Difference between revisions of "Rhodococcus equi"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Introduction) |
|||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{unfinished}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Overview=== | |
| − | + | *Gram-positive aerobic saprophyte found worldwide | |
| − | + | *Found in soil and intestinal tract of animals | |
| + | *Replicates at warm temperatures in soils contaminated by faeces of herbivores | ||
| + | *Opportunistic respiratory pathogen of foals under 6 months causing suppurative [[Respiratory Bacterial Infections - Pathology#Rhodococcus equi|bronchoneumonia]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Characteristics=== | |
| − | + | *Grows on non-enriched media | |
| + | *Salmon-pink mucoid colonies due to capsule and pigment production | ||
| + | *No haemolysis on blood agar | ||
| + | *No growth on MacConkey agar | ||
| + | *Aerobic, non-motile | ||
| + | *CAMP test-positive | ||
| + | *Catalase positive, oxidase negative, weakly acid-fast | ||
| + | *Found as cocci and rods | ||
| + | *Intracellular pathogen | ||
| − | == | + | ===Pathogenesis and pathogenicity=== |
| − | + | *Organism present in faeces or healthy foals as well as adult horses | |
| + | *Pastures can become heavily contaminated, leading to outbreaks | ||
| + | *Transmission via inhalation of dust contaminated with ''R. equi'' | ||
| + | *Organisms survive inside cells | ||
| + | *Virulence associated with specific surface antigens encoded by a large plasmid | ||
| + | *Capsular polysaccharide and mycolic acids in cell wall prevent phagocytosis | ||
| + | *Cell mediated response required to clear infection | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Clinical infections=== | |
| − | + | *[[Respiratory Bacterial Infections - Pathology#Rhodococcus equi|Bronchoneumonia]] and lung abscessation in foals less than 4 months | |
| + | *Infection associated with under-developed cell-mediated immunity | ||
| + | *Acute disease in 1 month-old foals: acute fever, anorexia, bronchopneumonia | ||
| + | *Insidious disease in 2-4 month-old foals with coughing, dyspnoea, weight loss, exercise intolerance, loud, moist rales on lung auscultation | ||
| + | *Occasionally diarrhoea | ||
| + | *Granulomatous ulcerative enterocolitis, mesenteric lymphadenitis and [[Peritonitis|peritonitis]] in some foals following ingestion of contaminated sputum | ||
| + | *Foals over 6 months refractory to pulmonary infection | ||
| + | *Superficial abscesses in horses over 6 months | ||
| + | *Occasional infections in pigs and cattle, causing cervical lymphadenopathy | ||
| + | *Subcutaneous abscesses and mediastinal granulomas in cats | ||
| + | *Pneumonia in HIV patients | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Diagnosis=== | |
| − | + | *History of disease on the farm, age of foals affected and clinical signs | |
| + | *Auscultation and rediography of thorax confirms pulmonary disease | ||
| + | *Specimens: tracheal aspirates and pus from lesions | ||
| + | *Culture aerobically on blood and MacConkey agar for 24-48 hours | ||
| + | *Colony characteristics and biochemical profile | ||
| + | *Quantitative faecal culture on selective media | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Treatment/control=== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Oral rifampin and erythromycin for 4-10 weeks | |
| − | + | *Rehydration therapy; bronchodilators; expectorants | |
| + | *Prevent build-up of bacteria in environment by removing manure from pastures regularly and rotating foals and mares onto clean pastures regularly | ||
| + | *Dusty conditions in paddocks should be avoided | ||
| + | *Hyperimmune serum from the dam may be given to the foal in the first month of life | ||
| − | |||
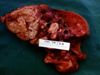
| − | + | [[Image:Pyogranulomatous lungs due to Rhodococcus Equi.jpg|right|thumb|100px|<small><center>Pyogranulomatous lesions due to Rhodococcus equi (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | |
| − | + | *Causative agent [[Rhodococcus equi|''Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi'']] | |
| + | *Important cause of sever, often fatal [[Lungs Inflammatory - Pathology#Granulomatous pneumonia|granulomatous]] [[Lungs Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of pneumonia|pneumonia]] in foals | ||
| + | *Clinical signs include depression, cough, weight loss, respiratory distress, diarrhoea, arthritis, subcutaneous abscesses | ||
| + | *Bacterium survives phagocytosis and multiplies | ||
| + | *Bacterial toxins -> caseous necrosis in lungs -> attracts inflammatory cells -> pyogranulomatous pneumonia | ||
| + | *Grossly: | ||
| + | **Multiple firm nodules, usually no encapsulation | ||
| + | **Partial [[Lungs Ventilation - Pathology#Atelectasis (Collapse)|atelectasis]] | ||
| + | *Histologically: | ||
| + | **Pyogranulomatous lesions | ||
| + | **Macrophages with ingested microorganisms in the alveoli | ||
| + | **Necrosis spreading through parenchyma | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | *pathogen of the equine lung (and intestine) | |
| + | *cutaneous abscesses, cellulitis in young horses | ||
| + | *CELLULITIS = deep suppurative infection often dissecting through tissue planes | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Category:Bacteria miscellaneous]][[Category:Gram_positive_bacteria]][[Category:Cocci]][[Category:Rods]][[Category:Horse Bacteria]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:To_Do_-_Bacteria]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Respiratory_Bacterial_Infections]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Alimentary_Disorders_-_Horse]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category: | ||
Revision as of 12:18, 29 July 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
Overview
- Gram-positive aerobic saprophyte found worldwide
- Found in soil and intestinal tract of animals
- Replicates at warm temperatures in soils contaminated by faeces of herbivores
- Opportunistic respiratory pathogen of foals under 6 months causing suppurative bronchoneumonia
Characteristics
- Grows on non-enriched media
- Salmon-pink mucoid colonies due to capsule and pigment production
- No haemolysis on blood agar
- No growth on MacConkey agar
- Aerobic, non-motile
- CAMP test-positive
- Catalase positive, oxidase negative, weakly acid-fast
- Found as cocci and rods
- Intracellular pathogen
Pathogenesis and pathogenicity
- Organism present in faeces or healthy foals as well as adult horses
- Pastures can become heavily contaminated, leading to outbreaks
- Transmission via inhalation of dust contaminated with R. equi
- Organisms survive inside cells
- Virulence associated with specific surface antigens encoded by a large plasmid
- Capsular polysaccharide and mycolic acids in cell wall prevent phagocytosis
- Cell mediated response required to clear infection
Clinical infections
- Bronchoneumonia and lung abscessation in foals less than 4 months
- Infection associated with under-developed cell-mediated immunity
- Acute disease in 1 month-old foals: acute fever, anorexia, bronchopneumonia
- Insidious disease in 2-4 month-old foals with coughing, dyspnoea, weight loss, exercise intolerance, loud, moist rales on lung auscultation
- Occasionally diarrhoea
- Granulomatous ulcerative enterocolitis, mesenteric lymphadenitis and peritonitis in some foals following ingestion of contaminated sputum
- Foals over 6 months refractory to pulmonary infection
- Superficial abscesses in horses over 6 months
- Occasional infections in pigs and cattle, causing cervical lymphadenopathy
- Subcutaneous abscesses and mediastinal granulomas in cats
- Pneumonia in HIV patients
Diagnosis
- History of disease on the farm, age of foals affected and clinical signs
- Auscultation and rediography of thorax confirms pulmonary disease
- Specimens: tracheal aspirates and pus from lesions
- Culture aerobically on blood and MacConkey agar for 24-48 hours
- Colony characteristics and biochemical profile
- Quantitative faecal culture on selective media
Treatment/control
- Oral rifampin and erythromycin for 4-10 weeks
- Rehydration therapy; bronchodilators; expectorants
- Prevent build-up of bacteria in environment by removing manure from pastures regularly and rotating foals and mares onto clean pastures regularly
- Dusty conditions in paddocks should be avoided
- Hyperimmune serum from the dam may be given to the foal in the first month of life
- Causative agent Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi
- Important cause of sever, often fatal granulomatous pneumonia in foals
- Clinical signs include depression, cough, weight loss, respiratory distress, diarrhoea, arthritis, subcutaneous abscesses
- Bacterium survives phagocytosis and multiplies
- Bacterial toxins -> caseous necrosis in lungs -> attracts inflammatory cells -> pyogranulomatous pneumonia
- Grossly:
- Multiple firm nodules, usually no encapsulation
- Partial atelectasis
- Histologically:
- Pyogranulomatous lesions
- Macrophages with ingested microorganisms in the alveoli
- Necrosis spreading through parenchyma
- pathogen of the equine lung (and intestine)
- cutaneous abscesses, cellulitis in young horses
- CELLULITIS = deep suppurative infection often dissecting through tissue planes