BRV) is found in cattle of which there are two serotypes; BRV 1 and 2. Breda virus in cattle can be detected in the dome epithelium and enterocytes of the intestines and differentiate within the epithelial cells of the villi; interrupting the | + | |
| + | The Berne virus (BEV) has been found in horses; whereas the Breda virus (BRV) is found in cattle of which there are two serotypes; BRV 1 and 2. Breda virus in cattle can be detected in the dome epithelium and enterocytes of the intestines and differentiate within the epithelial cells of the villi; interrupting the animal's absorptive capacity, although not as dramatically as the [[Rotaviruses|rotavirus]]. | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| Line 43: | Line 42: | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
| − | Diagnostic methods include a combination of electron microscopy, immuno-electron microscopy (IEM), haemagglutination inhibition or ELISA. Toroviruses can be differentiated from coronaviruses by using IEM <ref name="Woode, 1987">Woode, G.N., (1987). '''Breda and Breda-like viruses: diagnosis, pathology and epidemiology. Novel diarrhoea viruses'''., 175-191; '' | + | Diagnostic methods include a combination of electron microscopy, immuno-electron microscopy (IEM), [[Agglutination|haemagglutination]] inhibition or [[ELISA testing|ELISA]]. Toroviruses can be differentiated from coronaviruses by using IEM <ref name="Woode, 1987">Woode, G.N., (1987). '''Breda and Breda-like viruses: diagnosis, pathology and epidemiology. Novel diarrhoea viruses'''., 175-191; ''Ciba Foundation Symposium 128''; 23 ref.</ref>. |
| − | |||
Villus fusion and atrophy and thinning of intestinal wall can be seen on post-mortem. | Villus fusion and atrophy and thinning of intestinal wall can be seen on post-mortem. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
| − | There is no specific treatment. | + | There is no specific treatment. Animals can be supported with fluids to prevent dehydration as a result of the episodes of diarrhoea. Secondary bacterial infections can be treated with antibiotics. Culture and sensitivity is recommended. |
==Control== | ==Control== | ||
Isolation of infected animals and good hygiene and sanitary measures may help reduce the spread of the disease. | Isolation of infected animals and good hygiene and sanitary measures may help reduce the spread of the disease. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |flashcards = [[Toroviruses Flashcards]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | {{CABI source | ||
| + | |datasheet = [http://www.cabi.org/ahpc/?compid=3&dsid=61308&loadmodule=datasheet&page=2144&site=160 toroviruses] and [http://www.cabi.org/ahpc/?compid=3&dsid=61309&loadmodule=datasheet&page=2144&site=160 torovirus infections] | ||
| + | |date = 19 June 2011 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br><br><br> | ||
| + | {{review}} | ||
| − | + | ==Webinars== | |
| − | + | <rss max="10" highlight="none">https://www.thewebinarvet.com/infection-control-and-biosecurity/webinars/feed</rss> | |
| − | |||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Coronaviridae]] |
| + | [[Category:Horse Viruses]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Cattle Viruses]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pig Viruses]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Cat Viruses]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Intestinal Diseases - Cattle]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Small Intestinal Diseases - Horse]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Respiratory Diseases - Cattle]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Respiratory Diseases - Horse]] | ||
| + | [[Category:CABI Expert Review]][[Category:CABI AHPC Pages]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Nick L]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:25, 4 January 2023
Also known as: Torovirus Infections — Berne Virus — BEV — Breda Virus — BRV — Bovine Torovirus — BoTV — Equine Torovirus — ETV — Prototype Berne Virus — Porcine Torovirus.
| Toroviruses | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Virus |
| Order | Nidovirales |
| Family | Coronaviridae |
| Genus | Torovirus |
| Species | Toroviruses |
Introduction
Toroviruses are relatively new viruses belonging to the family Coronaviridae. They are enveloped positive sense single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) viruses that are pleomorphic, 120-140 nm in diameter and are relatively stable in acid or alkaline environment between pH 2.5-10. Toroviruses have been isolated from horses (Equine torovirus, ETV, prototype Berne virus) and calves with diarrhoea (bovine torovirus, BoTV, prototype Breda virus).
Signalment
Hosts include cattle, zebu, goats, horses, sheep, pigs, lagomorphs, rodents, domestic cats and humans.
Clinical Signs
The disease causes diarrhoea, pyrexia, dehydration, lethargy and depression in all ages of cattle. In calves it causes anorexia, mucoid faeces and the following neurological signs; generalised weakness, paralysis, inability to stand, trembling and sudden death. It can also cause respiratory problems such as laryngitis, tracheitis and pneumonia. Young, colostrum-deprived calves are particularly at risk.
In cats, diarrhoea and protruding nictitating membranes have been associated with feline torovirus infections.
Pigs can shed the torovirus without showing any symptoms of disease [1].
Epidemiology
Toroviruses are found in many species but little is known about the transmission or interspecies transmission of the virus. It is presumed that they are spread via the faecal-oral route and through subclinical or chronically infected cattle [2].
The Berne virus (BEV) has been found in horses; whereas the Breda virus (BRV) is found in cattle of which there are two serotypes; BRV 1 and 2. Breda virus in cattle can be detected in the dome epithelium and enterocytes of the intestines and differentiate within the epithelial cells of the villi; interrupting the animal's absorptive capacity, although not as dramatically as the rotavirus.
Distribution
Worldwide in cattle and horses.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic methods include a combination of electron microscopy, immuno-electron microscopy (IEM), haemagglutination inhibition or ELISA. Toroviruses can be differentiated from coronaviruses by using IEM [3].
Villus fusion and atrophy and thinning of intestinal wall can be seen on post-mortem.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment. Animals can be supported with fluids to prevent dehydration as a result of the episodes of diarrhoea. Secondary bacterial infections can be treated with antibiotics. Culture and sensitivity is recommended.
Control
Isolation of infected animals and good hygiene and sanitary measures may help reduce the spread of the disease.
| Toroviruses Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Toroviruses Flashcards |
References
- ↑ Kroneman, A., Cornelissen, L.A.H.M., Horzinek, M.C., Groot, R.J.de., Egberink, H.F., (1998) Identification and characterization of a porcine torovirus. Journal of Virology, 72(5):3507-3511; 35 ref.
- ↑ Koopmans, M., Horzinek, M.C., (1994) Toroviruses of animals and humans: a review. Advances in Virus Research, 43:233-273; many ref.
- ↑ Woode, G.N., (1987). Breda and Breda-like viruses: diagnosis, pathology and epidemiology. Novel diarrhoea viruses., 175-191; Ciba Foundation Symposium 128; 23 ref.

|
This article was originally sourced from The Animal Health & Production Compendium (AHPC) published online by CABI during the OVAL Project. The datasheet was accessed on 19 June 2011. |
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Webinars
Failed to load RSS feed from https://www.thewebinarvet.com/infection-control-and-biosecurity/webinars/feed: Error parsing XML for RSS