Difference between revisions of "Cryptosporidium"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m |
|||
| (41 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{review}} |
| − | {{ | + | |
| − | + | {{toplink | |
| − | + | |backcolour = | |
| − | + | |linkpage =Parasites | |
| − | + | |linktext =PARASITES | |
| − | | | + | |pagetype=Bugs |
| − | | | + | |sublink1=Protozoa |
| − | | | + | |subtext1=PROTOZOA |
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Recognition== |
[[Image:Cryptosporidium parvum.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Cryptosporidium parvum'' - Courtesy of the Laboratory of Parasitology, University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine]] | [[Image:Cryptosporidium parvum.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Cryptosporidium parvum'' - Courtesy of the Laboratory of Parasitology, University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine]] | ||
| − | [[Image:Cryptosporidium Life Cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Cryptosporidium Life Cycle | + | [[Image:Cryptosporidium muris.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''C. muris'' - Wikimedia Commons]] |
| + | [[Image:Cryptosporidium Life Cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Cryptosporidium'' Life Cycle - Alexander J. da Silva, PhD/Melanie Moser (PHIL #3386), 2002]] | ||
[[Image:Calf.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Calf - nabrown RVC]] | [[Image:Calf.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Calf - nabrown RVC]] | ||
[[Image:Cryptosporidium ruminant.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Ruminant ''Cryptosporidium'' - Joaquim Castellà Veterinary Parasitology Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona]] | [[Image:Cryptosporidium ruminant.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Ruminant ''Cryptosporidium'' - Joaquim Castellà Veterinary Parasitology Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona]] | ||
| − | + | *Minute protozoan parasite | |
| + | |||
| + | *Wide host range | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Parasitises epithelial cells lining the epithelial cells lining the ailimentary and respiratory tracts | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Developmental stages confined to the '''microvillous brish border''' | ||
| − | + | *''C. parvum'' most associated with disease in domestic animals and in humans | |
| + | **Other species affect birds | ||
| − | + | *Small oocysts of 4-5μm | |
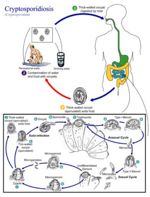
==Life Cycle== | ==Life Cycle== | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | *Direct life cycle | ||
| + | **Only one host | ||
| + | **Homoxenous | ||
| + | |||
| + | *1 week prepatent period | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Sporulated''' oocysts past in faeces | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Autoinfection can occur | ||
| + | **Thin walled oocysts | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Faecal-oral transmission also occurs | ||
| + | **Thick walled oocysts | ||
==Pathogenesis== | ==Pathogenesis== | ||
| − | + | *Causes outbreaks of [[Intestine Diarrhoea - Pathology|diarrhoea]] in young animals | |
| − | + | *Common cause of calf-hood scours | |
| + | **Older animals may be asymptomatic carriers | ||
| + | **Contributes to [[Intestines Catarrhal Enteritis - Pathology#Undifferentiated Neonatal Calf Diarrhoea|undifferentiated neonatal calf diarrhoea]] which is a mixed viral enteritis in calves | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Common infection in AIDS patients | ||
==Epidemiology== | ==Epidemiology== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Direct faecal-oral infection | |
| − | + | **E.g. School parties visiting farms | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | *Water-bourne infection | |
| − | + | **E.g. contaminated water supply may infect hundreds of people | |
| − | + | **Difficult to locate source | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Diagnosis== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | *Faecal smear | |
| − | + | **Ziehl-Neelson (ZN) stain | |
| − | + | **Oocysts stain red against a blue/green background | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | *Immunoassays | |
| − | + | **Detect oocysts in faeces | |
| + | |||
| + | ==Control== | ||
| + | *Isolate/quarantine brought-in calves | ||
| + | **Treat if signs of [[Intestine Diarrhoea - Pathology|diarrhoea]] present | ||
| − | + | *Good hygiene, adequate bedding, disinfection of calf pens is important | |
| − | + | *Prevention/treatment | |
| − | + | **Halofuginone | |
| − | + | ***Halocur or Intervet | |
| − | + | ***Oral dosage | |
| − | |||
Revision as of 14:47, 21 December 2008
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
|
|
Recognition
- Minute protozoan parasite
- Wide host range
- Parasitises epithelial cells lining the epithelial cells lining the ailimentary and respiratory tracts
- Developmental stages confined to the microvillous brish border
- C. parvum most associated with disease in domestic animals and in humans
- Other species affect birds
- Small oocysts of 4-5μm
Life Cycle
- Direct life cycle
- Only one host
- Homoxenous
- 1 week prepatent period
- Sporulated oocysts past in faeces
- Autoinfection can occur
- Thin walled oocysts
- Faecal-oral transmission also occurs
- Thick walled oocysts
Pathogenesis
- Causes outbreaks of diarrhoea in young animals
- Common cause of calf-hood scours
- Older animals may be asymptomatic carriers
- Contributes to undifferentiated neonatal calf diarrhoea which is a mixed viral enteritis in calves
- Common infection in AIDS patients
Epidemiology
- Direct faecal-oral infection
- E.g. School parties visiting farms
- Water-bourne infection
- E.g. contaminated water supply may infect hundreds of people
- Difficult to locate source
Diagnosis
- Faecal smear
- Ziehl-Neelson (ZN) stain
- Oocysts stain red against a blue/green background
- Immunoassays
- Detect oocysts in faeces
Control
- Isolate/quarantine brought-in calves
- Treat if signs of diarrhoea present
- Good hygiene, adequate bedding, disinfection of calf pens is important
- Prevention/treatment
- Halofuginone
- Halocur or Intervet
- Oral dosage
- Halofuginone