Difference between revisions of "Tissue cyst-forming coccidia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Redirected page to Category:Tissue Cyst Forming Coccidia) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | # | + | {{review}} |
| + | |||
| + | {{toplink | ||
| + | |backcolour = | ||
| + | |linkpage =Parasites | ||
| + | |linktext =PARASITES | ||
| + | |pagetype=Bugs | ||
| + | |sublink1=Protozoa | ||
| + | |subtext1=PROTOZOA | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Neospora== | ||
| + | *2 main species | ||
| + | **''Neospora caninum'' in the dog | ||
| + | **''Neospora hughesi'' in the horse | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Sporulated oocysts measuring just 10μm | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Oocyst contains 2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Route of transmission not fully understood | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Often misdiagnosed as ''Toxoplasma gondii'' | ||
| + | **''Sarcocystis'' cysts have thicker walls | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Infection diagnosed by IFAT, ELISA or PCR | ||
| + | **Identification of lesions and organisms in tissue using immunohistochemical staining | ||
| + | **Eliminate other causes of abortion first | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Life cycle''' | ||
| + | *Life cycle similar to ''Toxoplasma gondii'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Limited range of warm-blooded intermediate hosts | ||
| + | **Asexual reproduction occurs in intermediate host forming tissue cysts | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Host range of sexual stage is unknown for ''N.caninum'' | ||
| + | **Intermediate host for ''N.hughesi'' is the horse, but the definitive host is unknown | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Final host | ||
| + | **Dogs pass oocysts | ||
| + | **Role not fully understood in pathogenesis | ||
| + | **5 day prepatent period | ||
| + | **Other wild canids may also act as final definitive hosts | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Intermediate host | ||
| + | **Mostly cattle | ||
| + | **Natural infection has been documented in other herbivores | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Transmission | ||
| + | **Transplacental infection occurs in all intermediate hosts and in the canine final host | ||
| + | ***Transplacental transmission can occur in '''successive pregnancies''' | ||
| + | **In cattle, vertical transmission occurs | ||
| + | ***Post-natal infection occurs but is less common | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Pathogenesis''' | ||
| + | *Dogs | ||
| + | **Occurs mainly in puppies | ||
| + | **Causes ascending paralysis, especially of hind limbs, with muscle wasting | ||
| + | **Causes sudden collapse due to myocarditis | ||
| + | **More than 1 puppy in a litter may be affected, although this may not occur simultaneously | ||
| + | **Successive litters affected | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Cattle | ||
| + | **Commonest cause of infectious abortion in dairy cattle | ||
| + | **Congenitally infected calves can have encephalomyelitis and paresis | ||
| + | **Abortion usually occurs between 5-7 months of gestation but can occur as early as 3 months | ||
| + | **No other clinical signs in the cow | ||
| + | **Repeat abortions possible in same cow (persistently infected) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Horses | ||
| + | **Myeloencephalitis | ||
| + | **Transplacental infection occurs | ||
| + | **Disease only diagnosed in USA | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''Neospora caninum'' in [[Muscles Inflammatory - Pathology#Protozoa|myositis]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Prevention and Control''' | ||
| + | *Do not allow dogs access to calving cows, placental membranes and aborted or dead calves | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Do not allow dogs to defecate in cattle feeding areas | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Identify and cull seropositive cattle, or do not breed from them or their progeny | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Select seronegative cattle for breeding | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Vaccinate | ||
| + | **Only in the USA | ||
| + | **Neoguard or Intervet | ||
| + | **Killed protozoal vaccine for healthy, pregnant cows | ||
| + | **Dosed in first 3 weeks of pregnancy and then every 3-4 weeks during gestation | ||
| + | **Revaccination with 2 doses during each subsequent pregnancy | ||
| + | |||
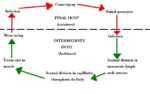
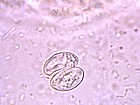
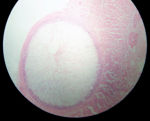
| + | ==Sarcocystis== | ||
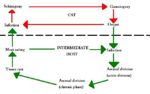
| + | [[Image:Sarcocystis Life Cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcocytis'' Life Cycle Diagram - Dennis Jacobs & Mark Fox RVC]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Sarcocystic.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcocytis'' - Joaquim Castellà Veterinary Parasitology Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Sarcocystis in sheep oesophagus.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcocystis'' in sheep oesophagus - Adam Cuerden]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis - Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Sarcocystis cruzi.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcocystis cruzi'' - Courtesy of the Laboratory of Parasitology, University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine]] | ||
| + | *Most infections are asymptomatic | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Heavy infections are causes of chronic wasting in large animals, hide condemnation and downgrading of carcasses | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''Sarcocystis'' should be differentiated from other tissue-cyst forming coccidia | ||
| + | |||
| + | *There are many species of ''Sarcocystis'' which differ in size from microscopic to several centimetres in length | ||
| + | **''S.neurona'' is an important equine pathogen in the USA | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Infective cyst in the intermediate host is called a '''sarcocyst''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Life Cycle''' | ||
| + | *The individual life cycle of some species is incompletely understood | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Indirect life cycle | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Life cycle alternates between the final and the obligatory intermediate host | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Only '''one''' final and '''one''' intermediate host | ||
| + | |||
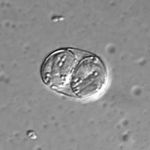
| + | *Sporulated oocyst has 2 sporocysts containing 4 sporozoites | ||
| + | **Naked sporocyst usually seen in faeces as the oocyst wall is very delicate | ||
| + | **Oocyst measures 15μm in length | ||
| + | |||
| + | *No schizogony in final host | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Gametogeny occurs deep in subepithelial tissue | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Faecal oocyst count is low | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Oocysts are sporulated when passed | ||
| + | **Difficult to find on faecal examination as the sporocysts are few in number and small | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Ingestion of sporocyst by intermediate host | ||
| + | **2 phases of rapid asexual reproduction in vascular endothelial cells | ||
| + | **Slow multiplication of bradyzoites in muscle tissue | ||
| + | **Sarcocyst forms with bradyzoites inside, surrounded by a cyst wall and divided into compartments | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Epidemiology''' | ||
| + | *Final hosts are carnivores and omnivores | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Intermediate hosts are herbivores and omnivores | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Humans are the final host for some species and the intermediate hosts for others | ||
| + | **Final host for species infecting cattle and pigs | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Dogs are final hosts for species infecting cattle, sheep, goats, pigs and horses | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Cats are final hosts for species infecting cattle, sheep and pigs | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Pathogenesis''' | ||
| + | *Widespread infection but mostly asymptomatic | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Cause meat inspection losses | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''Sarcocystis'' in [[Muscles Inflammatory - Pathology#Protozoa|myositis]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Experimental infections cause severe, acute pyrexic disease when the organism multiplies in the vascular endothelium | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Can cause chronic wasting disease in cattle and horses | ||
| + | **Causes abortion and post-natal disease in sheep | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis | ||
| + | **Necrotising encephalomyelitis affecting the grey and white matter of the CNS | ||
| + | **Caused by ''S.neurona'' | ||
| + | **Opossum thought to be the definitive host | ||
| + | **Horses thought to be accidental hosts | ||
| + | **Natural intermediate hosts currently unknown | ||
| + | **Western Blotting shows 50% of horses in the USA are seropositive | ||
| + | **Risk factors poorly understood | ||
| + | **Causes spinal cord dysfunction | ||
| + | ***Ataxia and paralysis | ||
| + | |||
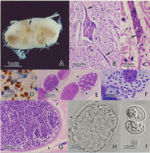
| + | ==Toxoplasma== | ||
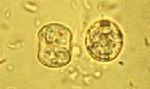
| + | [[Image:Toxoplasma gondii.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Toxoplasma gondii'' - Ke Hu and John Murray]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Toxoplasma sporulated oocyst.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Toxoplasma'' Sporulated Oocyst - Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Toxoplasma Tacchyzoites.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Toxoplasma'' Tacchyzoites - Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Toxoplasma Life Cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Toxoplasma'' Life Cycle Diagram - Dennis Jacobs & Mark Fox RVC]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Toxoplasma gondii 2.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Toxoplasma gondii'' - Courtesy of the Laboratory of Parasitology, University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine]] | ||
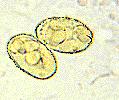
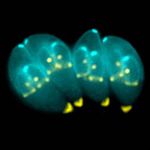
| + | *Major pathogenic species called ''Toxoplasma gondii'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Causes disease in a wide range of animal species including humans | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Important cause of abortion in sheep | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Zoonotic | ||
| + | **Can cause abortion | ||
| + | **Can cause congenitally aquired defects | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Forms a sporulated oocyst which is only 10μm | ||
| + | **Contains 2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Transmission through ingesting the intermediate host or via the faecal-oral route | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Life Cycle''' | ||
| + | *Complex | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Usually indirect | ||
| + | **Referred to as '''facultatively heteroxenous''' | ||
| + | **Intermediate host is not essential for completion of the life cycle | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Gametogony (sexual stage) is host specific for felids | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Any warm blooded animal can act as a facultative intermediate host | ||
| + | **Asexual reproduction occurs in the intermediate host forming tissue cysts | ||
| + | **Intermediate host swallows sporulated oocysts or tissue cysts | ||
| + | **Can be transferred between intermediate hosts by carnivorism | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Cats | ||
| + | **Sporulation occurs in 2-3 days | ||
| + | **Cats either swallow infective (sporulated) oocysts where ''Toxoplasma gondii'' has a prepatent period of 3 weeks | ||
| + | **Or eat the tissues of an infected intermediate host where ''Toxoplasma gondii'' has a prepatent period of 3-10 days | ||
| + | **Self-limiting infection | ||
| + | **Oocysts are shed for 1-2 weeks | ||
| + | ***Shedding can occur later if immunity wanes or cat is immuno-compromised | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Intermediate host | ||
| + | **3 sources of infection | ||
| + | ***Oocysts from environment contaminated by cat faeces | ||
| + | ***Eating cysts in tissues of other infected hosts through carnivorism or undercooked meat | ||
| + | ***Transplacental transmission in some host species during the acute phase of infection | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Acute phase of infection | ||
| + | **After infection of the intermediate host the organism undergoes a phase of rapid division and dissemination throughout the body | ||
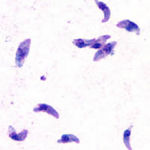
| + | ***Parasite enters cell and asexual reproduction occurs by '''endodyogeny''' (budding) producing 8-16 '''tachyzoites''' | ||
| + | ***Tachyzoites are released when host cell bursts | ||
| + | ***Haematogenous spread as more cells are infected | ||
| + | ***Infection continues until the animal develops immunity (around 2 weeks) at which point the infection enters the chronic phase | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Chronic phase of infection | ||
| + | **Occurs once the host's immune response has become effective | ||
| + | ***Groups of slow growing intracellular '''bradyzoites''' become walled off forming infective '''cysts''' | ||
| + | ***Bradyzoites inside cysts are protected from the host immune response whereas extracellular tachyzoites are killed | ||
| + | ***Cysts remain viable for months to years and are particularly numerous in muscle and nervous tissue | ||
| + | ***If immunity is suppressed the infection can revert to the acute form | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Pathogenesis''' | ||
| + | *Cat | ||
| + | **In the intestinal phase of infection only the superficial cells at the tips of the villi are affected | ||
| + | **Little significant pathogenicity | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Sheep | ||
| + | **Mostly asymptomatic | ||
| + | **However, if a non-immune ewe is infected during pregnancy the consequences will be serious | ||
| + | ***Infection during the first trimester leads to resorption | ||
| + | **Infection during the second trimester leads to foetal death and mummification | ||
| + | **Infection during the last trimester leads to a weak or stillborn lamb | ||
| + | **Aborted ewes show focal necrotic placentitis with white lesions in the cotyledons and foetal tissue | ||
| + | **Diagnosis is confirmed by Giemsa and serology of the ewe's blood | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Clinical outbreaks of toxoplasmosis are '''sporadic''' | ||
| + | **Immunity is acquired before tupping | ||
| + | **Significant ill-effects are unlikely if immune ewes are infected during pregnancy | ||
| + | **Not shed from sheep to sheep so predicting outbreaks is difficult | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Humans | ||
| + | **Mostly asymptomatic | ||
| + | **Virulent strains cause flu-like symptoms, malaise and/or lymphadenopathy | ||
| + | **In immunodeficient patients, disease can even be caused by avirulent strains | ||
| + | **If a non-immune women is infected during pregnancy, abortion or the birth of a congenitally infected child can result | ||
| + | ***E.g. Hydrocephalus, opthalmitis, mental retardation | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Dogs | ||
| + | **Complication of canine distemper | ||
| + | **Causes [[Respiratory Parasitic Infections - Pathology#Toxoplasmosis|pneumonia]] and encephalitis | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Cattle and horses | ||
| + | **Sometimes infectious causing opthalmitis | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Toxoplasma can cause [[Pancreas Inflammatory - Pathology#Acute haemorrhagic pancreatitis|acute interstitial pancreatitis]] in systemic toxoplasmosis | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''Toxoplasma gondii'' causes [[Muscles Inflammatory - Pathology#Protozoa|myositis]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Epidemiology''' | ||
| + | *Serology | ||
| + | **Sabin-Feldman Dye test (old method) | ||
| + | **ELISA | ||
| + | **Mouse inoculation for confirmation | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Cat | ||
| + | **30-80% test seropositive | ||
| + | **Each cat sheds oocysts for 1-2 weeks of its life | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Human | ||
| + | **30% seropositive in UK, 70% seropositive in France | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Meat animals | ||
| + | **Significant proportion of cattle, sheep, pigs and rabbits can tissue cysts | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Prevention''' | ||
| + | *Cat | ||
| + | **Impossible if cat is allowed outdoors due to hunting | ||
| + | **If kept indoors, only canned food should be fed and vermin controlled | ||
| + | **ELISA to check if seropositive | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Human | ||
| + | **Avoid oocyst ingestion | ||
| + | ***Wash potentially contaminated raw food thoroughly | ||
| + | ***Wash hands after gardening or handling cats and especially before eating | ||
| + | ***Clean out cat litter trays every day before oocysts sporulate | ||
| + | **Avoid ingestion of tissue cysts | ||
| + | ***Do not eat undercooked meat | ||
| + | ***Wash hands after handling raw meat | ||
| + | ***Take care when lambing or dealing with sheep abortions and stillbirths | ||
| + | ***Pregnant women should avoid lambing altogether | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Sheep | ||
| + | **Toxovax vaccine | ||
| + | ***Live, avirulent strain of ''Toxoplasma'' | ||
| + | ***Does not form bradyzoites or tissue cysts | ||
| + | ***Killed by host immune system | ||
| + | ***Single dose given 6 weeks before tupping | ||
| + | ***Protects for 2 years | ||
| + | ***Immunity boosted by natural challenge | ||
| + | **Medicated feed can be given daily during the main risk period | ||
| + | ***14 weeks before lambing | ||
| + | **The best method of protection is to prevent cats from contaminating the pasture, lambing sheds and feed stores | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==[[Protozoa Flashcards - Wikibugs|Protozoa Flashcards]]== | ||
Revision as of 15:41, 7 January 2009
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
|
|
Neospora
- 2 main species
- Neospora caninum in the dog
- Neospora hughesi in the horse
- Sporulated oocysts measuring just 10μm
- Oocyst contains 2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites
- Route of transmission not fully understood
- Often misdiagnosed as Toxoplasma gondii
- Sarcocystis cysts have thicker walls
- Infection diagnosed by IFAT, ELISA or PCR
- Identification of lesions and organisms in tissue using immunohistochemical staining
- Eliminate other causes of abortion first
Life cycle
- Life cycle similar to Toxoplasma gondii
- Limited range of warm-blooded intermediate hosts
- Asexual reproduction occurs in intermediate host forming tissue cysts
- Host range of sexual stage is unknown for N.caninum
- Intermediate host for N.hughesi is the horse, but the definitive host is unknown
- Final host
- Dogs pass oocysts
- Role not fully understood in pathogenesis
- 5 day prepatent period
- Other wild canids may also act as final definitive hosts
- Intermediate host
- Mostly cattle
- Natural infection has been documented in other herbivores
- Transmission
- Transplacental infection occurs in all intermediate hosts and in the canine final host
- Transplacental transmission can occur in successive pregnancies
- In cattle, vertical transmission occurs
- Post-natal infection occurs but is less common
- Transplacental infection occurs in all intermediate hosts and in the canine final host
Pathogenesis
- Dogs
- Occurs mainly in puppies
- Causes ascending paralysis, especially of hind limbs, with muscle wasting
- Causes sudden collapse due to myocarditis
- More than 1 puppy in a litter may be affected, although this may not occur simultaneously
- Successive litters affected
- Cattle
- Commonest cause of infectious abortion in dairy cattle
- Congenitally infected calves can have encephalomyelitis and paresis
- Abortion usually occurs between 5-7 months of gestation but can occur as early as 3 months
- No other clinical signs in the cow
- Repeat abortions possible in same cow (persistently infected)
- Horses
- Myeloencephalitis
- Transplacental infection occurs
- Disease only diagnosed in USA
- Neospora caninum in myositis
Prevention and Control
- Do not allow dogs access to calving cows, placental membranes and aborted or dead calves
- Do not allow dogs to defecate in cattle feeding areas
- Identify and cull seropositive cattle, or do not breed from them or their progeny
- Select seronegative cattle for breeding
- Vaccinate
- Only in the USA
- Neoguard or Intervet
- Killed protozoal vaccine for healthy, pregnant cows
- Dosed in first 3 weeks of pregnancy and then every 3-4 weeks during gestation
- Revaccination with 2 doses during each subsequent pregnancy
Sarcocystis
- Most infections are asymptomatic
- Heavy infections are causes of chronic wasting in large animals, hide condemnation and downgrading of carcasses
- Sarcocystis should be differentiated from other tissue-cyst forming coccidia
- There are many species of Sarcocystis which differ in size from microscopic to several centimetres in length
- S.neurona is an important equine pathogen in the USA
- Infective cyst in the intermediate host is called a sarcocyst
Life Cycle
- The individual life cycle of some species is incompletely understood
- Indirect life cycle
- Life cycle alternates between the final and the obligatory intermediate host
- Only one final and one intermediate host
- Sporulated oocyst has 2 sporocysts containing 4 sporozoites
- Naked sporocyst usually seen in faeces as the oocyst wall is very delicate
- Oocyst measures 15μm in length
- No schizogony in final host
- Gametogeny occurs deep in subepithelial tissue
- Faecal oocyst count is low
- Oocysts are sporulated when passed
- Difficult to find on faecal examination as the sporocysts are few in number and small
- Ingestion of sporocyst by intermediate host
- 2 phases of rapid asexual reproduction in vascular endothelial cells
- Slow multiplication of bradyzoites in muscle tissue
- Sarcocyst forms with bradyzoites inside, surrounded by a cyst wall and divided into compartments
Epidemiology
- Final hosts are carnivores and omnivores
- Intermediate hosts are herbivores and omnivores
- Humans are the final host for some species and the intermediate hosts for others
- Final host for species infecting cattle and pigs
- Dogs are final hosts for species infecting cattle, sheep, goats, pigs and horses
- Cats are final hosts for species infecting cattle, sheep and pigs
Pathogenesis
- Widespread infection but mostly asymptomatic
- Cause meat inspection losses
- Sarcocystis in myositis
- Experimental infections cause severe, acute pyrexic disease when the organism multiplies in the vascular endothelium
- Can cause chronic wasting disease in cattle and horses
- Causes abortion and post-natal disease in sheep
- Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis
- Necrotising encephalomyelitis affecting the grey and white matter of the CNS
- Caused by S.neurona
- Opossum thought to be the definitive host
- Horses thought to be accidental hosts
- Natural intermediate hosts currently unknown
- Western Blotting shows 50% of horses in the USA are seropositive
- Risk factors poorly understood
- Causes spinal cord dysfunction
- Ataxia and paralysis
Toxoplasma
- Major pathogenic species called Toxoplasma gondii
- Causes disease in a wide range of animal species including humans
- Important cause of abortion in sheep
- Zoonotic
- Can cause abortion
- Can cause congenitally aquired defects
- Forms a sporulated oocyst which is only 10μm
- Contains 2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites
- Transmission through ingesting the intermediate host or via the faecal-oral route
Life Cycle
- Complex
- Usually indirect
- Referred to as facultatively heteroxenous
- Intermediate host is not essential for completion of the life cycle
- Gametogony (sexual stage) is host specific for felids
- Any warm blooded animal can act as a facultative intermediate host
- Asexual reproduction occurs in the intermediate host forming tissue cysts
- Intermediate host swallows sporulated oocysts or tissue cysts
- Can be transferred between intermediate hosts by carnivorism
- Cats
- Sporulation occurs in 2-3 days
- Cats either swallow infective (sporulated) oocysts where Toxoplasma gondii has a prepatent period of 3 weeks
- Or eat the tissues of an infected intermediate host where Toxoplasma gondii has a prepatent period of 3-10 days
- Self-limiting infection
- Oocysts are shed for 1-2 weeks
- Shedding can occur later if immunity wanes or cat is immuno-compromised
- Intermediate host
- 3 sources of infection
- Oocysts from environment contaminated by cat faeces
- Eating cysts in tissues of other infected hosts through carnivorism or undercooked meat
- Transplacental transmission in some host species during the acute phase of infection
- 3 sources of infection
- Acute phase of infection
- After infection of the intermediate host the organism undergoes a phase of rapid division and dissemination throughout the body
- Parasite enters cell and asexual reproduction occurs by endodyogeny (budding) producing 8-16 tachyzoites
- Tachyzoites are released when host cell bursts
- Haematogenous spread as more cells are infected
- Infection continues until the animal develops immunity (around 2 weeks) at which point the infection enters the chronic phase
- After infection of the intermediate host the organism undergoes a phase of rapid division and dissemination throughout the body
- Chronic phase of infection
- Occurs once the host's immune response has become effective
- Groups of slow growing intracellular bradyzoites become walled off forming infective cysts
- Bradyzoites inside cysts are protected from the host immune response whereas extracellular tachyzoites are killed
- Cysts remain viable for months to years and are particularly numerous in muscle and nervous tissue
- If immunity is suppressed the infection can revert to the acute form
- Occurs once the host's immune response has become effective
Pathogenesis
- Cat
- In the intestinal phase of infection only the superficial cells at the tips of the villi are affected
- Little significant pathogenicity
- Sheep
- Mostly asymptomatic
- However, if a non-immune ewe is infected during pregnancy the consequences will be serious
- Infection during the first trimester leads to resorption
- Infection during the second trimester leads to foetal death and mummification
- Infection during the last trimester leads to a weak or stillborn lamb
- Aborted ewes show focal necrotic placentitis with white lesions in the cotyledons and foetal tissue
- Diagnosis is confirmed by Giemsa and serology of the ewe's blood
- Clinical outbreaks of toxoplasmosis are sporadic
- Immunity is acquired before tupping
- Significant ill-effects are unlikely if immune ewes are infected during pregnancy
- Not shed from sheep to sheep so predicting outbreaks is difficult
- Humans
- Mostly asymptomatic
- Virulent strains cause flu-like symptoms, malaise and/or lymphadenopathy
- In immunodeficient patients, disease can even be caused by avirulent strains
- If a non-immune women is infected during pregnancy, abortion or the birth of a congenitally infected child can result
- E.g. Hydrocephalus, opthalmitis, mental retardation
- Dogs
- Complication of canine distemper
- Causes pneumonia and encephalitis
- Cattle and horses
- Sometimes infectious causing opthalmitis
- Toxoplasma can cause acute interstitial pancreatitis in systemic toxoplasmosis
- Toxoplasma gondii causes myositis
Epidemiology
- Serology
- Sabin-Feldman Dye test (old method)
- ELISA
- Mouse inoculation for confirmation
- Cat
- 30-80% test seropositive
- Each cat sheds oocysts for 1-2 weeks of its life
- Human
- 30% seropositive in UK, 70% seropositive in France
- Meat animals
- Significant proportion of cattle, sheep, pigs and rabbits can tissue cysts
Prevention
- Cat
- Impossible if cat is allowed outdoors due to hunting
- If kept indoors, only canned food should be fed and vermin controlled
- ELISA to check if seropositive
- Human
- Avoid oocyst ingestion
- Wash potentially contaminated raw food thoroughly
- Wash hands after gardening or handling cats and especially before eating
- Clean out cat litter trays every day before oocysts sporulate
- Avoid ingestion of tissue cysts
- Do not eat undercooked meat
- Wash hands after handling raw meat
- Take care when lambing or dealing with sheep abortions and stillbirths
- Pregnant women should avoid lambing altogether
- Avoid oocyst ingestion
- Sheep
- Toxovax vaccine
- Live, avirulent strain of Toxoplasma
- Does not form bradyzoites or tissue cysts
- Killed by host immune system
- Single dose given 6 weeks before tupping
- Protects for 2 years
- Immunity boosted by natural challenge
- Medicated feed can be given daily during the main risk period
- 14 weeks before lambing
- The best method of protection is to prevent cats from contaminating the pasture, lambing sheds and feed stores
- Toxovax vaccine