Difference between revisions of "Fleas"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Redirected page to Category:Fleas) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{review}} | ||
| + | <categorytree mode=pages style="float:right; clear:right; margin-left:1ex; border:1px solid gray; padding:0.7ex; background-color:white;">Insecta</categorytree> | ||
| − | # | + | |
| + | [[Flea Structure]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==[[Flea Life Cycle]]== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Flea Habitat and Control]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Habitats== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Only approximately '''5%''' of the flea population will be on the animal at any one time (and usually it is a much smaller percentage) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The rest of the population are in the '''environment''' | ||
| + | **E.g. Eggs, larvae, pupae and unfed adults | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Fleas accumulate in certain '''hot spots''' where the animal spends the majority of its time | ||
| + | **E.g. Warm, shady, humid ares | ||
| + | **E.g. Outdoors in warmer climates or inside in temperate climates | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Very large numbers of eggs are found in areas where cats land after jumping as they have been dislodged | ||
| + | **E.g. Beside sofas | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Control== | ||
| + | [[Image:Flea Dirt.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Flea Dirt - Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
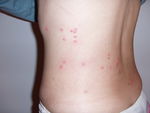
| + | [[Image:Flea Bites.jpg|right|Thumb|150px|Flea bites on a human - Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| + | *Single or occasional treatments will only give temporary relief from fleas as the majority of the population is '''in the environment''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Appropriate action must be taken to stop re-infestation | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The animal must be rid of its resident flea population | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The animal should be protected against subsequent re-infestation | ||
| + | **From within the home | ||
| + | **From outside the home | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The environmental reservoir population should be eliminated | ||
| + | **Animal treatment to deplete reservoir | ||
| + | ***Adulticides | ||
| + | ***Adulticides with larvicidal effects | ||
| + | ***Insect growth regulators (IGR's) | ||
| + | **Direct chemical treatment of domestic environment | ||
| + | ***Insecticides | ||
| + | ***Insect growth regulators | ||
| + | ***Inorganic chemicals | ||
| + | ***Entomophagous nematodes (These are parasitic nematodes which predate other parasite eggs) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *To prevent resistance occurring, control methods should not rely solely on chemical methods | ||
| + | **Hygiene such as regular vacuuming and washing of the animal's bedding should also occur for the most effective treatment | ||
| + | |||
| + | *For more information on the chemicals used for flea treatment click [[Ectoparasiticides|here]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Species of veterinary importance== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <big> | ||
| + | '''[[Ctenocephalides felis|''Ctenocephalides felis'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Ctenocephalides canis|''Ctenocephalides canis'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Ceratophyllus gallinae|''Ceratophyllus gallinae'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Pulex irritans|''Pulex irritans'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Spilopsyllus cuniculi|''Spilopsyllus cuniculi'']] | ||
| + | </big> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Other important flea species=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Fleas of wildlife can sometimes infect domestic animals | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Tunga penetrans|''Tunga penetrans'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Nosopsyllus fasciatus|''Nosopsyllus fasciatus'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Echisnophaga gallinacea|''Echisnophaga gallinacea'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Archaeopsylla erinacei|''Archaeopsylla erinacei'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==[[Fleas Flashcards]]== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Links== | ||
| + | ''Internal'' | ||
| + | *[[Skin Immunologic - Pathology#Flea bite hypersensitivity|Flea allergic dermatitis (FAD)]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Fleas act as intermediate hosts for [[Dipylidium|'''''Dipylidium'' tapeworms''']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Fleas act as vectors for [[Myxomatosis|myxomatosis]] in rabbits | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''External'' | ||
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flea Wikipedia- Fleas] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Fleas]] | ||
Revision as of 22:37, 19 May 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Flea Life Cycle
Habitats
- Only approximately 5% of the flea population will be on the animal at any one time (and usually it is a much smaller percentage)
- The rest of the population are in the environment
- E.g. Eggs, larvae, pupae and unfed adults
- Fleas accumulate in certain hot spots where the animal spends the majority of its time
- E.g. Warm, shady, humid ares
- E.g. Outdoors in warmer climates or inside in temperate climates
- Very large numbers of eggs are found in areas where cats land after jumping as they have been dislodged
- E.g. Beside sofas
Control
- Single or occasional treatments will only give temporary relief from fleas as the majority of the population is in the environment
- Appropriate action must be taken to stop re-infestation
- The animal must be rid of its resident flea population
- The animal should be protected against subsequent re-infestation
- From within the home
- From outside the home
- The environmental reservoir population should be eliminated
- Animal treatment to deplete reservoir
- Adulticides
- Adulticides with larvicidal effects
- Insect growth regulators (IGR's)
- Direct chemical treatment of domestic environment
- Insecticides
- Insect growth regulators
- Inorganic chemicals
- Entomophagous nematodes (These are parasitic nematodes which predate other parasite eggs)
- Animal treatment to deplete reservoir
- To prevent resistance occurring, control methods should not rely solely on chemical methods
- Hygiene such as regular vacuuming and washing of the animal's bedding should also occur for the most effective treatment
- For more information on the chemicals used for flea treatment click here
Species of veterinary importance
Other important flea species
- Fleas of wildlife can sometimes infect domestic animals
Fleas Flashcards
Links
Internal
- Fleas act as intermediate hosts for Dipylidium tapeworms
- Fleas act as vectors for myxomatosis in rabbits
External