Difference between revisions of "Immunoglobulin G"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with '{{review}} <p>''Shortened to IgG''</p> thumb|150px|right|'''IgG''' thumb|right|150px|IgG - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008 <p>IgG is the major antib…') |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{review}} |
| − | + | <p>''Shortened to IgG''</p> | |
| − | [[Image:LH IgG.png|thumb| | + | [[Image:LH IgG.png|thumb|150px|right|'''IgG''']] |
| − | [[Image:IgG.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:IgG.jpg|thumb|right|150px|IgG - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] |
| − | + | <p>IgG is the major antibody in blood plasma and constitutes at least 80% of all antibody in the body. It is the smallest immunoglobulin so it can readily leave the blood plasma and enter tissues.</p> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | IgG is the major antibody in blood plasma | ||
| − | |||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| − | + | <p>IgG is Y-shaped with three constant regions and a heavy chain subunit type γ. There are several different IgG subclasses depending on the species coded for by the IGHG gene. | |
| − | IgG is Y-shaped | + | *Ruminants have three subclasses |
| − | + | **G1-G3 | |
| − | + | **IgG1 is the major antibody in ruminant mucosal secretions and colostrum | |
| − | + | * Dogs, rodents (and cats?) have four subclasses | |
| − | + | **Dogs: G1-G4 | |
| − | + | **Rodents: G1-G3 (G2a, G2b) | |
| − | + | *Pigs have five subclasses | |
| − | + | **G1-G4 (G2a, G2b) | |
| − | + | *Horses have six subclasses | |
| − | + | **G1-G6</p> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Production== | ==Production== | ||
| − | + | <p>IgG is produced by plasma cells in the spleen, bone marrow and lymph nodes.</p> | |
| − | IgG is produced by | ||
| − | |||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
| − | + | <p> | |
| − | Some IgG subclasses can activate complement via the classical pathway | + | *Some IgG subclasses can activate complement via the classical pathway |
| − | + | *Some subclasses act as targets for macrophages, eosinophils and [[Neutrophils|neutrophils]] | |
| − | + | ** It is therefore the major antibody in tissue fluids and lymph | |
| − | + | *IgG specifically binds to antigens on bacteria | |
| − | [[Immunoglobulins|Immunoglobulins]] | + | **Causing agglutination and opsonisation</p> |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | [[Immunoglobulin A|Immunoglobulin A]] | + | ---- |
| − | + | <center><b><sup>[[Immunoglobulins|Immunoglobulins]]: [[Immunoglobulin A|Immunoglobulin A]], [[Immunoglobulin D|Immunoglobulin D]], [[Immunoglobulin E - WikiBlood|Immunoglobulin E]], [[Immunoglobulin G - WikiBlood|Immunoglobulin G]] & [[Immunoglobulin M - WikiBlood|Immunoglobulin M]]</sup></b></center> | |
| − | [[Immunoglobulin D|Immunoglobulin D]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[Immunoglobulin E|Immunoglobulin E]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[Immunoglobulin M|Immunoglobulin M]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | < | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 16:25, 12 June 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Shortened to IgG
IgG is the major antibody in blood plasma and constitutes at least 80% of all antibody in the body. It is the smallest immunoglobulin so it can readily leave the blood plasma and enter tissues.
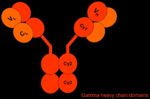
Structure
IgG is Y-shaped with three constant regions and a heavy chain subunit type γ. There are several different IgG subclasses depending on the species coded for by the IGHG gene.
- Ruminants have three subclasses
- G1-G3
- IgG1 is the major antibody in ruminant mucosal secretions and colostrum
- Dogs, rodents (and cats?) have four subclasses
- Dogs: G1-G4
- Rodents: G1-G3 (G2a, G2b)
- Pigs have five subclasses
- G1-G4 (G2a, G2b)
- Horses have six subclasses
- G1-G6
Production
IgG is produced by plasma cells in the spleen, bone marrow and lymph nodes.
Function
- Some IgG subclasses can activate complement via the classical pathway
- Some subclasses act as targets for macrophages, eosinophils and neutrophils
- It is therefore the major antibody in tissue fluids and lymph
- IgG specifically binds to antigens on bacteria
- Causing agglutination and opsonisation