Difference between revisions of "Immunoglobulin E"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - 'Immunoglobulin E - WikiBlood' to 'Immunoglobulin E') |
m (Text replace - 'IgM' to 'IgM') |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Image:LH IgE.png|thumb|150px|right|'''IgE''']] | [[Image:LH IgE.png|thumb|150px|right|'''IgE''']] | ||
[[Image:IgE.jpg|thumb|right|150px|IgE - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | [[Image:IgE.jpg|thumb|right|150px|IgE - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | ||
| − | <p>Unlike IgM, IgG and [[IgA]], IgE does not function as a soluble antibody and is found in low levels in blood plasma. Like [[IgA]] it is produced by plasma cells and is mainly localised to mucosal surfaces.</p> | + | <p>Unlike [[IgM]], IgG and [[IgA]], IgE does not function as a soluble antibody and is found in low levels in blood plasma. Like [[IgA]] it is produced by plasma cells and is mainly localised to mucosal surfaces.</p> |
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
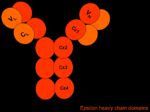
<p>IgE is Y-shaped with heavy chain type ε, and exists as a monomer.</p> | <p>IgE is Y-shaped with heavy chain type ε, and exists as a monomer.</p> | ||
Revision as of 16:30, 12 June 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Shortened to IgE
Unlike IgM, IgG and IgA, IgE does not function as a soluble antibody and is found in low levels in blood plasma. Like IgA it is produced by plasma cells and is mainly localised to mucosal surfaces.
Structure
IgE is Y-shaped with heavy chain type ε, and exists as a monomer.
Note: Janeway [1] states that IgE has no hinge region whereas Tizard [2] indicates that it does.
Production
It is produced when Th2 cells stimulate CD40 and produce Il-4 and Il-13 which causes B cell differentiation to plasma cells and class switching to IgE production.
Function
- IgE triggers acute inflammation by binding to the FCεRI receptors on mast cells in the lamina propria and basophils, causing degranulation
- It is involved in type I hypersensitivity reactions
- Cross-linking of IgE molecules by antigen triggers mast cell degranulation and an inflammatory response
- IgE has considerable involvement in producing immunity to parasitic worms and particularly nematode parasites
- It may mediate their expulsion or killing via mast cell activity, cytotoxic eosinophils, macrophages, and so on
References