Difference between revisions of "Lizard Cardiovascular Disease"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Redirected page to Reptile Cardiovascular Disease#Lizards) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{review}} | |
| + | Cardiovascular disease may be primary or secondary. | ||
| + | [[Image:Cardiovascular_lizard.jpg|400px|thumb|right]] | ||
| + | '''Aetiology''' - it may be infectious, parasitic, congenital or nutritional (e.g. calcification of large vessels) | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Clinical signs''' - Clinical signs of cardiovascular disease are usually non-specific such as anorexia and weight loss. Signs such as swelling in the area of the heart, peripheral oedema and ascites warrant investigation of the cardiovascular system. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Diagnosis''' | ||
| + | *History | ||
| + | *[[Lizard Physical Examination|Physical examination]], especially auscultation | ||
| + | *Blood culture | ||
| + | *Radiography | ||
| + | *Ultrasound | ||
| + | *Doppler flow detector | ||
| + | *Electrocardiography though interpretation may be a problem | ||
| + | *[[Lizard Necropsy|Necropsy]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Treatment''' - Includes supportive treatment, antimicrobial if infectious, and correction of [[Lizard Husbandry Requirements|husbandry]]. | ||
[[Category:Lizard_Diseases|C]] | [[Category:Lizard_Diseases|C]] | ||
Revision as of 18:23, 28 April 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
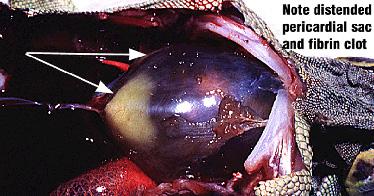
Cardiovascular disease may be primary or secondary.
Aetiology - it may be infectious, parasitic, congenital or nutritional (e.g. calcification of large vessels)
Clinical signs - Clinical signs of cardiovascular disease are usually non-specific such as anorexia and weight loss. Signs such as swelling in the area of the heart, peripheral oedema and ascites warrant investigation of the cardiovascular system.
Diagnosis
- History
- Physical examination, especially auscultation
- Blood culture
- Radiography
- Ultrasound
- Doppler flow detector
- Electrocardiography though interpretation may be a problem
- Necropsy
Treatment - Includes supportive treatment, antimicrobial if infectious, and correction of husbandry.