Difference between revisions of "Lizard Oral Granuloma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{review}} | {{review}} | ||
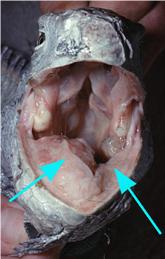
| − | [[Image:Oral_granuloma.jpg|300px|thumb|right|'''A large swelling can be seen on the lower jaw accompanied by several abscesses along the upper gingiva''' (Copyright © RVC)]] | + | [[Image:Oral_granuloma.jpg|300px|thumb|right|'''A large swelling can be seen on the lower jaw accompanied by several abscesses along the upper gingiva''' (Copyright © RVC and its licensors, Sean Bobbit, Sue Evans, Andrew Devare and Claire Moore. All rights reserved)]] |
| − | Oral abscesses are not uncommon in captive lizards. They may occur as an extension of | + | Oral abscesses are not uncommon in captive lizards. They may occur as an extension of periodontal disease or due to [[Lizard Traumatic Wounds|trauma]]. The main cause is a bacterial infection. |
*'''Clinical signs''' include swelling and anorexia. | *'''Clinical signs''' include swelling and anorexia. | ||
*'''Diagnosis''' - history, [[Lizard Physical Examination|physical examination]], culture and radiology. | *'''Diagnosis''' - history, [[Lizard Physical Examination|physical examination]], culture and radiology. | ||
*'''Treatment''' - surgical debridement and antibiotics as indicated by culture. | *'''Treatment''' - surgical debridement and antibiotics as indicated by culture. | ||
| − | *'''Prevention''' - Appropriate [[ | + | *'''Prevention''' - Appropriate [[Lizard Diet|diet]]. |
[[Category:Lizard_Gastrointestinal_Diseases|O]] | [[Category:Lizard_Gastrointestinal_Diseases|O]] | ||
Revision as of 17:54, 2 April 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Oral abscesses are not uncommon in captive lizards. They may occur as an extension of periodontal disease or due to trauma. The main cause is a bacterial infection.
- Clinical signs include swelling and anorexia.
- Diagnosis - history, physical examination, culture and radiology.
- Treatment - surgical debridement and antibiotics as indicated by culture.
- Prevention - Appropriate diet.