Difference between revisions of "Theileria"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
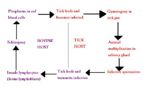
| − | + | [[Image:Theileria parva life cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Theileria parva'' Life Cycle Diagram - Dennis Jacobs & Mark Fox RVC]] | |
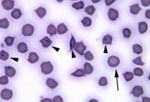
| − | + | [[Image:Lymph node smear East Coast Fever.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Lymph node smear of a cow with East Coast Fever - Drs. Elizabeth Howerth and Bruce LeRoy, Department of Pathology, UGA College of Veterinary Medicine]] | |
| − | + | [[Image:H and E stain brain East Coast Fever.jpg|thumb|right|150px|H and E stain of brain and meningal vessels of a cow with East Coast Fever - Drs. Elizabeth Howerth and Bruce LeRoy, Department of Pathology, UGA College of Veterinary Medicine]] | |
| − | + | [[Image:Theileria cervi.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Theileria cervi'' (deer) - Drs. Elizabeth Howerth and Bruce LeRoy, Department of Pathology, UGA College of Veterinary Medicine]]# | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Image:Theileria parva life cycle.jpg|thumb|right| | ||
| − | [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | ''''' | + | *Main species of veterinary importance is ''Theileria parva'' |
| + | **Causes '''East Coast Fever''' | ||
| + | ***Severe, proliferative lymphatic disease of cattle | ||
| + | ***Central and Eastern Africa | ||
| + | ***Transmitted by [[Hard Ticks - Overseas|''Rhipicephalus appendiculatus'']] | ||
| + | ***[[Ticks#Disease Transmission|Trans-stadial]] transmission | ||
| − | Other species cause | + | *Other ''Theileria'' species cause production losses in cattle and sheep in the Middle East, Mediterranean and in Northern Africa |
| − | + | '''Life Cycle''' | |
| − | + | *Incubation phase lasts 1 week | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Lymphoblast proliferation | |
| + | **Local [[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph node]] first infected then spreads through body | ||
| + | **Occurs in week two | ||
| − | + | *Lymphoid depletion | |
| + | **[[Lymphocytes|Lymphocytes]] killed | ||
| + | **Decreases lymphopoiesis | ||
| + | **Occurs in week 3 | ||
| − | + | *Total incubation period takes about 18 days | |
| − | + | '''Diagnosis''' | |
| + | *Clinical signs | ||
| + | **Pyrexia | ||
| + | **Enlarged local [[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph node]] | ||
| + | ***Usually parotid [[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph node]] as [[Hard Ticks - Overseas|''Rhipicephalus appendiculatus'']] feeds in the ear | ||
| + | **Loss of condition | ||
| − | + | *Examine Giemsa stained smears of: | |
| + | **Local [[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph node]] aspirated for schizonts | ||
| + | **Blood smears for piroplasms in red blood cells | ||
| − | + | *Post-mortem | |
| + | **Pulmonary oedema | ||
| + | **Gut mucosal haemorrhages | ||
| + | **[[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|Lymph node]] and [[Spleen - Anatomy & Physiology|splenic]] cellular atrophy | ||
| − | + | '''Control''' | |
| − | [[ | + | *Integrated control of both the [[Tick Control|tick vector]] and disease |
| + | **[[Vaccines - WikiBlood|Vaccination]] and [[Ectoparasiticides]] | ||
| − | + | *Current [[Vaccines - WikiBlood|vaccination]] is live unattentuated | |
| − | + | **Contains frozen stabilate of ground up tick gut containing infective sporozoites | |
| + | **Long lasting oxytetracycline administered at the same time to slow down schizogony giving the immune response time to develop[[Category:Piroplasmida]] | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[Category:To_Do_-_Parasites]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 12:08, 2 August 2010
File:Lymph node smear East Coast Fever.jpg
Lymph node smear of a cow with East Coast Fever - Drs. Elizabeth Howerth and Bruce LeRoy, Department of Pathology, UGA College of Veterinary Medicine
File:H and E stain brain East Coast Fever.jpg
H and E stain of brain and meningal vessels of a cow with East Coast Fever - Drs. Elizabeth Howerth and Bruce LeRoy, Department of Pathology, UGA College of Veterinary Medicine
#
- Main species of veterinary importance is Theileria parva
- Causes East Coast Fever
- Severe, proliferative lymphatic disease of cattle
- Central and Eastern Africa
- Transmitted by Rhipicephalus appendiculatus
- Trans-stadial transmission
- Causes East Coast Fever
- Other Theileria species cause production losses in cattle and sheep in the Middle East, Mediterranean and in Northern Africa
Life Cycle
- Incubation phase lasts 1 week
- Lymphoblast proliferation
- Local lymph node first infected then spreads through body
- Occurs in week two
- Lymphoid depletion
- Lymphocytes killed
- Decreases lymphopoiesis
- Occurs in week 3
- Total incubation period takes about 18 days
Diagnosis
- Clinical signs
- Pyrexia
- Enlarged local lymph node
- Usually parotid lymph node as Rhipicephalus appendiculatus feeds in the ear
- Loss of condition
- Examine Giemsa stained smears of:
- Local lymph node aspirated for schizonts
- Blood smears for piroplasms in red blood cells
- Post-mortem
- Pulmonary oedema
- Gut mucosal haemorrhages
- Lymph node and splenic cellular atrophy
Control
- Integrated control of both the tick vector and disease
- Current vaccination is live unattentuated
- Contains frozen stabilate of ground up tick gut containing infective sporozoites
- Long lasting oxytetracycline administered at the same time to slow down schizogony giving the immune response time to develop