Difference between revisions of "Actinobacillosis - Cattle"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (moved Actinobacillosis to Actinobacillosis - Cattle) |
|||
| (61 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{unfinished}} | |
| − | + | *"Wooden tongue" | |
| + | *In cattle - very widespread in world, but rather sporadic, less common now than it was. | ||
| − | == | + | ====Clinical==== |
| − | + | *Seen in youngish animals in beef breed, especially sucklers on poor forage. | |
| − | + | *Starts like [[Picornaviridae#Foot and Mouth Disease Virus|foot and mouth disease]] - dull, salivating (if only one animal is unlikely to foot and mouth). - nearly always sporadic. | |
| − | + | *ongue feels like a big lump of wood especially dorsal part of posterior 2/3rds. | |
| − | == | + | *Small areas of ulceration are often found on side of [[Oral Cavity - Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|tongue]]. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ====Pathogenesis==== | |
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
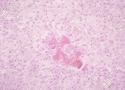
[[Image:woodentongue2.gif|right|thumb|125px|<small><center>'Sulpher body' of Actinobacillosis (Courtesy of Alun Williams (RVC))</center></small>]] | [[Image:woodentongue2.gif|right|thumb|125px|<small><center>'Sulpher body' of Actinobacillosis (Courtesy of Alun Williams (RVC))</center></small>]] | ||
| + | *Very similar to [[Mandibular Osteomyelitis|Mandibular Osteomyelitis]] ("lumpy jaw"). | ||
| − | + | *'''Causal agent''': [[Actinobacillus lignieresii]] (small gram -ve) gets into [[Oral Cavity - Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|tongue]] via small abrasions. | |
| + | **Pathogen is very widespread in environment. | ||
| + | *Progressive disease - low virulence but high persistence so animal may stop eating and eventually die but can be treated. | ||
| − | + | ====Pathology==== | |
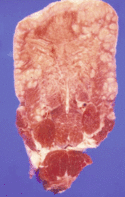
| − | + | [[Image:Woodentongue1.gif|thumb|125px|<small><center>Fibrous Stroma - Cut Surface of actinobacillosis affected tongue (Courtesy of Alun Williams (RVC))</center></small>]] | |
| − | + | *If cut into [[Oral Cavity - Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|tongue]], substance of [[Oral Cavity - Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|tongue]] changed to fibrous stroma with raised red nodules. (2-3mm across). | |
| − | + | *This lesion is a pyogenic granuloma with central '''sulphur body'''. | |
| − | == | + | *Can spread from [[Oral Cavity - Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|tongue]] to other tissues e.g. retropharyngeal [[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph nodes]] and palate. |
| − | + | *This type of lesion is caused by the host response to the pathogen, rather than directly a pathogen effect. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | =====Other sites===== |
| − | + | *Occasionally can see generalised infections but more commonly spreads to local lymph nodes of [[Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology|alimentary tract]]. | |
| + | *Organism can be inhaled causing [[Actinobacillus lignieresii|actinobacillus pneumonia]]. | ||
| + | *Can affect [[The Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology|rumen]] wall. | ||
| + | *In skin forms a neoplastic like mass in dermis. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Also called '''Actinobacillosis''' | |
| − | + | *Caused by ''[[Actinobacillus lignieresii]]'' | |
| − | + | *Usually due to direct penetration into tongue of cattle | |
| + | *Small granulomatous lesions containing 'sulfa granules' of large numbers of gram-negative rods | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Category:Tongue_-_Pathology]][[Category:Cattle]] | |
| − | [[Category:Tongue_-_Pathology]][[Category: | + | [[Category:To Do - Caz]] |
| − | [[Category: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 20:37, 26 July 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
- "Wooden tongue"
- In cattle - very widespread in world, but rather sporadic, less common now than it was.
Clinical
- Seen in youngish animals in beef breed, especially sucklers on poor forage.
- Starts like foot and mouth disease - dull, salivating (if only one animal is unlikely to foot and mouth). - nearly always sporadic.
- ongue feels like a big lump of wood especially dorsal part of posterior 2/3rds.
- Small areas of ulceration are often found on side of tongue.
Pathogenesis
- Very similar to Mandibular Osteomyelitis ("lumpy jaw").
- Causal agent: Actinobacillus lignieresii (small gram -ve) gets into tongue via small abrasions.
- Pathogen is very widespread in environment.
- Progressive disease - low virulence but high persistence so animal may stop eating and eventually die but can be treated.
Pathology
- If cut into tongue, substance of tongue changed to fibrous stroma with raised red nodules. (2-3mm across).
- This lesion is a pyogenic granuloma with central sulphur body.
- Can spread from tongue to other tissues e.g. retropharyngeal lymph nodes and palate.
- This type of lesion is caused by the host response to the pathogen, rather than directly a pathogen effect.
Other sites
- Occasionally can see generalised infections but more commonly spreads to local lymph nodes of alimentary tract.
- Organism can be inhaled causing actinobacillus pneumonia.
- Can affect rumen wall.
- In skin forms a neoplastic like mass in dermis.
- Also called Actinobacillosis
- Caused by Actinobacillus lignieresii
- Usually due to direct penetration into tongue of cattle
- Small granulomatous lesions containing 'sulfa granules' of large numbers of gram-negative rods